# DP 1: DP on Strings
---
## Problem 1 Longest Common Subsequence(LCS)
Given two strings. Find the length of longest common subsequence in two strings.
### Example
**Example 1**
s1 = abbcdgf
s2 = bacdegf
Ans: 5 ((a, c, d, g, f) / (b, c, d, g, f))
**Example 2**
s1 = klagrip
s2 = lgigkm
Ans: 3 (l, g, i)
---
### Brute Force Apporach
- Generate all subsequences of one string and compare with the other.
- Consider the one having maximum length.
---
### Optimized Approach
*Thought Process:*
- Can we break the problem into subproblems and use recursive approach?
- We need to find the `LCS(s1[0, n - 1], s2[0, m - 1])` (i.e., LCS of strings s1 (from 0 to n -1) and s2 (from 0 to m - 1)). To break the problem, we need to eliminate the characters.
- We have two choices: start from first index or last index.
- **Case 1:** *starting from first index*
- There can be two possibilities: `s1[0] == s2[0] and s1[0] != s2[0]`
- If `s1[0] == s2[0]`, then 0th character must be included in longest common subsequence of the two strings and we need to look for first index character of both the strings.
- **Case 2:** *starting from last index*
- Similarly, there can be two possibilities: `s1[n - 1] == s2[m - 1] and s1[n - 1] != s2[m - 1]`
- **If s1[n-1] == s2[m-1]**, then it's sure shot that these characters will be the part of solution.
- because if subsequence has the last character as part of it, then that subsequence will be longest as there isn't any character after the last character to generate any other longest subsequence.
- In that case, we can consider these characters as part of solution and start looking for the subsequence in the remaining string.
- Therefore, `LCS(s1[0, n - 1], s2[0, m - 1]) = 1 + LCS(s1[0, n - 2], s2[0, m - 2]), if s1[n - 1] == s2[m - 1]`
- **If s1[n - 1] != s2[m - 1]**, then it's sure shot that both of these characters cannot co-exist in the solution.
- *Why?*
- Let's say `s1[n - 1] = 'a'` and `s2[m - 1] = 'b'`. Then, if `s1[n - 1]` is part of solution then `'a'` should be present in `s2` somewhere before index `m - 1` as `m - 1` is the last index. And thus, `s2[m - 1]` will be out of the solution. Vice versa for the `s1[n - 1]` when `s2[m - 1]` will be part of the solution.
- In that case, we can consider one of the two as part of solution and start looking for the subsequence in the remaining string.
- Therefore, LCS(s1[0, n - 1], s2[0, m - 1]) = max(LCS(s1[0, n - 2], s2[0, m - 1]), LCS(s1[0, n - 1], s2[0, m - 2])), if s1[n - 1] != s2[m - 1]
<img src="https://d2beiqkhq929f0.cloudfront.net/public_assets/assets/000/051/314/original/upload_9cf453804a369829d5523d69f7068e07.png?1695965041" width=500px>
> Note: Above problem has optimal substructure.
---
### Dry Run
Example:
s1 = abcd
s2 = abce
<img src="https://d2beiqkhq929f0.cloudfront.net/public_assets/assets/000/051/315/original/upload_bcdb401b6b356ef0f2b3e1491e64c79a.png?1695965111" width=500px>
> In the above tree, we can see overlapping subproblems.
Since there are overlapping sub problems and optimal sub structure, dynamic progamming can be used here.
---
### LCS - DP Approach
- Recursive Relation
<img src="https://d2beiqkhq929f0.cloudfront.net/public_assets/assets/000/051/316/original/upload_7911bea1bc03e94c4ff4969213ce37c6.png?1695965182" width=500px>
- *Find the number of parameters changing above.* There are two paramters: (1) ending of string s1 and (2) ending of string s2.
- Therefore, the dp size for this problem will be `dp[n][m]`.
- We will initialize the `dp` matrix with -1, representing unsolved state. *Why -1 and not 0?* Because 0 can be a possible answer.
- *What should be the base case, `i == 0 || j == 0`?* No, because `i` and `j` are indices here and not the characters left. Therefore, we should have the base condition when there are no more characters left, i.e, `i < 0 || j < 0`.
