# LeetCode | Data Structure I | 14 Days Challenge | Day 7-8
###### tags: `LeetCode` `Data Structure I` `14 Days Challenge`
## Day 7
### [141. Linked List Cycle](https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/?envType=study-plan&id=data-structure-i)
### 題目敘述
>*Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.*
>*There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer.*
>*Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail's next pointer is connected to. Note t*
>*Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.*
### 測資
Example 1:

:::info
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
:::
Example 2:

:::info
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node.
:::
Example 3:

:::info
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: false
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
:::
### 數值範圍
The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 10^4^].
-10^5^ <= Node.val <= 10^5^
pos is -1 or a valid index in the linked-list.
### 核心概念
==pointer、Linked List==
### 想法
恭喜我撐到了第七天!但是,題目也開始難了喔,學linked list需要有指標這個前備知識,不然會學得很辛苦喔~同時linked list也是資料結構很重要的一部分!之後會再發一篇貼文講解(老高上身)。
這題參考了大佬解法,利用兩指標(fast、slow)循序,fast每次走兩步,slow每次走一步,若fast遇見slow,代表這是個cycle,若fast都走到nullptr了(盡頭了),都還沒遇到,則代表只是個單向linked list。
***time : 10-15 mins
time complexity : $O(n)$
space complexity : $O(n)$***
### 程式碼
```c++=1
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == nullptr) return false;
ListNode *fast = head;
ListNode *slow = head;
while(fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast == slow) return true;
}
return false;
}
};
```
### [21. Merge Two Sorted Lists](https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/?envType=study-plan&id=data-structure-i)
### 題目敘述
>*You are given the heads of two sorted linked lists list1 and list2.*
>*Merge the two lists in a one sorted list. The list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.*
>*Return the head of the merged linked list.*
### 測資
Example 1:

:::info
Input: list1 = [1,2,4], list2 = [1,3,4]
Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4]
:::
Example 2:
:::info
Input: list1 = [], list2 = []
Output: []
:::
Example 3:
:::info
Input: list1 = [], list2 = [0]
Output: [0]
:::
### 數值範圍
The number of nodes in both lists is in the range [0, 50].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
Both list1 and list2 are sorted in non-decreasing order.
### 核心概念
==pointer、linked list==
### 想法
對於merge的部分,我一直都是持在原資料型態上直接merge,而不是另闢一新資料型態儲存結果,一方面是不想浪費空間(降低space complexity),另一方面也是訓練自己的能力,想到一些比較不直觀的解法,多擠一些腦汁出來XD
我的想法是**插入Node**,在原有的list1更改各Node連接,讓節點插入,用到了兩個指標(ptr1、ptr2),分別指向list1、list2的當前Node,利用ptr1和ptr1->next的指標關係插入node,以圖示來解說好了。
如圖:

上圖是原先的Node關係,下圖為插入後的關係,
***time : 40~45 mins
time complexity : $O(n)$
space complexity : $O(1)$***
### 程式碼
```c++=1
class Solution {
public:
/*void Print(ListNode* pre_list1, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode* test1 = pre_list1;
ListNode* test2 = list2;
cout << '\n';
while (test1 != nullptr) {
cout << test1->val << ' ';
test1 = test1->next;
}
cout << '\n';
while (test2 != nullptr) {
cout << test2->val << ' ';
test2 = test2->next;
}
cout << '\n';
}*/
void SwapList(ListNode* &list1, ListNode* &list2) {
ListNode* temp = list1;
list1 = list2;
list2 = temp;
}
void InsertNode(ListNode*& ptr1, ListNode*& ptr2) {
ListNode* temp = new ListNode;
temp->val = ptr2->val;
temp->next = ptr1->next;
ptr1->next = temp;
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
}
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
if (list1 == nullptr) return list2;
if (list2 == nullptr) return list1;
// swap
if (list2->val < list1->val) SwapList(list1, list2);
ListNode* ptr1 = list1;
ListNode* ptr2 = list2;
bool flag = false;
while (ptr1 != nullptr && ptr2 != nullptr) {
if (ptr1->next == nullptr && ptr2 != nullptr) {
ptr1->next = ptr2;
//Print(pre_list1, list2);
break;
}
else if (ptr2->val >= ptr1->val && ptr2->val < ptr1->next->val) {
InsertNode(ptr1, ptr2);
}
else {
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
}
//Print(pre_list1, list2);
}
return list1;
}
};
```
### [203. Remove Linked List Elements](https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/?envType=study-plan&id=data-structure-i)
### 題目敘述
>*Given the head of a linked list and an integer val, remove all the nodes of the linked list that has Node.val == val, and return the new head.*
### 測資
Example 1:

