# Sliding Window & Contribution Technique
## Problem 1 : Find the max sum out of all possible subarray of the array
### Problem Statement
Given an array of integers, find the total sum of all possible subarrays.
**#Note:** This question has been previously asked in *Google* and *Facebook*.
### Solution
* We can use the previous approach, where we calculated all sum subarray using Carry Forward technique.
* Instead of keeping track of maximum, we can simply add the sums in a variable.
### Pseudocode
```cpp
int sumOfAllSubarraySums(int arr[], int n) {
int total_sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int subarray_sum = 0;
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
subarray_sum += arr[j];
total_sum += subarray_sum;
}
}
return total_sum;
}
```
### Time and Space Complexity
* TC - O(n^2)
* SC - O(1)
## Problem 2 : Contribution Technique
We can optimize the above solution further by observing a pattern in the subarray sums.
Let's take the example array ``[1, 2, 3]``. The subarrays and their sums are:
```
[1] -> 1
[1, 2] -> 3
[1, 2, 3] -> 6
[2] -> 2
[2, 3] -> 5
[3] -> 3
Total Sum = 1+3+6+2+5+3 = 20
```
Instead of generating all subarrays, we can check that a particular element appears in how many subarrays and add its contribution that many times to the answer.
* the first element 1 appears in 3 subarrays: [1], [1, 2], and [1, 2, 3].
* the second element 2 appears in 4 subarrays: [2], [1, 2], [2, 3], and [1, 2, 3].
* the third element 3 appears in 3 subarrays: [3], [2, 3], and [1, 2, 3].
Total = $(1*3) + (2*4) + (3*3) = 20$
:::warning
Please take some time to think about "How to calculate the number of subarrays in which A[i] appears?" on your own before reading further.....
:::
### Question
In how many subarrays, the element at index 1 will be present?
A: [3, -2, 4, -1, 2, 6 ]
**Choices**
- [ ] 6
- [ ] 3
- [x] 10
- [ ] 8
**Explanation:** The subarrays in which the element at index 1 is present are -
[3, -2], [3, -2, 4], [3, -2, 4, -1], [3, -2, 4, -1, 2], [3, -2, 4, -1, 2, 6], [-2], [-2, 4], [-2, 4, -1], [-2, 4, -1, 2], [-2, 4, -1, 2, 6 ]. There are total 10 such subarrays.
### Question
In how many subarrays, the element at index 2 will be present?
A: [3, -2, 4, -1, 2, 6 ]
**Choices**
- [ ] 6
- [x] 12
- [ ] 10
- [ ] 8
**Explanation:** The subarrays in which the element at index 1 is present are -
[3, -2, 4], [3, -2, 4, -1], [3, -2, 4, -1, 2], [3, -2, 4, -1, 2, 6], [-2, 4], [-2, 4, -1], [-2, 4, -1, 2], [-2, 4, -1, 2, 6], [4], [4, -1], [4, -1, 2], [4, -1, 2, 6 ]. There are total 12 such subarrays.
### Find sum of all Subarrays sums continued
**Generalized Calculation -**
The start of such subarrays can be $0, 1, ..i$
The end of such subarrays can be $i, i+1, i+2, ...n-1$
Elements in range [0 i] = $i+1$
Elements in range [i n-1] = $n-1-i+1 = n-i$
Thus, the total number of subarrays containing arr[i] is i+1 multiplied by n-i.
This gives us the expression `(i+1) * (n-i)`.
We can use this pattern to compute the total sum of all subarrays in O(n) time complexity. The steps are as follows:
* Initialize a variable total_sum to zero.
* Iterate over all elements of the input array arr. For each element arr[i], compute `arr[i] * (i+1) * (n-i)` and add it to total_sum.
* Return total_sum as the output of the function.
#### Pseudocode
```cpp
int sumOfAllSubarraySums(arr[]) {
int n = arr.size();
int total_sum = 0;
// Iterate over all elements of the array and compute the sum of all subarrays containing that element
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
total_sum += arr[i] * (i + 1) * (n - i);
}
return total_sum;
}
```
#### Time and Space Complexity
* TC - O(n)
* SC - O(1)
### Total number of subarrays of length K
Number of subarrays of length K = Total number of start indices of subarrays of length K.
| length (K) | start of first window | start of last window |
| -------- | -------- | -------- |
| 1 | 0 | N-1 |
| 2 | 0 | N-2 |
| 3 | 0 | N-3 |
| 4 | 0 | N-4 |
| K | 0 | N-K |
All start positions for length K, will be within range **[0 N-K]**. Therefore total is N-K+1.
