---
tags: Code
title: Code Library
author: TomDev
license: Private Use
---
:::info
:::spoiler Table of contents
[TOC]
:::
# Tips khi đi thi
- Phải dùng `freopen` theo file của đề cho
- Không dùng `bits/stdc++.h`
- Khi nhân phải dùng `long long int` - $2*10^{31}$
- `int` chỉ chứ được $2*10^9$
- Chỉ dùng mảng khi độ dài là $10^6$
- Tạo hàm/namespace cho từng sub
- Không khai báo các biến chiếm bộ nhớ lớn trong hàm
- Khi tạo file trâu phải tạo lại ngay từ đầu (ko copy) để tránh sai sót
- Dùng `cerr` để in ra màn hình khi có `freopen()`
## Máy chấm là c++98 và đây là những hạn chế
1. Freopen phải có thư viện (`<cstdio>`, `<bits/stdc++.h>`)
2. Những hành động di chuyển/copy vector, string sẽ chậm hơn
3. Không có `emplace_back()`
4. Không được set giá trị của vector khi khởi tạo
5. Không có range based for loop (phải dùng iterator để thay thế)
6. Không được dùng `INT_MAX` và `INT_MIN`
7. Không được dùng `to_string()`
## Ước lượng
1. Số lượng số nguyên tố từ $1 \rightarrow n$ $\approx \frac{n}{ln(n)-1}$
2. Công thức tính dung lượng bị chiếm (MB): $$\frac{\text{Số phần tử}*\text{Size of type (bytes)}}{10^6}$$
| Kiểu dữ liệu | Kích thước (bytes) |
|:--------------------:|:------------------:|
| `bool`,`char` | 1 |
| `int` | 4 |
| `long long`,`double` | 8 |
| `bitset` | 1/8 (1 bit) |
3. Cách tính $log_a{x}$:
$$log_a{x} = \frac{log(x)}{log(a)}$$
## Danh sách số nguyên tố dùng cho kỳ thi
```yaml=
[1234567891, 1e9+6967, 1e9+6697, 1e9+4567, 1e9+4569]
```
# I.Câu lệnh cần nhớ
## I.a Lấy file .inp và .out
### C++
#### Basic version
```cpp=
#include <cstdio> //no need for modern compiler
freopen("input.inp", "r", stdin);
freopen("output.out", "w", stdout);
```
### Basic version with custom name
```cpp=
void openfile(string name){
freopen((name+".in").c_str(), "r", stdin); // or .inp
freopen((name+".out").c_str(), "w", stdout);
}
```
#### Advanced version (read when needed) - must #include `<fstream>`
##### Int
```cpp!
int n;
ifstream MyReadFileName("input.inp"); // ifstream = input fstream
MyReadFile >> n;
MyReadFileName.close(); // optional, because it only get value from file when you call out
ofstream MyOutputFileName("output.out"); // ofstream = output fstream
MyOutputFileName << n;
```
#### Basic version but only cin and cout in file when needed
```cpp!
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Save original stdin and stdout
FILE* original_stdin = stdin;
FILE* original_stdout = stdout;
// Redirect stdin and stdout to files
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
// Your code that reads from input.txt and writes to output.txt
int x;
cin >> x;
cout << "Value read: " << x << endl;
// Restore original stdin and stdout
stdin = original_stdin;
stdout = original_stdout;
// Use original stdin and stdout again
cout << "Back to original stdout." << endl;
}
```
---
##### String (if there is space)
```cpp!
string str;
ifstream MyReadFileName("input.inp"); // ifstream = input fstream
getline(MyReadFileName, str);
MyReadFile.close(); // optional, because it only get value from file when you call out
ofstream MyOutputFileName("output.out"); // ofstream = output fstream
MyOutputFileName << str;
```
---
##### String (get all string in file)
```cpp!
int main() {
ifstream file("input.inp"); // Open the file
if (!file.is_open()) { // Check if the file is open
cerr << "Unable to open file";
return 1;
}
string line;
while (getline(file, line)) { // Read each line from the file
cout << "String read from file: " << line << endl;
}
file.close(); // Close the file
}
```
### Python
```python=
import sys
sys.stdin = ("input.inp", "r")
sys.stdout = ("output.out", "w")
```
## I.b Input
### Getline/Cin
:::spoiler Lỗi khi getline sau cin ❌
Code:
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string name;
int age;
cout << "Enter your age: ";
cin >> age;
cout << "Enter your name: ";
getline(cin, name);
cout << "Tên của bạn là: " << name << "\n" << "Tuổi: " << age;
}
```
:::
### Input methods (chi tiết: Star Edu ngày 29/12/2024 & 28/12/2024 - STL)
```cpp=
#include <functional>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <vector>
#include <bitset>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
// lặp lại đúng n lần, n số int, n > 0
#define REP(n) for (int (i) = int(n) - 1; (i) >= 0; (--(i)))
#define FOR(n, i) for (int (i) = 0, e = int(n); (i) < e; (++(i)))
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define ALL(x) begin(x), end(x)
#define sz(x) ((int)(x.size()))
int readInt() { int x; cin >> x; return x; }
long long readLong() { long long x; cin >> x; return x; }
float readFloat() { float x; cin >> x; return x; }
string readString() { string x; cin >> x; return x; }
bool getInt(int &x) { return !!(cin >> x); }
bool getLong(long long &x) { return !!(cin >> x); }
bool getFloat(float &x) { return !!(cin >> x); }
bool getString(string &x) { return !!(cin >> x); }
struct student {
string name; string id;
student(string new_name, string new_id)
: name(std::move(new_name)), id(std::move(new_id)) {}
};
namespace subtask1
{
auto solve(const vector<int> &a)
{
set<int> S(all(a));
vector<int> b(all(S));
return b;
}
}
namespace subtask2
{
auto solve(const vector<int> &a)
{
vector<int> b(all(a));
sort(all(b));
b.erase(unique(all(b)), b.end());
// b.resize(unique(all(b)) - b.begin());
return b;
}
}
void output(const vector<int> &a)
{
cout << "a[" << a.size() << "] = { ";
for (int x : a) {
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << "}" << endl;
}
int uniquecount(const vector<int> &a)
{
vector<int> b;
for (int x : a) if (b.empty() || b.back() != x) {
b.push_back(x);
}
output(b);
return b.size();
}
int main()
{
{
vector<int> a = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 };
vector<int> b = { 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 };
vector<int> c;
c.reserve(a.size() + b.size());
FOR(a.size(), i) c.emplace_back(a[i]);
FOR(b.size(), i) c.emplace_back(b[i]);
output(c);
vector<int> d(a.size() + b.size());
merge(ALL(a), ALL(b), d.begin());
output(d);
sort(all(d));
cout << boolalpha << binary_search(all(d), 5) << endl;
for (auto x : d) {
cout << x << " -> 0b" << bitset<8>(x) << endl;
}
auto funcA = [](int n) {
if (n <= 0) {
return 0LL;
}
else {
return 1LL * n * (n - 1) / 2;
}
};
auto funcB = [](int n) -> long long {
if (n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
else {
return 1LL * n * (n - 1) / 2;
}
};
cout << funcA(10) << endl;
cout << funcB(10) << endl;
}
{ // generator
vector<int> a(readInt());
generate(all(a), readInt);
output(a);
}
{ // readInt
vector<int> a(readInt());
for (int &x : a)
cin >> x;
output(a);
}
{ // readInt - slower
vector<int> a(readInt());
for (int &x : a)
x = readInt();
output(a);
}
{ // readInt + iterator
vector<int> a(readInt());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); ++it)
*it = readInt();
output(a);
}
{ // readInt + define FOR
vector<int> a(readInt());
FOR(sz(a), i)
cin >> a[i];
output(a);
}
{ // readInt + emplace_back
vector<int> a;
REP(readInt())
a.emplace_back(readInt());
output(a);
}
{ // readInt + push_back - slower
vector<int> a;
REP(readInt())
a.push_back(readInt());
output(a);
}
{ // readInt + push_back
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a;
FOR(n, i)
a.push_back(readInt());
output(a);
}
{ // readInt + reserve + emplace_back
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a;
a.reserve(n);
FOR(n, i)
a.emplace_back(readInt());
output(a);
}
{ // normal push_back
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int x;
cin >> x;
a.push_back(x);
}
output(a);
}
{ // reserve + normal emplace back
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a;
a.reserve(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int x;
cin >> x;
a.emplace_back(x);
}
output(a);
}
{ // copy + stream
vector<int> a(readInt());
copy_n(istream_iterator<int>(cin), a.size(), a.begin());
output(a);
}
{ // direct lambda expression + stream
vector<int> a = [&](int n = readInt()) -> vector<int> { return {(istream_iterator<int>(cin)), istream_iterator<int>()}; }();
output(a);
}
// { // functional lambda expression + stream
// auto func = [&](int n = readInt()) -> vector<int> {
// return {(istream_iterator<int>(cin)), istream_iterator<int>()};
// };
// vector<int> a = func();
// output(a);
// }
// { // stream
// readInt();
// vector<int> a((istream_iterator<int>(cin)), istream_iterator<int>());
// output(a);
// }
// { // cin tới khi eof + emplace_back
// vector<int> a;
// a.reserve(readInt());
// for (int x; getInt(x); )
// a.emplace_back(x);
// output(a);
// }
// { // cin tới khi eof + push_back
// readInt();
// vector<int> a;
// for (int x; cin >> x; )
// a.push_back(x);
// output(a);
// }
return 0;
}
```
### Input optimizations
- Dùng `emplace_back()` cùng với `reserve()` trước đó sẽ giúp nhanh hơn `push_back()` thông thường
## I.c. Define combo
```cpp=
#define all(x,bonus) (x).begin()+(bonus),(x).end()
#define rall(x,bonus) (x).rbegin(),(x).rend()-(bonus)
#define fastio ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(NULL);
#define fi first
#define se second
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
using ll = long long;
using ull = unsigned long long;
using pii = pair<int,int>;
using vi = vector<int>;
using vll = vector<long long>;
```
### Bits/stdc++.h
:::danger
Không được dùng như sau
```cpp!