:::info
Input: head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
:::
Example 2:
:::info
Input: head = [], val = 1
Output: []
:::
Example 3:
:::info
Input: head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
Output: []
:::
### 核心概念
==pointer、linked list==
### 數值範圍
The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 10^4^].
1 <= Node.val <= 50
0 <= val <= 50
### 想法
利用兩指標進行傳回頭部和處理刪除節點(pre_ptr、ptr),ptr指向當前節點,pre_ptr為**傳回頭部的前一位**,因為有可能頭節點被刪除,頭部就會跑掉,因此指標要往前挪一位。
利用ptr和ptr->next進行刪除更改指向~
而在寫心得的當下也有更多想法,就又回去優化程式了哈哈。
***time : 15 mins
time complexity : $O(n)$
space complexity : $O(1)$***
### 程式碼
```c++=1
/**
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
if (head == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* pre_ptr = new ListNode;
pre_ptr->next = head;
ListNode* ptr = pre_ptr;
while (ptr->next != nullptr) {
if (ptr->next->val == val) {
ListNode* dump = ptr->next;
ptr->next = ptr->next->next;
delete dump;
}
else ptr = ptr->next;
}
return pre_ptr->next;
}
};
};
```
## Day 8
### [206. Reverse Linked List](https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/?envType=study-plan&id=data-structure-i)
### 題目敘述
>*Given the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.*
### 測資
Example 1:

:::info
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
:::
Example 2:

:::info
Input: head = [1,2]
Output: [2,1]
:::
Example 3:
:::info
Input: head = []
Output: []
:::
### 核心概念
==pointer、linked list==
### 數值範圍
The number of nodes in the list is the range [0, 5000].
-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
### 想法
原本想用遞迴做QQ,但一直做不成功,只好另覓解法,最後利用以下概念自己實做出來了
這題想分享一位大佬的解法,他還有附動畫!!太猛了。
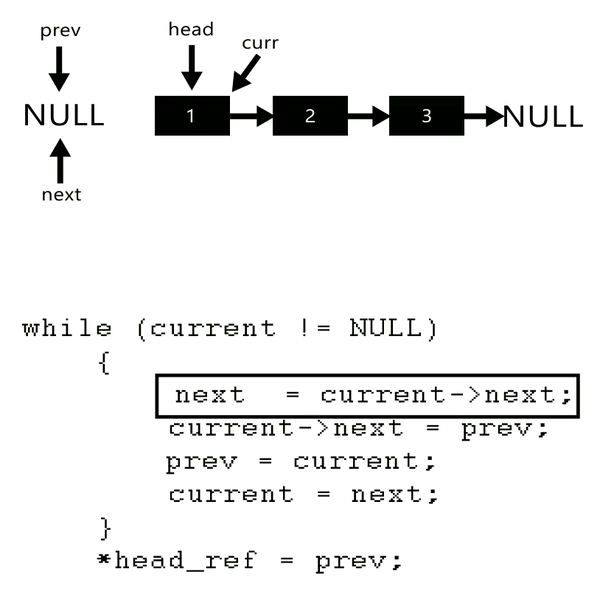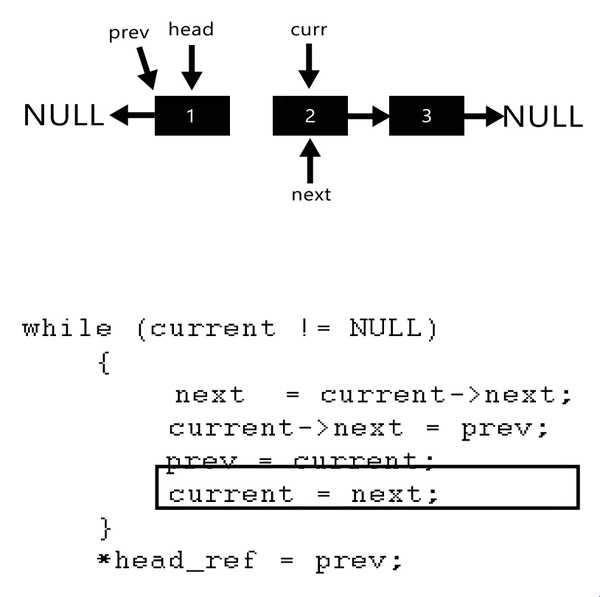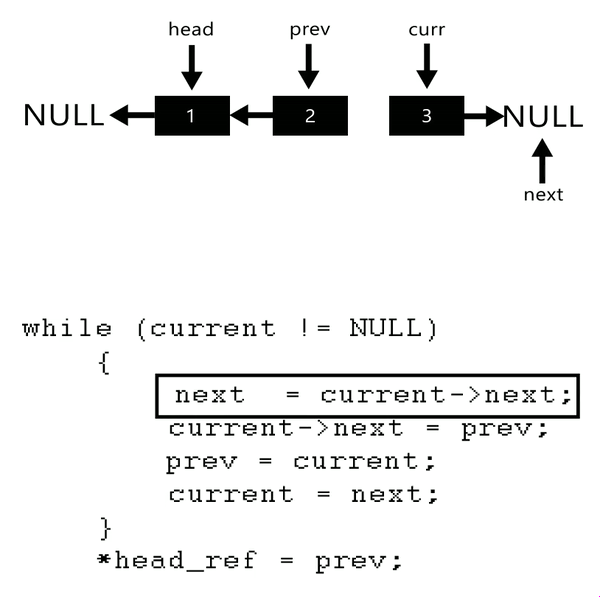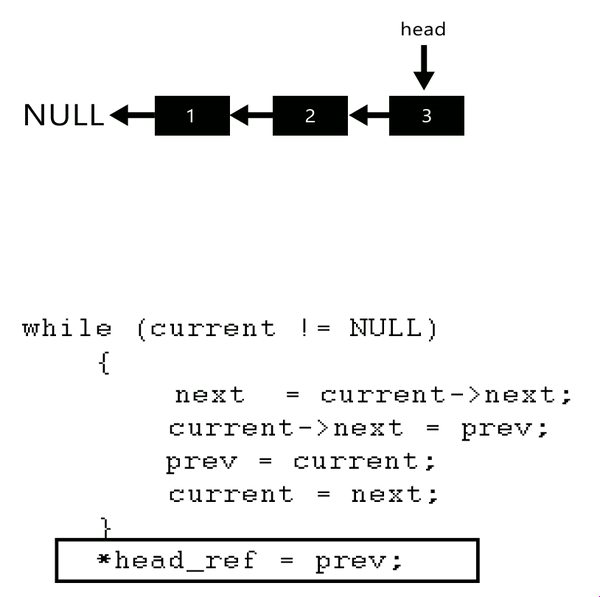
***time : 40~60 mins
time complexity : $O(n)$
space complexity : $O(1)$***
### 程式碼
```c++=1
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* next, *cur, * prev = nullptr;
cur = next = head;
while (cur != nullptr) {
next = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
head = prev;
return head;
}
};
```
### [83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List](https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/?envType=study-plan&id=data-structure-i)
### 題目敘述
>*Given the head of a sorted linked list, delete all duplicates such that each element appears only once. Return the linked list sorted as well.*
### 測資
Example 1:

:::info
Input: head = [1,1,2]
Output: [1,2]
:::
Example 2:

:::info
Input: head = [1,1,2,3,3]
Output: [1,2,3]
:::
Example 3:
### 核心概念
==pointer、linked list==
### 數值範圍
The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 300].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
**The list is guaranteed to be sorted in ascending order.**
### 想法
由於數字是non-decreasing(increasing),所以重複的數字都會併排在一起,太放水了,這樣的難度就直線下降了,只要判斷當前node和node->next的val是否相同即可。
可以自行加上以下幾行,將要刪除的node記憶體釋放掉,減少memory。
```
ListNode* dump = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete dump;
```
***time : 3~5 mins
time complexity : $O(n)$
space complexity : $O(1)$***
### 程式碼
```c++=1
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *cur = head;
while (cur != nullptr && cur->next) {
if (cur->val == cur->next->val) {
cur->next = cur->next->next;
} else {
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
```