<style>
hr{display:none}
section h1 span{font-size:30%}
section h1,section h2,section h3{color: #EAC100!important},section h4,section h5,section h6,section p,section blockquote
{color: yellow !important}section a{color:#337ab7!important}section img{border:0!important}</style>
3D列印與組織工程
===
> [name=胡悰皓 ][color=#4d80e6]
> [name=吳定遠 ][color=#4d80e6]
> [name=劉書翰 ][color=#4d80e6]
+ Slide:https://reurl.cc/jk58XL\
+ Note : https://reurl.cc/Y96vvO
:::spoiler <h2 style="display:inline">目錄</h2> {state=open}
[ToC]
:::
---
## 器官移植&生物列印
---
### 器官移植
<font style="display:inline" >器官移植可分為活體移植與腦死移植</font>
* 活體移植:從健康成人體內取出一部份的器官或是整個器官,捐贈給另一個人。
* 腦死移植:從腦死亡者體內取出器官移植給需要的人。
----
### 器官捐贈者不足
器官捐贈條件:
腦死移植:
* 亡者須被兩位醫生被判定為腦死
* 亡者在生前以書面或是遺囑同意捐贈
* 必須取得兩位捐贈者家屬的同意書
活體移植:
* 須年滿20歲
* 身分需為需求者的五等親內
----
### 生物列印的理想
可以<font color=#4d80e6>直接將整個器官列印</font>出來,將來將不會有等待他人捐贈器官的需求者,需求者只需要提供自己的基因變可將受傷的器官替換下來,在藥物測式上也不需要白老鼠,可以直接列印該器官在上面做藥物測式,在將來也不需要大體老師,可以透過3D列印來製作。
---
### 一般3D列印
先透過電腦製圖,然後將3D的檔案,一層一層分解再透過3D列印機堆疊起來
----
### Bioprinting
與一般的3D列印相同,都是將材料一層一層疊起,不同在於使用的材料與過程,bioprinting使用生物墨水作為基底來製作器官或是組織
----
### 生物3D列印的實際發展限度
目前生物3D列印只能出組織或是器官的一部分,而較複雜的器官還在研究中
---
## 生物墨水
*`bioink`* 生物墨水
>是指含有生物相容性成分且具有良好的流變特性的任何天然或合成聚合物。
----
### 生物墨水的特性
* 具備非常好的生物活性。
* 具有很好的流動性。
* 列印後能很快固化以便於固定成型。
生物墨水的這些特性能夠暫時或永久地支撐細胞活力,促進細胞在成熟過程中的黏附、增殖和分化。
----
### 生物墨水分類
* 離子交聯型
* 溫敏型
* 光敏型
* 剪下變稀型
---
## 實例 : 半月板
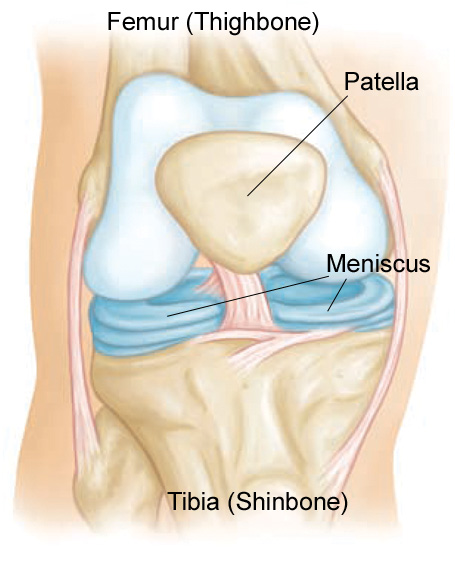
*`Chondrocytes`* 軟骨細胞
---
## 如何實作立體列印生物組織?
三維生物列印技術,通過空間控制各個要素的列印信息,逐層精確位置列印生物材料。
首先要準備好材料,並選擇合適的列印方法。
---
簡單分為三步驟
----
### Pre-bioprinting : **`Bioimaging`**
可以理解成3D列印所需的.stl檔案,在bioprinting上使用X-ray,CT 和 MRI 掃描成我們需要列印的藍圖。

----
### Bioprinting
主要有三種列印法
* *`Inkjet`* 噴墨式
* *`Microestrusion`* 擠出式
* *`Laser-Assisted`* 雷射輔助
----
### Inkjet printer
[Bioprinted Accelerate Healing of Skin Wounds](https://stemcellsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.5966/sctm.2012-0088)
----
### Extrusion bioprinting

----
### Post-bioprinting : **`Crosslinked`**
印好的組織有些墨水會立即變硬,而其他則需要通過`交聯`來使結構穩定。常見的方法有<font color=#4d80e6>UV Light</font>,<font color=#4d80e6>化學方法(pH)</font>和<font color=#4d80e6>物理方法(溫度)</font>。
---
## 3D Bioprinting design approaches
* *`Biomimicry`* 生物仿生法
* *`Autonomous self-assembly`* 自主自組裝
* *`Mini-tissues`* 微小組織構件
----
### Biomimicry
>通過複製組織的特定細胞,使用與其成分相同製造的複製品。須了解複製目標的微環境,ECM成分,細胞特定排列和材料合適等。
[Tissue Engineering and Developmental Biology: Going Biomimetic](https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/abs/10.1089/ten.2006.12.3265)
----
### Autonomous self-assembly
> *`self-assembly`* 意思即不在外界人力干擾下,使自行聚集,組織成有規則的結構。發育組織會自行產生自己的ECM成分。使用的細胞需有能領導組織組成,定位,結構,功能。通常使用 **`cellular spheroid `** 來模擬發育中的組織。
----
#### 培養自組裝細胞球

[reference link](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51970782_Efficient_formation_of_cell_spheroids_using_polymer_nanofibers)
----
### Mini-tissues
>結合上述兩種策略,使用具有功能,但更微小的細胞。例如 **腎單元**,通過設計、自組裝或兩者方法的組合來組成更大的構造。
---
## A typical process for bioprinting 3D tissues

[3D bioprinting of tissues and organs](https://www.nature.com/articles/nbt.2958)
---
## <h2 style="display:inline">Heart pump 3D bioprinting</h2>
{%youtube HDgUjJsMuYo %}
---
### Reference
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19176247/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0168165610001124
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142961209000052?casa_token=ES45FVC_YVsAAAAA:PfLvi_26ADIv8WDk3NwjQQ2HZmejdX40FTktBIJWQEED4vTXvEF_sBsfkHjW6zrBEFC2aHs_EQ
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095809920302496
---
## END
{"metaMigratedAt":"2023-06-16T17:11:34.288Z","metaMigratedFrom":"YAML","title":"3D列印與組織工程","breaks":true,"slideOptions":"{\"progress\":false,\"loop\":true,\"transition\":\"slide\"}","contributors":"[{\"id\":\"4039c7c6-929e-4623-bcab-ee47f79a408c\",\"add\":4410,\"del\":2031},{\"id\":\"8b98d25e-ac6a-4f45-ba1d-2d16e4dc9b2b\",\"add\":924,\"del\":277},{\"id\":\"a835a528-9e3b-4265-a9ec-aaf101244b90\",\"add\":995,\"del\":201}]"}