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
```
Vì sẽ bị trùng namespace, giảm tốc độ và lỗi tumlum
:::
**Input:**
> 12
> hello
**Output:**
> Tên của bạn là:
> Tuổi: 12
---
### Cách sửa lỗi:
#### 1.
```cpp!
std::getline(std::cin >> std::ws, name); // ws = white space
```
#### 2.
```cpp!
std::cin.ignore();
```
### Các loại getline:
```cpp!
getline(cin, variable); // to get input to string
```
```cpp!
cin.getline(array, size); // to get input to array
```
### Các hàm cin đáng nhớ:
```cpp!
cin.ignore(); // xoá bộ nhớ đệm
```
```cpp!
cin.fail(); // kiểm tra nếu input lỗi
```
```cpp!
cin.clear(); // clear input error to continue action
```
## I.c Output
### In khi lỗi
```cpp!
std::cerr << output;
```
## I.d File
### Kiểm tra end file
```cpp!
if(file.eof());
```
---
### Kiểm tra file fail
```cpp!
if(file.fail());
```
---
### Kiểm tra file error
```cpp!
if(file.bad());
```
---
### Kiểm tra nếu không có lỗi
```cpp!
if(file.good());
```
## I.e Headers
### Template
```cpp!
template <typename T> // T is just a name
```
```cpp!
template <class T> // T is just a name
```
:::spoiler Usage 🔥
:::info
For function overloading or set type
:::
---
### Typedef
```cpp!
typedef long long ll;
```
```cpp!
typedef int i;
```
::: success
Dùng cho viết tắt kiểu dữ liệu 🚀
:::
---
### Define
```cpp!
#define FOR(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
```
```cpp!
#define findMax(a, b) cout << (a > b ? a : b) << endl;
```
---

---
### Using
```cpp!
using ll = long long;
using ii = pair<int, int>;
using kitu = char;
```
# II.Hàm đáng nhớ
## II.a Tính toán
:::info
Các hàm sau dùng `<cmath>` hoặc `<algorithm>` 🔢
:::
---
### Tìm số lớn nhất
```cpp!
std::max(a,b);
```
---
### Tìm số nhỏ nhất
```cpp!
std::min(a,b);
```
---
### Số mũ
```cpp!
pow(a,b); // a^b
```
---
### Căn bậc 2
```cpp!
sqrt(a);
```
---
### Số tuyệt đối
```cpp!
#include <cstdlib>
abs(a);
```
---
### Làm tròn gần nhất
```cpp!
round(a);
```
---
### Làm tròn số lên
```cpp!
ceil(a);
```
---
### Làm tròn số xuống
```cpp!
floor(a);
```
---
### Ước chung lớn nhất
```cpp!
#include <algorithm>
__gcd(a,b);
```
:::danger
Không nên dùng vì cần c++17 🚫
:::
---
### Hoán vị lớn hơn
```cpp!
next_permutation(v.begin(), v.end(), /* custom compare is optional here, default is ascending order */);
```
```
Permutations:
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 1 3
2 3 1
3 1 2
3 2 1
```
---
### Hoán vị nhỏ hơn
```cpp!
prev_permutation(v.begin(), v.end(), /* custom compare is optional here, default is descending order */);
```
```
Permutations in reverse order:
3 2 1
3 1 2
2 3 1
2 1 3
1 3 2
1 2 3
```
## II.b String
:::info
std::string name; 🟰
:::
### Tính độ dài
```cpp!
name.length();
```
**hoặc**
```cpp!
name.size();
```
---
### Kiểm tra string có trống không?
```cpp!
if(name.empty()){
//do something
}
```
---
### Xoá giá trị string
```cpp!
name.clear();
```
---
### Thêm vào cuối string
```cpp!
name.append();
```
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
cout << "Enter your name: ";
getline(cin >> ws, name);
name.append("@gmail.com");
cout << "Your email: " << name;
```
:::
---
### Vị trí của string 🕶️
```cpp!
name.at(n); // n = name index and it also counts spaces
```
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
cout << "Enter your name: ";
cin >> name;
cout << name.at(0);
```
**Input:**
```yaml!
TomDev
```
**Output:**
```yaml!
T
```
:::
---
### Thêm string vào vị trí được chọn của string
```cpp!
name.insert(i, "str") // i = index, str = string thêm vào
```
:::warning
Chỉ áp dụng cho string :100:
:::
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
cout << "Enter you name: ";
getline(cin >> ws, name);
name.insert(0, "@");
cout << name;
```
**Input:**
```yaml!
hello
```
**Output:**
```yaml!
@hello
```
:::
---
### Tìm phần tử trong string
```cpp!
name.find('c'); // c = char cần tìm
```
:::warning
Nên dùng char cho parameter và hàm chỉ cho chúng ta index tìm được đầu tiên :heavy_check_mark:
:::
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
cout << "Enter you name: ";
getline(cin >> ws, name);
cout << name.find('e');
```
**Input:**
```yaml!
hello
```
**Output:**
```yaml!
1
```
:::
---
### Xoá phần tử của string
```cpp!
name.erase(start, stop); //start và stop là int
```
```cpp!
it = v.erase(it); // trỏ về phần tử đứng sau phần tử vừa bị xoá
```
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
cout << "Enter you name: ";
getline(cin >> ws, name);
cout << name.erase(0,3);
```
**Input:**
```yaml!
TomDev
```
**Output:**
```yaml!
Dev
```
:::
---
### Remove()
```cpp!
remove(a.begin(), a.end(), 0 /*value to be removed*/);
```
:::warning
Remove() sẽ đẩy hết những giá trị cần xoá về cuối mảng và trả về pointer chỉ về phần tử kết thúc mới của mảng
* Lưu ý: remove() không thay đổi gì trong vector cả và phải dùng `<algorithm>`
:::
Người ta thường dùng chung với `erase()` để xoá những giá trị không mong muốn
```cpp!
v.erase(remove(v.begin(), v.end(), 0), v.end());
```
---
### Tìm string trong chuỗi
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char a[] = "codelearn_hoctap";
char b[] = "learn";
cout << strstr(a,b);
}
```
:::spoiler Output
```yaml
learn_hoctap
```
:::
---
### Bắt đầu/Kết thúc của string
```cpp!
str.begin();
str.end();
```
---
### Create new string from string
```cpp!
str.substr(start position - 1, number of digit from start position - 1);
```
**or new string from a specific index to end**
```cpp!
str.substr(start position, stop position counts from start+1);
```
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
// string::substr
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str="We think in generalities, but we live in details.";
// (quoting Alfred N. Whitehead)
std::string str2 = str.substr (3,5); // "think"
std::size_t pos = str.find("live"); // position of "live" in str
std::string str3 = str.substr (pos); // get from "live" to the end
std::cout << str2 << ' ' << str3 << '\n';
}
```
```yaml!
think live in details.