---
### Psuedocode
```java
int dp[n][m]; // Initialised with -1
int lcs(s1, s2, int i, int j) {
if(i < 0 || j < 0) return 0; // if either of strings become empty
if(dp[i][j] != -1) return dp[i][j];
if(s1[i] == s2[j]) {
dp[i][j] = 1 + lcs(s1, s2, i - 1, j - 1);
} else {
dp[i][j] = max(lcs(s1, s2, i - 1, j), lcs(s1, s2, i, j - 1));
}
return dp[i][j];
```
**Time Complexity:** O(N * M) as we are solving a total of N * M problems in constant time.
**Space Complexity:** O(N * M) as the `dp` table has the size N * M.
---
### Dry Run of Tabulation
- Consider the state of the `dp` table:
| `(i - 1, j - 1)` | `(i - 1, j )` |
|:----------------:|:-------------:|
| `(i, j - 1)` | `(i, j)` |
- If characters are equal then `dp[i][j] = 1 + dp[i - 1][j - 1]`
- Otherwise, `dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j])`
- It implies that to fill the value of `dp[i][j]`, the values of `dp[i - 1][j]`, `dp[i][j - 1]` and `dp[i - 1][j - 1]` should be known before hand.
- It suggests that we need to traverse the matrix left to right and top to bottom to achieve the above.
**Example**:
*s1: KAIYA
s2: MAICA*
- For this, we need the matrix `dp` of size 5 * 5.
- At (0, 0), since 'K' and 'M' do not match, we should look for `dp[-1][0]` and `dp[0][-1]`. But they do not exist, so `dp[0][0] = 0`.
- Similarly, **dp[0][1] = dp[0][2] = dp[0][3] = dp[0][4] = dp[1][0] = dp[2][0] = dp[3][0] = dp[4][0] = 0**
- At(1, 1), 'A' and 'A' matches. So, `dp[1][1] = 1 + dp[0][0] = 1 + 0 = 1`
- Similarly, we fill the remaining table.
<img src="https://d2beiqkhq929f0.cloudfront.net/public_assets/assets/000/051/317/original/upload_ae85f3d155816c83462f027ec73a5da9.png?1695965581" width=500px>
- Hence, the length of LCS is 3.
*Can we figure out the LCS from the above table?*
The idea is to figure out the path that resulted in answer 3.
Observation:
- If the characters match, the value stored there must have been came from corresponding left corner, i.e., (i - 1, j - 1) for (i, j)
- If the characters don't match, the value stored there must have been came from max(immediate left, immediate top), i.e., max((i - 1, j), (i, j - 1)) for (i, j).
Following this, we can deduce that the LCS is AIA.
---
## Problem 2 Edit Distance
Given two strings s1 and s2. Convert string s1 to s2. You are allowed to delete, insert or replace a character from string s1. Every operation has a cost; insertion has a cost i, delete has a cost d, replacement has a cost r. Find the minimum cost of convertion. [not allowed to make changes in string s2]
### Example
1. **cost i = 2; cost d = 2; cost r = 3**
s1 = a, c
s2 = a, b, c
* here we can insert b so minimum cost will be 2
2. **cost i = 2; cost d = 2; cost r = 3**
s1 = a, b, c, d
s2 = a, b, e
* here we can replace c with e and delete d, so minimum cost will be 5
3. **cost i = 2; cost d = 2; cost r = 3**
s1 = a, c, d, x, y
s2 = a, b, c, g, x
* here we can insert b replace d with d and delete y, so minimum cost will be 7
> Through the examples we can see that there are choices present in this question as well as optimatization present
---
### Edit Distance Algorithm
<img src="https://d2beiqkhq929f0.cloudfront.net/public_assets/assets/000/051/319/original/upload_a2b5ea44600bf95d24963684df29a84d.png?1695965980" width=500px>
* we can break the above into subproblems and use the recursive appoarch exactly as same as the LCS approach
* we will compare last characters of the string s1 and s2, if `s1(n - 1) == s2(m - 1)` then the minimum cost will be mincost(s1(0,n - 2), s2(0, m - 2))
* if `s1(n - 1) != s2(m - 1)`, then we will either insert or delete or replace
* so the minimum cost in this case during inserting will be costi + mincost(s1(0, n - 1), s2(0, m - 2))
* the minimum cost in case of deletion will be costd + mincost(s1(0, n - 2), s2(0, m - 1))
* the minimum cost in case of replacing will be costr + mincost(s1(0, n - 2), s2(0, m - 2))
<img src="https://d2beiqkhq929f0.cloudfront.net/public_assets/assets/000/051/318/original/upload_68bd0aa00a7470354eb26ebd170fd37c.png?1695965783" width=500px>
* now using the similar appoarch as LCS we can ingore the starting index of s1 & s2 is it is costant and re-draw the tree likewise.