Hence, total number of subarrays of length K = **N-K+1**.
### Question
Given N=7, K=4, what will be the total number of subarrays of len K?
**Choices**
- [ ] 3
- [x] 4
- [ ] 5
- [ ] 6
## Problem 3 Given an array, print start and end indices of subarrays of length K.
Given an array of size N, print start and end indices of subarrays of length K.
**Example**
If N=8, K=3
All start and end indices are
| start | end |
| ----- | ----- |
| 0 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 5 |
| 4 | 6 |
| 5 | 7 |
[start end] = K
end - start + 1 = K
end = K + start - 1
#### Pseudocode
```cpp=
//Iterate over all the start indices
for (int i = 0; i <= N - K; i++) {
int j = K + i - 1;
print(i, j);
}
```
> Note: Now we know how to iterate over windows of length K.
## Problem 4 : Given an array, print maximum subarray sum with length K
Given an array of N elements. Print maximum subarray sum for subarrays with length = K.
**Example**
```
N=10 K=5
```
| -3 | 4 | -2 | 5 | 3 | -2 | 8 | 2 | -1 | 4 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |:---:|
**Explanation**
| s | e | sum |
| -------- | -------- | -------- |
| 0 | 4 | 7 |
| 1 | 5 | 8 |
| 2 | 6 | 12 |
| 3 | 7 | 16 |
| 4 | 8 | 10 |
| 5 | 9 | 11 |
Maximum: **16**
:::warning
Please take some time to think about the solution approach on your own before reading further.....
:::
### Problem 4 : Bruteforce Approach
We have to calculate the sum of all subarrays of size k and find the maximum out of them
#### Pseudeocode
```cpp
function maxSubarrayOfLengthK(A[], N, K) {
ans = INT_MIN
//first window
i = 0
j = k - 1
while (j < N) {
sum = 0
for (idx = start; idx <= end; idx++) {
sum += A[idx]
}
ans = max(sum, ans)
//going to next subarray of length k
i++
j++
}
print(ans)
}
```
#### Complexity
For what value of k will the iterations be highest ?

:::warning
Please take some time to think about the optimised solution approach on your own before reading further.....
:::
## Problem 4 : Optimized Approach using Prefix Sum Array
We can use **Prefix Sum Array** since we have to find sum within a range.
### Pseudeocode
```cpp
function maxSubarrayOfLengthK(A[], N, K) {
// calculate prefix sum array
pf[N]
pf[0] = A[0]
for (idx = 1; idx < N; idx++) {
pf[idx] = pf[idx - 1] + A[idx];
}
ans = INT_MIN
i = 0
j = K - 1
// calculate for each pair of indicies
while (j < N) {
sum = pf[j] - (i == 0 ? 0 : pf[i - 1])
ans = max(sum, ans)
i++
j++
}
print(ans)
}
```
### Question
What is Time Complexity and Space Complexity respectively?
**Choices**
- [ ] O(N^2) and O(N)
- [x] O(N) and O(N)
- [ ] O(N) and O(N^2)
- [ ] O(1) and O(N)
---
### Problem 4 Optimized Approach : using Sliding Window
We want to reduce the space complexity without modifying the given array, but how?
#### Observations
* We can get sum of next subarray using current subarray sum as follows:-
* By adding a new element to current sum.
* By subtracting the first element of current subarray.
Given array :-
| -3 | 4 | -2 | 5 | 3 | -2 | 8 | 2 | -1 | 4 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |:---:|
First subarray from 0 to 4:-
| -3 | 4 | -2 | 5 | 3 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
Converting first to second subarray :-
| <span style="color:red"> ~~-3~~ </span> | 4 | -2 | 5 | 3 | <span style="color:green"> -2 </span> |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
Based upon above observation can we say:-
<div class="alert alert-block alert-warning">
sum of all elements of next subarray = sum of elements of current subarray - first element of current subarray + new element
</div>
This approach is known as **Sliding window approach**.