```
:::
---
### Replace
```cpp!
str.replace(cstr start index, cstr stop index, rstr);
str.replace((cstr start index, cstr stop index, rstr, rstr start index, rstr stop index);
```
:::info
cstr = curent string
rstr = replacing string
start index begins with 1
stop index counts from start index
:::
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string base="this is a test string.";
std::string str2="n example";
std::string str3="sample phrase";
std::string str4="useful.";
// replace signatures used in the same order as described above:
// Using positions: 0123456789*123456789*12345
std::string str=base; // "this is a test string."
str.replace(9,5,str2); // "this is an example string." (1)
str.replace(19,6,str3,7,6); // "this is an example phrase." (2)
str.replace(8,10,"just a"); // "this is just a phrase." (3)
str.replace(8,6,"a shorty",7); // "this is a short phrase." (4)
str.replace(22,1,3,'!'); // "this is a short phrase!!!" (5)
}
```
:::
---
### String maker
```cpp!
std::string s0 = "Initial string";
std::string s2 (s0);
std::string s3 (s0, 8, 3);
std::string s4 ("A character sequence");
std::string s5 ("Another character sequence", 12);
std::string s6a (10, 'x');
std::string s6b (10, 42); // 42 is the ASCII code for '*'
std::string s7 (s0.begin(), s0.begin()+7);
```
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
string s0 ("Initial string");
// constructors used in the same order as described above:
string s1;
string s2 (s0);
string s3 (s0, 8, 3); // print from index 8 to 3
string s4 ("A character sequence"); // like normal
string s5 ("Another character sequence", 12); // limit in 12 digit
string s6a (10, 'x'); // print x 10 times
string s6b (10, 42); // 42 is the ASCII code for '*'
string s7 (s0.begin(), s0.begin()+7);
cout "s2: " << s2 << "\ns3: " << s3;
cout << "\ns4: " << s4 << "\ns5: " << s5 << "\ns6a: " << s6a;
cout << "\ns6b: " << s6b << "\ns7: " << s7 << '\n';
}
```
```yaml!
s2: Initial string
s3: str
s4: A character sequence
s5: Another char
s6a: xxxxxxxxxx
s6b: **********
s7: Initial
```
:::
---
### Insert
```cpp!
str.insert(cstr start, cstr stop, rstr, rstr start, rstr stop);
```
:::info
cstr = curent string
rstr = replacing string
start index begins with 1
stop index counts from start index
:::
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str="to be question";
std::string str2="the ";
std::string str3="or not to be";
std::string::iterator it;
// used in the same order as described above:
str.insert(6,str2); // to be (the )question
str.insert(6,str3,3,4); // to be (not )the question
str.insert(10,"that is cool",8); // to be not (that is )the question
str.insert(10,"to be "); // to be not (to be )that is the question
str.insert(15,1,':'); // to be not to be(:) that is the question
it = str.insert(str.begin()+5,','); // to be(,) not to be: that is the question
str.insert (str.end(),3,'.'); // to be, not to be: that is the question(...)
str.insert (it+2,str3.begin(),str3.begin()+3); // (or )
std::cout << str << '\n';
}
```
`to be, or not to be: that is the question...`
:::
---
### Find
```cpp!
str.find(str); // return the position of first letter
```
---
### Npos (Từ đầu đến cuối)
```cpp!
if(found != std::string::npos){
// do something
}
```
:::info
Usually use for find() when they didn't find the target in string :man-shrugging:
:::
---
### Replace whole string
```cpp!
str.assign(start, stop);
```
:::info
start index begins with 1
stop index counts from start index
:::
---
### Thêm phần tử vào cuối
```cpp!
str.push_back(value);
```
---
### Bớt giá trị ở cuối
```cpp!
str.pop_back(value);
```
---
### Transform
:::info
Có thể áp dụng lẫn string và arr :raised_hands:
:::
```cpp!
transform(iterator inputBegin, iterator inputEnd, iterator OutputBegin, unary_operation)
```
[Details :bulb:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/transform-c-stl-perform-operation-elements/)
:::danger
iterator sử dụng `#include <iterator>` :robot_face:
:::
---
### UPPERCASE/lowercase
```cpp
char c = (char)tolower('A'); // do nothing with special characters
char c = (char)toupper('a');
transform(s1.begin(), s1.end(), s1.begin(), ::toupper); // apply transform
transform(s1.begin(), s1.end(), s1.begin(), ::tolower);
```
---
### UPPERCASE/lowercase thủ công
```cpp
if(c >= 'a' && c <= 'z'){
c -= 32; // Uppercase c - ASCII
}
else{
c += 32; // lowercase c - ASCII
}
---
### Kiểm tra UPPER/lower
```cpp
isupper(c);
islower(c);
```
---
---
### Kiểm tra nếu thuộc Alphabet
```cpp
isalpha(c); // --> bool
```
---
### Kiểm tra nếu thuộc Alphabet thủ công
```cpp
if(c >= 'a' && c <= 'z' || c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z'){
cout << c << " is alphabet!";
}
```
---
### Remove điều kiện
```cpp!
std::remove_if(vec2.begin(), vec2.end(), IsOdd /* condition */);
```
[Tham khảo :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stdremove-stdremove_if-c/)
---
### Remove
```cpp!
std::remove(vec.begin(), vec.end(), target);
```
:::danger
Returns iterator to the new end of that range
:exclamation: This doesn't change the size of vector or delete any element
:::
---
### Cách biến char/string thành số
- Char:
```cpp!
char c = '3';
int n = c - '0';
```
- String:
```cpp!
string s = "123";
stoi(s);
```
---
### Cách biến số thành char
[Resources :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/cpp-program-for-int-to-char-conversion/)
```cpp!
// cách 1
int n = 65;
cout << char(n); // kết quả là `A` do bảng ASCII
// cách 2
int n = 65;
char c = n;
cout << c; // kết quả là `A` do bảng ASCII
// cách 3
int n = 65;
cout << static_cast<char>(n);
```
## II.c Thời gian
### Random
```cpp!
#include <cstdlib> // for srand() and rand()
#include <ctime> // for time()
srand(time(NULL));
rand() % n1 + n2;
start + rand() % (end - start + 1); // random trong array
```
```cpp=
#include <cstdlib> // for srand() and rand()
#include <ctime> // for time()
/* include <time.h> is a alternative method */
srand(time(NULL)); // or srand(time(0));
/* rand % num = divide time by num and take remainder */
int num = rand() % 6; // random 0 - 5
int num1 = rand() % 6 + 1 // random 0 - 6
```
---
### Better random
#### Numbers
```cpp!
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Create a random device
random_device rd; // custom rd name
// Use the random device to seed the random number generator
mt19937 gen(rd()); // must be the same with random_device custom name
// gen is custom name too
// Define the distribution range [1, 100]
uniform_int_distribution<> int_dis(1, 100);
// Define the distribution range [0.0, 1.0]
uniform_real_distribution<> float_dis(0.0, 1.0);
// Generate a random number
int random_number = int_dis(gen); // custom int_dis name
double random_float = float_dis(gen); // custom float_dis name
// must be same as the mt19937's name
// Output the random number
cout << "Random number: " << random_number << endl;
cout << "Random float: " << random_float << endl;
}
```
#### Vector
```cpp!
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <random>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Create a list (vector)
vector<int> list = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
// Create a random device and initialize Mersenne Twister generator
random_device rd;
mt19937 gen(rd());
// Define the distribution range for indices
uniform_int_distribution<> dis(0, list.size() - 1);
// Generate a random index and select the element
int random_index = dis(gen);
int random_element = list[random_index];
// Output the random element
cout << "Random element: " << random_element << endl;
}
```
#### Shuffle values in vector
```cpp!
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm> // std::shuffle
#include <random>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Create a list (vector)
vector<int> list = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
// Create a random device and initialize Mersenne Twister generator
random_device rd;
mt19937 gen(rd());
// Shuffle the list
shuffle(list.begin(), list.end(), gen);
// Output the shuffled list
cout << "Shuffled list: ";
for (int element : list) {
cout << element << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
```
---
### Dừng thời gian
#### 1. Hàm hệ thống:
```cpp!
#include <unistd.h> // For sleep() and usleep() mac
sleep(3); // Pause for 3 seconds
usleep(3000000); //Pause for 3,000,000 microseconds (3 seconds)
usleep(3000*1000); //Pause for 3000 miliseconds (3 seconds)
```
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h> // For sleep() and usleep() windows
#include <unistd.h> // For sleep() and usleep() mac
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Pausing for 3 seconds..." << endl;
sleep(3); // Pause for 3 seconds
cout << "Pausing for 3 seconds..." << endl;
usleep(3000000); //Pause for 3,000,000 microseconds (3 seconds)
cout << "Pausing for 3 seconds..." << endl;
usleep(3000*1000); //Pause for 3000 miliseconds (3 seconds)
cout << "Resuming execution." << endl;
}
```
#### 2. Hàm chrono:
```cpp!
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(1));
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(500));
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::microseconds(1));
```
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Pausing for 1 second..." << endl;
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(1));
cout << "Pausing for 0,5 seconds..." << std::endl;
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(500));
cout << "Pausing for 1 microsecond..." << endl;
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::microseconds(1));
```
## II.d iomanip
```cpp!
setfill(char); // set character to replace spaces
```
---
```cpp!
setw(n); // set output width (also count the value width)
```
---
```cpp!
cout << fixed; // use with setprecision to show decimal number
setprecision(n); //format number of digit in float and also count the available value's digit
```
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
#include <iostream> // std::cout, std::endl
#include <iomanip> // std::setfill, std::setw
using namespace std;
int main () {
cout << setfill('x') << setw(10);
cout << 77 << endl;
}
```
```yaml!
xxxxxxxx77
```
```cpp=
#include <iostream> // std::cout, std::fixed
#include <iomanip> // std::setprecision
int main () {
double f =3.14159;
std::cout << std::setprecision(5) << f << '\n';
std::cout << std::setprecision(9) << f << '\n';
std::cout << std::fixed;
std::cout << std::setprecision(5) << f << '\n';
std::cout << std::setprecision(9) << f << '\n';
}
```
```yaml!
