# Architecting
---
## Separation of concerns
Front end focus:
* HTML, CSS and JavaScript
* Search engine optimization (SEO)
* Usability and accessibility testing
* Graphic design and image editing tools
* Web performance and browser compatibility
Back end focus:
* Programming and scripting languages like PHP, Python and C#
* Automated testing frameworks
* Database management and data transformation
* Cybersecurity and data backup practices
---
## Client side vs server side scripting
++ Client side:
* Allow for more interactivity by immediately responding to users’ actions
* Execute quickly because they do not require a trip to the server (example: validation - you don't need to submit a form to see smth is not correct)
++ Server side:
* The end user could have javascript switched off
* Performance. When running code on the server, it often has a faster load time and processing time than a client script
* Can perform complex database lookups
* Not affected by type of browser
* Client side validation can be bypassed/manipulated
In case of validation: always validate server-side and do client-side additionally to provide user experience
---
## Isomorphic Code
### server side language = client side language
Executing JavaScript on the server is a natural thing to do, because you can then concentrate on learning one language. You can even refactor out common code that will execute both on the client and the server - this is called isomorphic code.
**positives** include not having to learn new languages
**negatives** Javascript migth not be the easiest way to implement the app goals
## Non-Isomorphic Code
### h2server side language ≠ cliet side language
NodeJS is the best known and most popular way of executing JavaScript on the server. If you have existing investments in Java and see the benefits of using the Java VM, then NodeJS might not be an ideal approach. Luckily, the JVM provides Javascript support and with it many alternatives to NodeJS
**positives** other languages might be faster/ more resorce friendly on the backend hardware, making it cheaper to run
**negatives** damn son! it's a whole other language! maybe moah!
### Other back-end languages and runtime inviroments
include Java, PHP, Ruby on Rails, Python, and .Net
with the above mentioned Java VM.
### Backend vs Frontend javascript
* In the browser, most of the time what you are doing is interacting with the DOM, or other Web Platform APIs like Cookies. Those do not exist in Node.
* In the browser, we don’t have all the nice APIs that Node.js provides through its modules, like the filesystem access functionality.
* In Node.js you control the environment. Unless you are building an open source application that anyone can deploy anywhere, you know which version of Node you will run the application on. Compared to the browser environment, where you don’t get the luxury to choose what browser your visitors will use, this is very convenient.
* you can write all the modern ES6-7-8-9 JavaScript that your Node version supports.
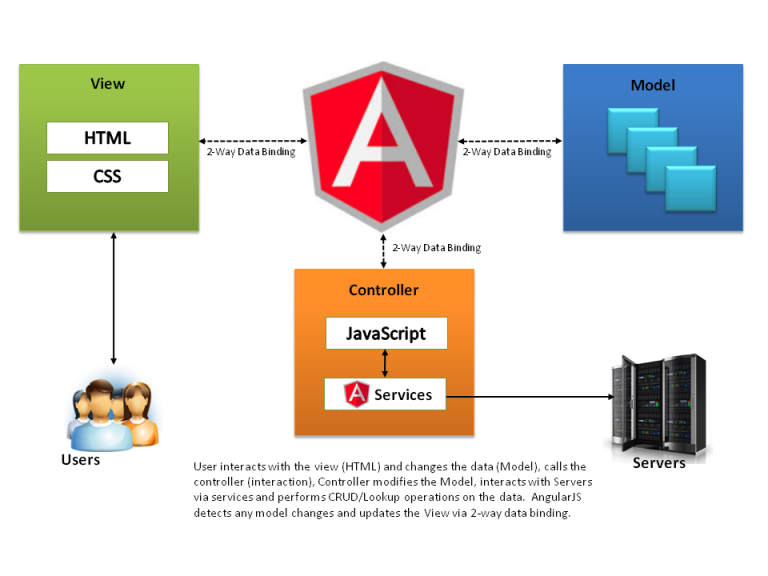
## Javascript frameworks
some of the most known/ used javascript frameworks
* Angular-js
* React.JS (not a full framework but it makes viewing data much easier)
___