#### Dry Run
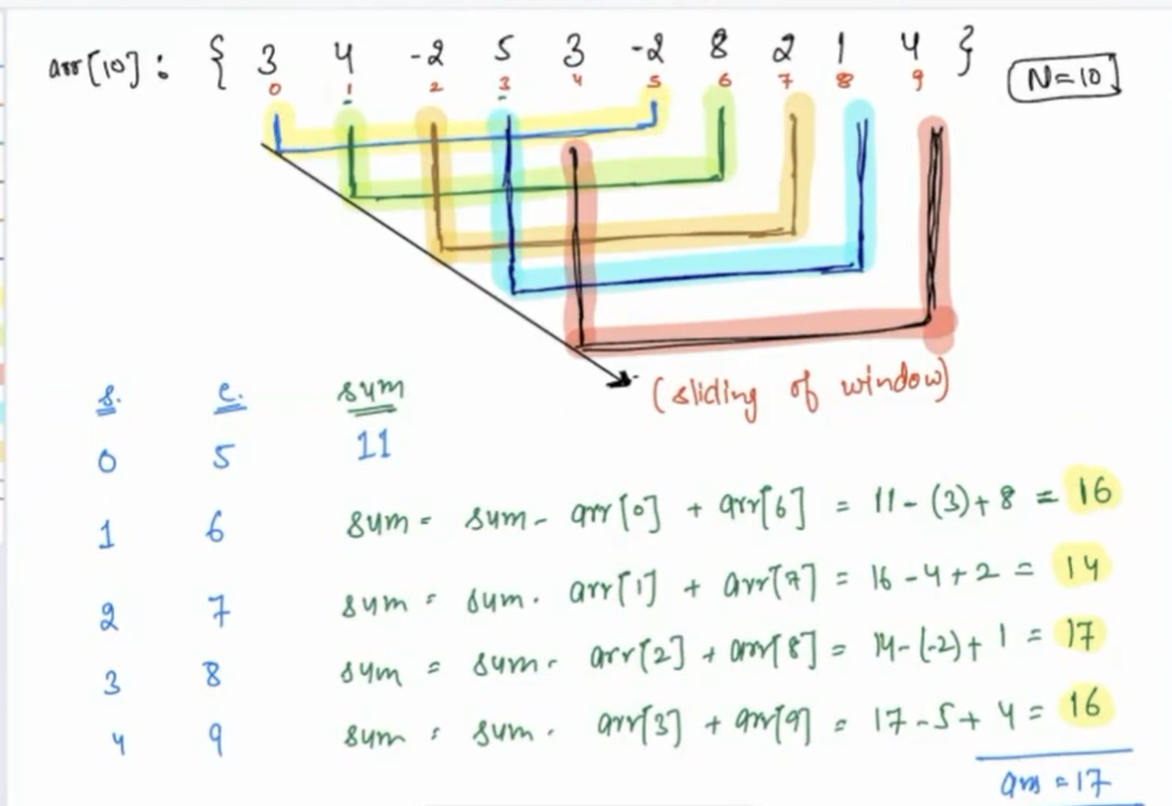
**We can clearly observe the window sliding in above run.**
#### Pseudeocode
```cpp
function maxSubarrayOfLengthK(A[], N, K) {
ans = INT_MIN
i = 0
j = K - 1
sum = 0 // here k iterations
for (int idx = i; idx <= j; idx++) {
sum += A[idx]
}
ans = max(sum, ans)
j++
i++
while (j < N) {
sum = sum + A[j] - A[i - 1]
ans = max(sum, ans)
// here N-k iterations
i++
j++
}
print(ans)
}
```
***Time Complexity : O(N)**
**Space Complexity : O(1)***
## Observations for solving problems on Subarrays.
### Observations
Following are the observations that can be useful when solving problems related to subarrays:
* Subarrays can be visualized as contiguous part of an array, where the starting and ending indices determine the subarray.
* The total number of subarrays in an array of length n is n*(n+1)/2.
* To print all possible subarrays, O(n^3) time complexity is required.
* The sum of all subarrays can be computed in O(n^2) time complexity and O(1) space complexity by using Carry Forward technique.
* The sum of all subarrays can be computed in O(n^2) time complexity and O(n) space complexity using the prefix sum technique.
* The number of subarrays containing a particular element arr[i] can be computed in O(n) time complexity and O(1) space complexity using the formula (i+1)*(n-i). This method is called `Contribution Technique`.