3.1416
3.14159
3.14159
3.141590000
```
:::
## II.e Conversion
### Int to string
```cpp!
to_string(int);
```
---
### String to int
```cpp!
stoi(str); // stoi = string to int
```
## II.f Tách phần tử
:::info
[Reference :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stringstream-c-applications/)
:::
### stringstream
```cpp!
#include <sstream>
stringstream ss(str);
ss >> element1 >> element2 >> element3...; // no need
```
---
### stringstream nhưng tách theo ký tự tự chọn
```cpp!
#include <sstream>
stringstream ss(str);
ss >> element1 >> element2 >> element3...; // no need
string word;
while((getline(ss, word, '-')){
// cout words or do sth
}
```
:::info
Nếu muốn tách với nhiều ký tự thì thay toàn bộ chúng bằng dấu cách
ss chỉ là tên đặt :warning:
:::
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s = "28tech,hoc.lap!!trinh???C++ dsa";
//Thay hết delimiter bằng dấu cách
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
if(s[i] == '?' || s[i] == '!' || s[i] == '.' || s[i] == ','){
s[i] = ' ';
}
}
//Khai báo stringstream ss và gán cho nó nội dung của s
stringstream ss(s);
string word;
int dem = 0;
while(ss >> word){
++dem;
cout << "Tu thu " << dem << " tach duoc : " << word << endl;
}
}
```
```yaml!
Tu thu 1 tach duoc : 28tech
Tu thu 2 tach duoc : hoc
Tu thu 3 tach duoc : lap
Tu thu 4 tach duoc : trinh
Tu thu 5 tach duoc : C++
Tu thu 6 tach duoc : dsa
```
:::
## II.g Type
### Print data type
```cpp!
#include <typeinfo>
typeid(data).name();
```
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 5;
double b = 3.14;
string c = "Hello, world!";
cout << "Type of a: " << typeid(a).name() << endl;
cout << "Type of b: " << typeid(b).name() << endl;
cout << "Type of c: " << typeid(c).name() << endl;
}
```
> Type of a: i
Type of b: d
Type of c: NSt3__112basic_stringIcNS_11char_traitsIcEENS_9allocatorIcEEEE
:::
---
### Change data type
```cpp
static_cast<new_type>(target); // any type
target = (new_type)(target);
```
[Details :bulb:]([/null](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/static_cast-in-cpp/))
## II.h Shorten code
### Count
```cpp
count(vect.begin(), vect.end(), target)
```
## II.g CCType
:::info Ability
Check if value is something ⚡
:::
[Details :bulb:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/ctype-hcctype-library-in-c-c-with-examples/)
# III.Better code / Code knowledge
## III.0 Random
### Vòng lặp for có thể bị khuyết
```cpp=
for( ; ; ){
cout << "ambatokam";
}
```
---
### Vòng lặp con có biến cục bộ của nó nên không bị ảnh hưởng tới vòng lặp con
```cpp=
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
cout << "an ba to com";
}
}
```
## II.h climits (limits.h)
[References :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/climits-limits-h-cc/)
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "CHAR_MIN : " << CHAR_MIN << endl;
cout << "CHAR_MAX : " << CHAR_MAX << endl;
cout << "SHRT_MIN : " << SHRT_MIN << endl;
cout << "SHRT_MAX : " << SHRT_MAX << endl;
cout << "USHRT_MAX : " << USHRT_MAX << endl;
cout << "INT_MIN : " << INT_MIN << endl;
cout << "INT_MAX : " << INT_MAX << endl;
cout << "UINT_MAX : " << UINT_MAX << endl;
cout << "LONG_MIN : " << LONG_MIN << endl;
cout << "LONG_MAX : " << LONG_MAX << endl;
cout << "ULONG_MAX : " << ULONG_MAX << endl;
cout << "LLONG_MIN : " << LLONG_MIN << endl;
cout << "LLONG_MAX : " << LLONG_MAX << endl;
cout << "ULLONG_MAX : " << ULLONG_MAX << endl;
}
```
## III.a Loops
### Do while loops
```cpp=
do{
cout << "Enter a positive number: ";
cin >> number
}while(number < 0);
```
:::success
Use this if you want to loop while input is wrong :tada:
:::
---
### Duyệt qua từng input
```cpp!
for(int x; cin >> x;){
// code
}
while(cin >> x){
// code
}
```
## III.b Các giá trị/dữ liệu
### Tuỳ kiểu dữ liệu mà máy tính có thể lưu giá trị với độ lớn khác nhau (byte)
:::spoiler VD
1. int 32 bit của số 10:
- 0 (dương) 0000000000000000000000000001010 (31 bit còn lại để lưu giá trị)
2. int 16 bit của số -10:
- 1 (âm) 000000000001010 (15 giá trị còn lại để lưu giá trị)
:::success
Tip để nhớ giá trị tối đa:
VD: int 32 bit dùng 1 bit để đánh dấu âm/dương và 31 bit còn lại để lưu giá trị, vậy giá trị tối đa lưu được là --> 2^31
VD: long long int: int 64 bit dùng 1 bit để đánh dấu âm/dương và 63 bit còn lại để lưu giá trị, vậy giá trị tối đa lưu được là --> 2^63
:::
:::warning
Nên ghi nhớ số lượng bộ nhớ của từng kiểu dữ liệu :warning:
:::

:::info
1 byte = 8 bit :information_source:
:::
:::warning
Phạm vi giá trị thực = phạm vi giá trị lý thuyết - 1 (do mất 1 bit để lưu âm/dương), khi bị vượt quá giá trị thì chương trình sẽ tự chỉnh bit âm/dương, do đó biến sẽ bị đổi dấu âm/dương (gọi là bị tràn) :warning:
||Có thể dùng để troll/ảo thuật||
:::
---
### Công thức kiểu dữ liệu
#### 1. int + int = int
#### 2. long long int + int = long long int
#### 3. int + float = int
#### 4. double + int = double
---
### Biến chỉ lấy giá trị cuối khi trong ngoặc và được tách với nhau bằng dấu `,`
```cpp=
z = (10 * 20, 30 * 40, 50 * 60); //output: 50*60 = 3000
```
---
### Biến chỉ lấy giá trị đầu khi không có ngoặc và được tách với nhau bằng dấu `,`
```cpp=
z = 10 * 20, 30 * 40, 50 * 60; //output: 10*20 = 200
```
:::warning
Khi có toán tử là dấu `,` thì câu lệnh sẽ chạy từ trái sang phải rồi lấy giá trị cuối cùng :end:
:::
---
### Kiểu static
#### 1. Static local variables: Giữ nguyên giá trị giữa các lần gọi hàm.
#### 2. Static global variables: Chỉ truy cập được trong tệp tin mà nó được khai báo.
#### 3. Static member variables: Biến chung cho tất cả các đối tượng của lớp.
#### 4. Static member functions: Có thể được gọi mà không cần tạo đối tượng của lớp.
## III.c Đệ quy
### Fibonacci
```cpp!
int fibo(int n) {
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fibo(n-1) + fibo(n-2);
}
```
**hoặc**
```cpp!