Here we can notice overlapping subproblems and optimal sub-structure so dynamic programming can be used.
---
### Base cases:
```java
if(i < 0 && j < 0) return 0
else if(i < 0){
//only option is to insert remianing characters
return costi * (j + 1)
}
else if (j < 0){
return costd * (i + 1) //only option is to delete all the characters
}
```
### Recursive Relation
> * if `s1(i) == s2(j)` then `dp[i][j] = dp(i - 1)(j - 1)`
> * else dp[i][j] = min((cost i + dp[i][j - 1]), (cost d + dp[i - 1][j]), cost r + dp[i - 1][j - 1])
---
### Problem 3 Wildcard Pattern Matching
Given are two strings. Find if they exaclty match or not.
**Example**
1. **s :** a, b, a, c, d
**p :** a, b, a, c, d
**Answer :** True
2. **s :** a, b, a, c, d
**p :** a, ?, a, ?, d
> "`?`" in example 2 is called wild card. It can be replaced with exactly one character.
>
In the above question we can replace ? with `b and c`
3. **s :** a, b, b, a, c
**p :** a, * , c
> " `*` " in example 3 is called wild card. It can be replaced with 0 or more character.
In the above question we can replace * with `b, b, a`
4. **s :** x, b, b, z, z, c
**p :** x * z * x
**Answer :** True
5. **s :** x, b, b, z, z, c
**p :** x * z * *
Here first * can be replaced with b and b. Second * can be replaced with z and the third * can be replaced with c
6. **s :** x, b, b, z, z,
**p :** x * z * * * ? z
**Answer :** False
From the above examples we can see that element of choice exit in these questions.
---
### Algorithm
<img src="https://d2beiqkhq929f0.cloudfront.net/public_assets/assets/000/051/319/original/upload_a2b5ea44600bf95d24963684df29a84d.png?1695965980" width=500px>
* Now, here we first check if string `s(0,n - 1) `matches with pattern `p(0,m - 1)` or if `pattern(m - 1) == ?`
* if `s(0,n - 1) == p(0,m - 1)` we will check from the remaining string ie `s(0,n - 2) == p(0,m - 2)`
* we will check if `p(0,m - 1)` is "` * `"
* if `p(0,m - 1)` is "` * `" we will either replace it with nothing ie 0 characters so it would be `s(0,n - 1), p(0,m - 2)`. Or replace with character and finally is `s(0,n - 2) and p(0,m - 1)`
* we will first check if string `s(0,n - 1) != p(0, m - 1) `
* if it is not equal we will return false
---
### Dry Run
<img src="https://d2beiqkhq929f0.cloudfront.net/public_assets/assets/000/051/321/original/upload_3da04f5d3cf379bd4b06db7ed7d680dc.png?1695967997" width=500px>
> Here we can notice in the above algorithm that the question contians overlapping subproblem as well as optimal substructure so it can be solved using dynamic programming.
---
### Wildcard Pattern Matching Recursive Relation
<img src="https://d2beiqkhq929f0.cloudfront.net/public_assets/assets/000/051/322/original/upload_de9fc895a112a89697ecf9cf68f270f4.png?1695968022" width=500px>
---
### Base Cases:
```java
if(i < 0 && j < 0) return true
else if(j < 0) return false
else if(i < 0){
if only "*" remaining return true
else false
}
```
> The above problem works better in recursion than in tabulation method. Why?
>
> *To solve with tabulation, we need to always fill the complete table of size N * M which would cost O(N * M) time, but in case of recursion, there could be cases that we found our match much before that.*
> **Example:**
> "xyz" and "xyz" will only require O(N) time for matching via Recursion. The same would cost 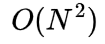 for filling the table in tabulation.