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
int a = 0 /* previous */, b = 1 /* current */, c = 0; // next
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
cout << (n == 1 ? 1 : c);
}
```
:::info
Fibonacci là gọi lại hàm với giá trị mới và cộng kết quả của từng hàm giá trị nhỏ lại :loop:
:::
## III.d Độ phức tạp thuật toán
### Cách tính thời gian thực hiện C++
==$$\frac{O(n)}{2*10^8}$$==
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ OR -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
==$$\frac{O(n)}{2e8}$$==

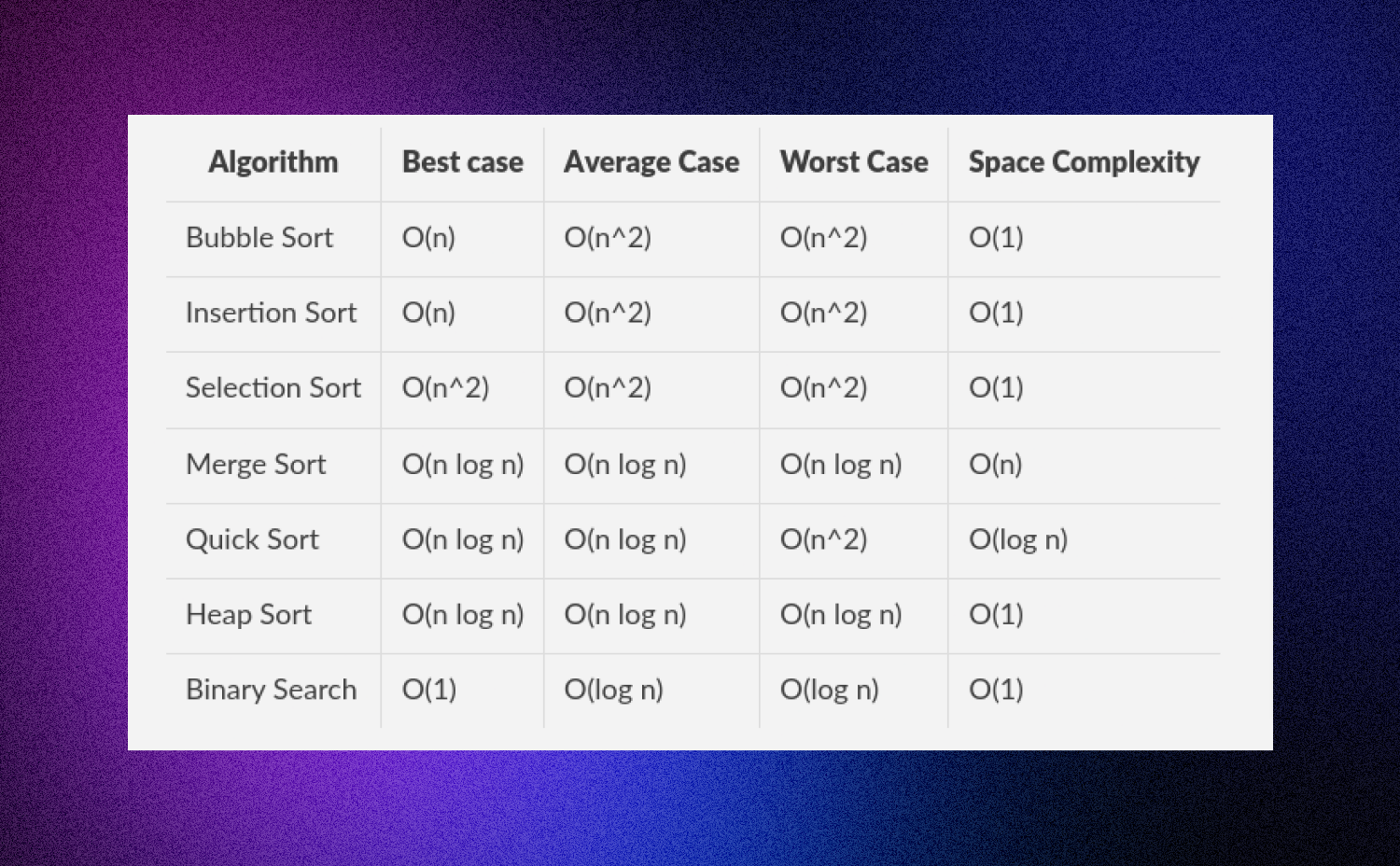
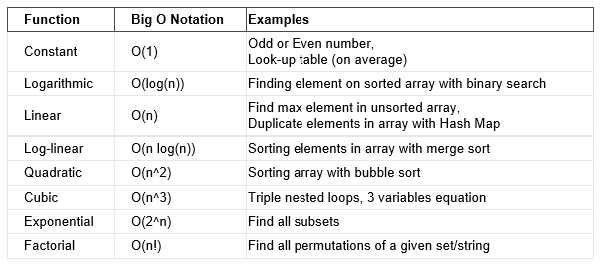

## III.e Các dạng bài toán
### Tìm một số suất hiện trong các số
```!
Gọi số đề cho là n và số cần tìm là x
```
```cpp!
if(n%10 == x){
count++;
n /= 10;
}
else{
n /= 10;
}
```
## III.f Lỗi thường gặp
:::danger
main() chỉ có thể chứa arr <= 1e6 :no_entry:
nếu muốn dùng thì phải khai báo ngoài main() :heavy_check_mark:
:::
## III.g Throw - Catch error
### Catch out of range error
```cpp=
catch (const std::out_of_range& e) {
std::cerr << "Key not found: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
```
### Example of throw - catch error
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
float mySqrt(float value) {
if (value < 0) {
throw runtime_error("Negative numbers not allowed");
}
return sqrt(value);
}
int main() {
float posNumber = 4.41;
float negNumber = -1.0;
try {
cout << "Square root of " << posNumber << " is " << mySqrt(posNumber) << "\n";
cout << "Square root of " << negNumber << " is " << mySqrt(negNumber) << "\n";
}
catch (runtime_error error) {
cout << "ERROR: " << error.what() << "\n";
}
}
```
[Resource :book:](https://www.codecademy.com/resources/docs/cpp/exceptions)
## III.h Tips & Tricks c++
https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/74684
https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/15643
### `||`, `&&` and `!` replacement
:::success
- `||` --> `or`
- `&&` --> `and`
- `!` --> `not`
:::
[more :tada:](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/operator_alternative)
[C++ Keywords :books:](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/keyword)
### Boolalpha
```cpp!
bool f = false;
cout << f << '\n';
cout << boolalpha << f;
```
**Output:**
```yaml!
0
false
```
### Assume 0 to false and every value != 0 to true
```cpp!
int n = 5;
cout << !!n;
```
**Output:**
```yaml!
1
```
### Binpow không tràn số
```cpp=
long long binpow(long long a, int k){
long long res = 1;
while(k > 0){
if(k&1){
if(res > lim/a) return lim;
res *= a;
}
if(a > lim/a) a = lim;
else a *= a;
k >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
```
### +1 nhanh cho số chẵn
```cpp=
int x = 10;
int y = x | 1; // y = 11
// Chỉ áp dụng được cho số chẵn vì đuôi binary của số chẵn là 0
```
## III.i Important methods
### Black Box
#### E.g:
1. **Use a DP Template:** Start with a DP template code relevant to the problem.
2. **Implement the Solution:** Adapt the template to fit the specific problem requirements.
3. **Learn During Implementation:** As you implement, learn and understand the principles of DP applied in that context.
4. **Study Theory:** After getting the implementation to work, study the theoretical aspects of DP to deepen your understanding.
## III.j Các độ phức tạp
- Count() —> O(logn)
- Container khi tác động vào 1 phần tử bất kỳ —> O(n)
- Cây nhị phân --> O(logn) <-- chiều cao của cây nhị phân
- Độ phức tạp khi thêm node vào cây nhị phân --> O(logn)
- Tác động vào phần tử của map --> O(logn)
- Tác động vào phần tử heap --> O(logn)
## III.k Lưu ý
### Vector bool
- Nên dùng `vector<int>` thay cho `bool` vì nó sẽ dễ bị lỗi, do quá trình chuyển đổi của `vector<bool>`
## III.l Tà thuật
### Lambda
```cpp=
#include <functional>
std::function<int(int,int)> plus = [](int &a, int &b){
return a+b;
}
```
- Có thể dùng `auto` thay thế cho `std::function<int(int,int)>`
- Cú pháp function: `function<kiểu trả về(tham số 1, tham số 2, ...)>`
- Cú pháp tạo hàm:
- Ngoặc vuông `[]`: capture list
- `[]`: chỉ truy cập giá trị tham số được truyền vào
- `[=]`: truy cập được tất cả các biến chung hàm (như hàm main) dưới dạng tham trị
- `[&]`: truy cập được tất cả các biến chung hàm (như hàm main) dưới dạng tham chiếu
- `[nhiều biến nào đó]`: truy cập được các biến này mà không cần dùng tham số
- `[x = 123]`: tạo biến sẵn, nếu muốn thay đổi biến này trong hàm, ta cần dùng `mutable` ở giữa ngoặc tham số và ngoặc nhọn
- `[&,x,y]` hay `[=,&x,&y]`: tất cả được lấy bằng tham chiếu/tham trị, ngoại trừ x,y
- Ngoặc tròn `()`: như tham số hàm bình thường
- Ngoặc nhọn `{}`: chỗ nhét câu lệnh
### Struct define
```cpp=
struct box{
int x,y,z;
box(int _x = 0, int _y = 0, int _z = 0): x(_x),y(_y),z(_z) {};
};
box temp(1,2,3);
```
- Đồng nghĩa với:
```cpp=
struct box{
int x,y,z;
box(int _x = 0, int _y = 0, int _z = 0){ // default = 0, hàm khởi tạo cho struct, giống class học ở codecademy
x = _x, y = _y, z = _z;
};
};
box temp(1,2,3);
// hoặc
struct box{
int x,y,z;
};
box temp = {1,2,3};
```
### Struct operator
- Ta có thể định nghĩa lại bất kỳ toán tử nào với operator như `<`, `>`, `=`, ,`==`,`+=`, `<<`,...
- Ta sử dụng dấu `<` để làm ví dụ sau:
```cpp=
struct Point{
int x,y;
bool operator<(const Point& other) const{ // tra ve true neu Point A < Point B
if(this->x == other.x) return this->y < other.y; // o day cho dau gi cung dc, mien dung y minh la A < B
return this->x < other.x;
}
}
vector<Point> a = {{1,2},{1,1},{3,0},{1,1}};
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
// Ket qua: a = {{1,1},{1,1},{1,2},{3,0}}
```
- Đặc biệt với toán tử `<<` ta phải cho cú pháp `friend` ở trước
```cpp=
struct box{
int x,y;
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const box& a){
os << a.x << a.y;
return os;
}
}
```
- Nếu muốn tham chiếu (điều chỉnh trực tiếp) kết quả đầu ra luôn thì ta làm như này:
```cpp=
struct box{
int x,y;
// Sử dụng dấu `&` sau giá trị return
box& operator+=(const box a){
this->x += a.x;
this->y += a.y;
return *this;
}
// Có thể truyền vào kiểu giá trị khác box cũng được
box& operator=(const int value){
this->x = value;
return *this;
}
}
```
# IV. Thuật toán / Quy Luật
## IV.a Chung Chung
### Tìm phần tử ở giữa array
```cpp!
int mid = start + (end - start)/2; // tránh overflow và chính xác
```
---
### Định lý thợ
https://tek4.vn/khoa-hoc/cau-truc-du-lieu-va-thuat-toan/uoc-luong-do-phuc-tap-cua-de-quy-bang-dinh-ly-tho-master-theorem 👷♂️
---
### Làm việc với từng input
```cpp
for (int x; cin >> x; ) {
//code
}
```
#### cin vào vec
```cpp
vector<int> a(n);
for(int &x : a){
cin >> x; // auto put in vector a
}
```
## IV.b Làm việc với số
### Tính tổng ước số / số ước
https://blog.28tech.com.vn/c-tinh-tong-uoc-so-nguyen
## IV.c Sort
==Dưới đây là danh sách các thuật toán sắp xếp phổ biến trong C++, sắp xếp theo độ phức tạp từ thấp đến cao, kèm theo mô tả và ví dụ mã nguồn.== 🥳
### 0. Sort tích hợp
```cpp=
#include <algorithm>
template <class T> // có thể sort nhiều dât types
bool funComparator(T x1, T x2)
{ // return type is bool
return x1 <= x2;
}
class Comparator { // we pass an object of this class as
// third arg to sort function...
public:
bool operator()(T x1, T x2)
{
return x1 < x2;
}
};
```
```cpp
sort(vector.begin(), vector.end());
sort(vector.begin(), vector.end(), greater<int>());
sort(vector.begin(), vector.end(), funComparator<int>); // change int to your desire type
sort(vector.begin(), vector.end(), Comparator<int>());
```
```cpp
sort(arr, arr + arr_size);
sort(arr, arr + arr_size, greater<int>());
sort(arr, arr + arr_size, funComparator<int>);
sort(arr, arr + arr_size, Comparator<int>());
```
[Source ℹ️](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/sort-c-stl/)
### 1. Sắp Xếp Chèn (Insertion Sort)
- **Độ phức tạp**: O(n²)
- **Giải thích**: Sắp xếp từng phần tử vào vị trí thích hợp trong dãy đã sắp xếp, hiệu quả cho dãy nhỏ hoặc dãy đã sắp xếp một phần.
```cpp=
void insertionSort(std::vector<int>& arr) {
for (int i = 1; i < arr.size(); i++) {
int key = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
```
---
### 2. Sắp Xếp Chọn (Selection Sort)
- **Độ phức tạp**: O(n²)
- **Giải thích**: Tìm phần tử nhỏ nhất trong mảng và hoán đổi nó với phần tử đầu tiên, lặp lại cho phần tử còn lại.
```cpp=
void selectionSort(std::vector<int>& arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size() - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.size(); j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
std::swap(arr[i], arr[minIndex]);
}
}
```
---
### 3. Sắp Xếp Bubblesort (Bubble Sort)
- **Độ phức tạp**: O(n²)
- **Giải thích**: So sánh từng cặp phần tử và hoán đổi nếu chúng không theo thứ tự, lặp lại cho đến khi không còn hoán đổi.
```cpp=
void bubbleSort(std::vector<int>& arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size() - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.size() - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
std::swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
```
---
### 4. Sắp Xếp Nhanh (Quicksort)
- **Độ phức tạp trung bình**: O(n log n)
- **Giải thích**: Chọn một phần tử làm pivot, phân chia mảng thành các phần nhỏ hơn và lớn hơn pivot, và đệ quy.
#### Lomuto
```cpp=
int randomPartition(vector<int> &arr, int low, int high) {
// Select a random index as the pivot
int pivotIndex = low + rand() % (high - low + 1);
swap(arr[pivotIndex], arr[high]); // Move pivot to the end
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (arr[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
swap(arr[i], arr[j]);
}
}
swap(arr[i + 1], arr[high]); // Move pivot to its final place
return i + 1;
}
void quicksort(vector<int> &arr, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pi = randomPartition(arr, low, high);
quicksort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quicksort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
```
#### Hoare
```cpp=
int hoarePartition(vector<int>& arr, int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[low];
int i = low - 1;
int j = high + 1;
while (true) {
do {
i++;
} while (arr[i] < pivot);
do {
j--;
} while (arr[j] > pivot);
if (i >= j)
return j;
swap(arr[i], arr[j]);
}
}
void quickSortHoare(vector<int>& arr, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int p = hoarePartition(arr, low, high);
quickSortHoare(arr, low, p);
quickSortHoare(arr, p + 1, high);
}
}
```
:::danger
Lomuto's pivot position: end :warning:
Hoare's pivot position: start :warning:
:::
---
### 5. Sắp Xếp Hợp Nhất (Mergesort)
- **Độ phức tạp**: O(n log n)
- **Giải thích**: Chia mảng thành hai nửa, sắp xếp từng nửa và hợp nhất chúng lại.
```cpp=
void merge(std::vector<int>& arr, int left, int mid, int right) {
int n1 = mid - left + 1;
int n2 = right - mid;
std::vector<int> L(n1), R(n2);
for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++) L[i] = arr[left + i];
for (int j = 0; j < n2; j++) R[j] = arr[mid + 1 + j];
int i = 0, j = 0, k = left;
while (i < n1 && j < n2) {
if (L[i] <= R[j]) arr[k++] = L[i++];
else arr[k++] = R[j++];
}
while (i < n1) arr[k++] = L[i++];
while (j < n2) arr[k++] = R[j++];
}
void mergeSort(std::vector<int>& arr, int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
mergeSort(arr, left, mid);
mergeSort(arr, mid + 1, right);
merge(arr, left, mid, right);
}
}
```
----
### 6. Sắp Xếp Heap (Heapsort)
- **Độ phức tạp**: O(n log n)
- **Giải thích**: Chuyển đổi mảng thành heap và sau đó trích xuất phần tử lớn nhất liên tục cho đến khi mảng trống.
```cpp=
void heapify(std::vector<int>& arr, int n, int i) {
int largest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
if (left < n && arr[left] > arr[largest])
largest = left;
if (right < n && arr[right] > arr[largest])
largest = right;
if (largest != i) {
std::swap(arr[i], arr[largest]);
heapify(arr, n, largest);
}
}
void heapSort(std::vector<int>& arr) {
int n = arr.size();
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
heapify(arr, n, i);
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
std::swap(arr[0], arr[i]);
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
```
---
### 7. Sắp Xếp Đếm (Counting Sort)
- **Độ phức tạp**: O(n + k) (k là phạm vi giá trị của mảng)
- **Giải thích**: Đếm số lần xuất hiện của mỗi giá trị, sau đó tái tạo mảng đã sắp xếp dựa trên các đếm.
```cpp=
void countingSort(std::vector<int>& arr, int k) {
std::vector<int> count(k + 1, 0);
std::vector<int> output(arr.size());
for (int num : arr) count[num]++;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) count[i] += count[i - 1];
for (int i = arr.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[arr[i]] - 1] = arr[i];
count[arr[i]]--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) arr[i] = output[i];
}
```
---
### 8. Sắp Xếp Radix (Radix Sort)
- **Độ phức tạp**: O(n * k) (k là số chữ số tối đa của các phần tử)
- **Giải thích**: Sắp xếp các phần tử theo từng chữ số, bắt đầu từ chữ số thấp nhất đến chữ số cao nhất.
```cpp=
void countingSortForRadix(std::vector<int>& arr, int exp) {
std::vector<int> output(arr.size());
int count[10] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]++;
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
count[i] += count[i - 1];
for (int i = arr.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10] - 1] = arr[i];
count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
arr[i] = output[i];
}
void radixSort(std::vector<int>& arr) {
int maxVal = *max_element(arr.begin(), arr.end());
for (int exp = 1; maxVal / exp > 0; exp *= 10)
countingSortForRadix(arr, exp);
}
```
---
### 9. Sắp Xếp Bucket (Bucket Sort)
- **Độ phức tạp**: O(n + k) (k là số bucket)
- **Giải thích**: Chia dữ liệu thành các bucket, sau đó sắp xếp từng bucket và gộp lại.
```cpp=
void bucketSort(std::vector<float>& arr) {
int n = arr.size();
std::vector<std::vector<float>> buckets(n);
for (float num : arr) {
int index = n * num; // Phân chia thành các bucket
buckets[index].push_back(num);
}
for (auto& bucket : buckets) {
std::sort(bucket.begin(), bucket.end()); // Sắp xếp từng bucket
}
int index = 0;
for (const auto& bucket : buckets) {
for (float num : bucket) {
arr[index++] = num; // Gộp các bucket lại
}
}
}
```
## IV.d Searching
## Tìm kiếm nhị phân
[References :book:](https://blog.28tech.com.vn/c-tim-kiem-nhi-phan)
```cpp=
int firstPos(int a[], int n, int x){
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
int pos = -1; // cập nhật kết quả
while(l <= r){
//Tính chỉ số của phần tử ở giữa
int m = (l + r) / 2;
if(a[m] == x){
pos = m; // lưu lại
//Tìm thêm bên trái
r = m - 1;
}
else if(a[m] < x){
//tìm kiếm ở bên phải
l = m + 1;
}
else{
//tìm kiếm ở bên trái
r = m - 1;
}
}
return pos;
}
```
## IV.e Các cách tối ưu code
### Lũy thừa đệ quy
```cpp=
ll binpow(int n, int k){
if(k == 0){
return 1;
}
ll X = binpow(n, k / 2); // n^(k/2)
if(k % 2 == 1){
return X * X * n;
}
else{
return X * X;
}
}
```
:::info
Số lẻ phải nhân thêm n là do khi n/2 2 lần, số bị mất sẽ = n
```
pow(x, 2k) = x*x*x*...*x (2k lần)
pow(x, 2k) = (x*x*x*...*x) * (x*x*x*...*x)
^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^
(k lần) (k lần)
= pow(x, 2k) * pow(x, 2k)
```
:::
[Tham khảo :mortar_board:](https://blog.28tech.com.vn/luy-thua-nhi-phan)
## IV.f Pointer
### New
```cpp!
int *pointerNum = NULL;
pointerNum = new int;
string *pointerString = NULL;
pointerString = new string;
```
---
### Delete
```cpp!
delete pointerNum;
delete pointerString;
```
:::success
Use this along with new to prevent memory leeks.
E.g: Store value into pointer and delete after using it.
:::
---
### Quick Dereference
```cpp!
(*ptr) //use this with your desire command as a dereferenced pointer
```
---
### Dot and Arrow
- Arrow is used for iterator or pointer (E.g: Access map first and second)
- Dot is used for already exist thing
#### 1. E.g of Dot
```cpp!
pair.first;
```
#### 2. E.g of Arrow
```cpp!
it->first (map)
it->second (map)
```
---
### this ->
```
Use to navigate object in class or struct
```
[Example :heavy_check_mark:](https://unstop.com/blog/this-pointer-in-cpp)
[Bro Code (cutted part):scissors:](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-TkoO8Z07hI&t=19920s)
---
### Getenv()
The getenv() function in C++ is used to return a pointer to the C string that contains the value of the environment variable passed as an argument.
[Details :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/cpp-getenv-function/)
# V. Data structures/types
## V.a Vector/Array
:::danger
Khi gọi ==[first,last]== của vector thì index thứ first sẽ được tính nhưng ==index last
chỉ được tính là last + 1==
==--> Khi muốn bao gồm luôn index last thì ta ghi last + 1==
**VD: `vector<int> x(a + l, a + m + 1);` // vector x lấy giá trị từ a[l] --> a[m]**
:::
### Xoá một phần tử trong vector
```cpp=
int valueToBeDeleted = 3;
auto it = find(vector.begin(), vector.end(),
valueToBeDeleted);
if (it != vector.end()) {
vector.erase(it);
}
```
---
### Size vec
```cpp!
vec.size();
vec.sizeof();
```
---
### Thêm phần tử vào cuối
```cpp!
vector.push_back(value);
vector.emplace_back(value); // nhanh hơn xíu
```
---
### Reserve nhanh hơn
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/using-stdvectorreserve-whenever-possible/
---
### Inserter & Back_insterter
[Inserter](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stdinserter-in-cpp/)
[Back_inserter](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stdback_inserter-in-cpp/)
---
### Bớt giá trị ở cuối
```cpp!
vector.pop_back(value);
```
---
### Cin vào một phần tử trong vec
```cpp!
cin >> vector[index];
```
---
### Fill giá trị
```cpp!
fill(begin, end, value);
```
---
### Resize giá trị
```cpp!
vector.resize(<wanted_size>);
```
---
### Loại bỏ giá trị trùng LIÊN TIẾP
```cpp!
vec.resize(unique(vec.begin(), vec.end()) - vec.begin());
// or
vec.erase(unique(vec.begin(), vec.end()) - vec.begin());
```
---
### Matrix multi-dimension
- Cách khai báo vector N chiều:
```cpp!
vector<int> a[N]
```
Ta có:
```cpp!
vector<vector<int>> a = vector<int> a[2];
```
#### 1. Vector:
```cpp!
vector<vector<int>> nums = {{1,2,3},
{4,5,6},
{7,8,9}}; // để ý data type
cout << nums[2][2];
```
#### 2. Array:
```cpp!
int nums[row][col] = {{1,2,3},
{4,5,6},
{7,8,9}};
cout << nums[2][2];
```
:::spoiler How to print a 2d matrix?
### Vector:
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<vector<int>> nums = {{1,2,3},
{4,5,6},
{7,8,9}}; // để ý data type
// 1
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < nums[i].size(); j++){
cout << nums[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
// or 2
for(vector<int> row : nums){
for(int col : row){
cout << col << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
```
### Array:
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Template function to print a 2D array
template <typename T, size_t rows, size_t cols>
void print2DArray(T (&array)[rows][cols]) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (size_t j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
cout << array[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
} // for way 3 only
int main() {
const int rows = 3;
const int cols = 3;
int array[rows][cols] = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6},
{7, 8, 9}
};
// can calculate size by
int rows = sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]);
int cols = sizeof(array[0])/sizeof(array[0][0]);
// 1
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
cout << array[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// or 2
for (int (&row)[cols] : array) { // row is a reference to an array of ints
for (int col : row) { // col is a reference to an int
cout << col << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// or 3
print2DArray(array);
}
```
:::
:::info
- Mỗi phần tử trong mảng 2d là 1 vector :warning:
- Các row và col trong array có thể dùng auto :100:
:::
---
### Kiểm tra vector trống
```cpp!
if(vector.empty()){
// do something
}
```
---
### Lấy index đầu và cuối
```cpp!
vector.front();
vector.back();
```
---
### Chỉnh kích thước của vec
```cpp!
// vector.resize(n, value);
vector<int> num = {1,2,3,4,5};
num.resize(4);
vector<int> num2 = {1,2,3,4,5};
num2.resize(7, 9);
```
```!
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5 9 9
```
---
### Tạo iterator cho vec
```cpp
vector<int>::iterator ptr; //pointer to interation of vec
```
---
### Tăng giá trị pointer trỏ về iterator
```cpp
// Using advance() to increment iterator position
// points to 4
advance(ptr, 3);
```
---
### Trả về giá trị tăng/giảm của iterator
```cpp
// Using next() to return new iterator
// points to 4
auto it = next(ptr, 3);
// Using prev() to return new iterator
// points to 3
auto it1 = prev(ftr, 3);
```
---
### Thêm vào iterator mới
```cpp
// copying 1 vector elements in other using inserter()
// inserts ar1 after 3rd position in ar
copy(ar1.begin(), ar1.end(), inserter(ar,ptr));
```
---
### Remove điều kiện
```cpp!
std::remove_if(vec2.begin(), vec2.end(), IsOdd /* condition */);
```
---
### Tìm số lớn nhất trong vec
```cpp!
std::max_element(start iterator, end iterator);
```
---
### Tìm số nhỏ nhất trong vec
```cpp!
std::min_element(start iterator, end iterator);
```
---
### Kiểm tra nếu 2 vector giống nhau
```cpp!
std::equal(vec1.begin(), vec1.end(), vec2.begin());
```
[References :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stdequal-in-cpp/)
---
### Lặp qua từng phần tử của vec
```cpp!
for(<data_type> <name> : <vector_name){
// code
}
```
---
### Tạo và lặp qua từng phần tử ngay trong vòng lặp
```cpp!
for(<data_type> <name> : {<values>}){
// code
}
```
**Example:**
```cpp!
for(int i : {0, 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 10, -11}){
// code
}
```
---
### Thay thế một đoạn phần tử
[Memset :brain:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/memset-in-cpp/)
## V.b Mảng
:::info
[Chi tiết :computer:](https://hackmd.io/@2SchoolGuideline/H1HY_VKbp)
:::
---
### Mảng cộng dồn 1 chiều
==- Mảng cộng dồn (prefix sum array) lưu trữ tổng các phần tử từ đầu mảng đến một vị trí cụ thể. Mục đích là để nhanh chóng tính tổng của bất kỳ đoạn con nào của mảng gốc==
[Tham khảo :book:](https://hackmd.io/@2SchoolGuideline/H1HY_VKbp#M%E1%BA%A3ng-c%E1%BB%99ng-d%E1%BB%93n-1-chi%E1%BB%81u)
:::spoiler VD
```cpp=
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> buildPrefixSum(const vector<int>& a) {
vector<int> prefix(a.size());
prefix[0] = a[0];
for (size_t i = 1; i < a.size(); ++i) {
prefix[i] = prefix[i - 1] + a[i];
}
return prefix;
}
int rangeSum(const vector<int>& prefix, int l, int r) {
if (l == 0) {
return prefix[r];
} else {
return prefix[r] - prefix[l - 1];
}
}
int main() {
vector<int> a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
vector<int> prefix = buildPrefixSum(a);
int l = 1, r = 3;
cout << "Sum from " << l << " to " << r << " is " << rangeSum(prefix, l, r) << endl; // Output: 9
}
```
:::
### Mảng hiệu 1 chiều
- Mảng hiệu 1 chiều là lấy $a[i]$ hiện tại - cho $a[i-1]$ và tạo thành mảng
:::success
**Tips:**
- Tạo mảng cộng dồn trên mảng hiệu sẽ ra được mảng gốc
- Chỉnh giá trị của 1 phần tử trong mảng sẽ ảnh hưởng đến tất cả các phần tử ở phía sau --> áp dụng để chỉnh một đoạn phần tử trong mảng hiệu mà không ảnh hưởng tới các phần tử khác bằng cách bù trừ
:::
## V.c Map
### Map
:::info
[References :books:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/map-associative-containers-the-c-standard-template-library-stl/)
[28tech :bulb:](https://blog.28tech.com.vn/stl-map-trong-c)
:::
:::info
### Basic map commands: :baby_bottle:
==begin()== – Returns an iterator to the first element in the map.
==end()== – Returns an iterator to the theoretical element that follows the last element in the map.
==size()== – Returns the number of elements in the map.
==max_size()== – Returns the maximum number of elements that the map can hold.
==empty()== – Returns whether the map is empty.
==pair insert(keyvalue, mapvalue)== – Adds a new element to the map.
==erase(iterator position)== – Removes the element at the position pointed by the iterator.
==erase(const g)== – Removes the key-value ‘g’ from the map.
==clear()== – Removes all the elements from the map.
==count()== – Kiểm tra nếu key tồn tại trong map mà không tốn dung lượng
:::
**- Có thể kiểm tra nếu key có trong map bằng cách: (giá trị trả về là 0)**
```cpp!
map<string,int> mp;
if(map["example"] == 0){
// code
}
```
### Note:
- Khi truy cập vào 1 key chưa tồn tại trước đó của map, map sẽ tạo 1 key mới trong map với giá trị mặc định = 0 --> lưu ý cho độ phức tạp vì size map sẽ tăng
- Do đó, nên dùng `count()` nếu muốn kiểm tra key có tồn tại trong map không để không tốn dung lượng
### Các cách in phần tử trong map
```cpp!
// Cách 1
for(auto &c : mp){
cout << c.first << ' ' << c.second << endl;
}
// Cách 2
for (auto it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); it++) {
cout << "Key: " << it->first << ", Value: " << it->second << endl;
}
```
#### Example:
```cpp=
// C++ program to illustrate the begin and end iterator
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Create a map of strings to integers
map<string, int> mp;
// Insert some values into the map
mp["one"] = 1;
mp["two"] = 2;
mp["three"] = 3;
// Get an iterator pointing to the first element in the
// map
map<string, int>::iterator it = mp.begin();
// Iterate through the map and print the elements
while (it != mp.end()) {
cout << "Key: " << it->first
<< ", Value: " << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
return 0;
}
```
---
### Multimap
:::info
Vẫn sắp xếp theo thứ tự tăng dần nhưng key có thể trùng nhau nên không thể truy cập bằng cú pháp map[key]
:::
**Cú pháp:** ==multimap<int, int> mp;==
[References :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/multimap-associative-containers-the-c-standard-template-library-stl/)
---
### Unordered_map
:::info
Không còn sắp xếp tăng dần
:::
**Cú pháp:** ==unordered_map<string, int> umap;==
[References :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/unordered_map-in-cpp-stl/)
## V.d Set
### Set
```cpp!
std::set<data type> name = {index, index,...};
// details version
std::set<data type> name(start, stop) = {index, index,...};
// sort ascending
std::set <data_type, greater<data_type>> set_name;
```
[Details :bulb:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/set-in-cpp-stl/)
:::info
Start could be a pointer to an array (points to first index) 🥇
Stop could be a pointer to an array (points to last index) :end:
:::
---
### Multiset
```cpp!
multiset<int> name;
```
[References :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/multiset-in-cpp-stl/)
---
### Unordered_set
:::info
Chỉ khác [std::set](#Set) ở chỗ là không được sắp xếp sẵn
:::
```cpp!
std::unordered_set<data_type> name;
```
[References :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/unordered_set-in-cpp-stl/)
:::danger
Maybe O(logn) if n >= 3000
:::
## V.e Pair
```cpp!
pair<int, int> v;
// pair<type, type> name;
```
---
## V.f Iterator
:::info comamnds
.**begin();
.end();
.rbegin();** //reverse_begin
**.rend();** //reverse end
:::
```cpp!
#include <iterator>
vector<int> v = {any data type};
vector<type>::iterator name1 = v.begin();
vector<type>::reverse_iterator name2 = v.rbegin();
cout << *name1 << *name2; // needs * to output position's value
name1++; // plus position by 1
name1--; // minus position by 1
/*
v.begin()
v.end()
v.rbegin();
v.rend();
*/
```
---
## V.g Stack
**Thao tác với giá trị cuối cùng**
[References :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stack-in-cpp-stl/)
---
## V.h Queue
### Queue
**Thao tác với giá trị đầu tiên**
[References :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/queue-cpp-stl/)
---
### Dequeue (Double ended queue)
**Theo tác với giá trị đầu tiên + cuối cùng**
[References :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/deque-cpp-stl/)
---
### Priority Queue
:::danger
- Khác queue ở chỗ là nó sort từ lớn đến bé theo mặc định (max-heap)
- Dùng `greater<value>` để sort thành từ bé đến lớn (min-heap)
- Có thể sort theo ý muốn giống sort(), nhưng logic nó hơi ngược
- Có thể kết hợp với bool operator() trong struct
:::
[Details :bulb:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/priority-queue-in-cpp-stl/)
## V.i Binary
### Bit to decimal
#### Example: 1011 = 13
1. **Bit 0:**
• Giá trị của bit: 1
• Vị trí: 0
• Tính giá trị: 1 * 2^0^ = 1
2. **Bit 1:**
• Giá trị của bit: 0
• Vị trí: 1
• Tính giá trị: 0 * 2^1^ = 0
3. **Bit 2:**
• Giá trị của bit: 1
• Vị trí: 2
• Tính giá trị: 1 * 2^2^ = 4
4. **Bit 3:**
• Giá trị của bit: 1
• Vị trí: 3
• Tính giá trị: 1 * 2^3^ = 8
**Tổng giá trị:** 1 + 0 + 4 + 8 = 13
---
### Bitwise operator
[References :book:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/bitwise-operators-in-c-cpp/)
#### `&` **(bitwise AND)**
- **bit a == 1 && bit b == 1? --> 1**
- bit a == 0 || bit b == 0? --> 0
#### `|` **(bitwise OR)**
- **bit a == 1 || bit b == 1? --> 1**
- bit a == 0 && bit b == 0? --> 0
#### `^` **(bitwise XOR)**
- **bit a != bit b? --> 1**
- bit a == bit b? --> 0
#### `<<` **(left shift)**
- **add bit to rightmost of number**
#### `>>` **(right shift)**
- **add bit to leftmost of number**
#### `~` **(bitwise NOT)**
- **reverse all bits**
---
### Các thuật ảo ma với bit
#### For nhanh qua các bit 1 của mask
```cpp
for (int mask = state; mask >= 1; mask &= (mask - 1))
```
:::spoiler Giải thích
`mask & -mask`: lấy bit 1 nhỏ nhất dưới dạng $2^k$ ([Tham khảo bài giải thích của Phan Thành Hưng](https://hackmd.io/@hungg261/blog1))
`mask &= (mask-1)`: loại bỏ bit 1 nhỏ nhất
:::
## V.j Structure/Enum
### Structure
[Details :bulb:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/structures-in-cpp/)
---
### Enum
[Details :bulb:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/enumeration-in-cpp/) and [w3school :school:](https://www.w3schools.com/cpp/cpp_enum.asp)
## V.k Tuple
- Basically, it is pair but store 3 values
[Resource :books:](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/tuples-in-c/)
>
:::spoiler Resources :nerd_face:
[<img src="https://hackmd.io/_uploads/Sky4BZ4_A.png)" width="20" height="20"> Bro Code YT C++](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-TkoO8Z07hI)
[:computer: Algorithms for Competitive Programming](https://cp-algorithms.com/index.html)
[:star: Star Edu](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1jVk1_XFaRu5wdTcHPfAQaAsqP8gdvF-FcNUFaHnLi0c/edit)
[:memo: Competitive Handbook](https://cses.fi/book/book.pdf)
[<img src="https://hackmd.io/_uploads/rk6iSb8F0.png)" width="20" height="20"> GFG Algorithm](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/fundamentals-of-algorithms/)
:::