---
tags: ARM 架構, 進階電腦系統理論與實作, NCKU Linux Kernel Internals, 作業系統
---
# 系列講座導論、架構與指令集
contributed by <`RusselCK` >
###### tags: `RusselCK`
## [導論](https://youtu.be/nvX5AF6pOzw) ( [回顧 ARM 架構](https://beta.hackfoldr.org/arm/https%253A%252F%252Fhackmd.io%252Fs%252FrykYKYXjg) )
- [ ] [《我是高頻交易工程師》](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25372263)
- [ ] 快閃大對決: 一場華爾街起義
- [ ] ==[投影片](https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B5GW0aIORHIBUjVvUXJ2NVhPckU/view?ths=true): ARM processor==
### 1. Evaluation of ARM


> Linaro 公司 : 致力加速 ARM 平台相關的開放原始碼專案,由 ARM、Freescale 也就是現在的 NXP、TI 等公司出錢出力發起 。

賣 IP,矽智財,與客戶互利共榮

> 1980 年代 Acorn Computers 財務危機、數度轉手
> 依靠 Apple、VLSI 聯手救起來
### 2. Evaluation of the ARM ISA

> 與 MIPS 不同的是,ARM 一出來就在做生意,客戶要什麼就得生出什麼
到目前為止,ARM 共 8 種 ISA 版本,也就是 ARMv1 ~ ARMv8。
> ARMv8 還有不同的分支
1990 年 ARM 成立後,第一個產品就是從 ARMv3 開始賣
> ARMv1、ARMv2 的智慧財產權已過期
ARMv3 開始則採用了 32 bits 位址範圍
>ARMv1 和 ARMv2 位址範圍只到 26 bits
>* [RFC: Remove the arm26 port](https://lwn.net/Articles/243610/)
* [Amber ARM](https://opencores.org/projects/amber)

ARM 處理器具有 16 個 32 bit 長度的暫存器,其中有 13 個為 **通用暫存器 (General Purpose Registers, GPRs)** , R13-R15 則有其他用途。
> MIPS 有 32個 GPR
:::warning
* 減少 Register 數量,可以減少 Context Switch
* 但會導致編譯器不好寫,能用的 Register 不多
:::

竟然可以幫 Java bytecode 加速 ([Jazelle 指令集](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jazelle))
> 但現在大家用的 Android 手機不用它,可以忘記這件事了

[Classic ARM](https://developer.arm.com/ip-products/processors/classic-processors) : ARMv3 ~ ARMv6
* ARMv4 : [范紐曼型架構(Von Neumann architecture)](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/冯·诺伊曼结构)
* ARMv5 : [哈佛架構(Harvard architecture)](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/哈佛结构)
> * 具備 Cache 、 5-stage pipeline
> * 邁向高速運算
> * 行車紀錄器 ...
* ARMv6
:::success
* [Thumb](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARM%E6%9E%B6%E6%A7%8B#Thumb)
* ARM 處理器的一種 16-bit 指令模式
* Nokia 當年用機海戰術賣便宜手機的秘訣
* 32-bit 的效能 + 16-bit 的儲存空間
* [Thumb-2](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARM架構#Thumb-2)
* 32-bit 和 16-bit 之間的切換,pipeline 要打掉重來
* function call 的資料也要打掉重來
:::
> * [SIMD](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SIMD) 是違反 RISC 精神的,但客戶想要,就得生出來 (ARM : 適者生存)
> * [**TrustZone**](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARM架構#安全性擴充(TrustZone)) : [功能型手機(Feature phone)](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/功能型手機)需要 **支付(payment)** 功能,因此而生的安全技術
* ARMv7
> * 系列名改為 **Cortex**
> * [Adv. SIMD (NEON)](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARM架構#進階SIMD(NEON))
:::warning
* 改名意味著商業模式的改變,早期還可以跟 ARM 談所謂的 "一口價",但改名後,ARM 授權的定價就有硬性規定
:::
* ARMv8
> * 加入 64-bit 模式
#### ISA extensions

ISA 擴充架構則又可以分為兩組:
* 通用暫存器 (General Purpose Registers, GPRs)
* FP (Floating Point) 和 Advanced SIMD (NEON)



> 上圖 w、x 寫反了,下面才是正確的
* [A64 - ARM - WikiChip](https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/arm/a64)
* Registers W0 through W30 are 32 bit and register X0 through X30 are 64 bits.


#### Thumb / Jazelle



> Decode 有 multiplexer

> RCT : Runtime Compilation Target
### 3. Approaches to Circuit Design

* Full custom
* 全部都自幹
* Intel
ARM 的 licence 有兩種:
1. Architecture licence
* 可以對 ARM 架構實作進行大改
* 高通、NVIDIA、Apple、Marvell
3. Implementation licence
* NEON、VFP 要跟 ARM 的行為一致
* 聯發科

:::warning
TODO : Dynamic power、Static power、Leakage power ?
:::

### ARM big.LITTLE technology
- [ ] ==[big.LITTLE technology 投影片](https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B5GW0aIORHIBLW0ycldfZHhieHc/view?ths=true)==

> 解決功耗問題
解法: 將 cores 分成 2 類:
* **big** : 執行時時刻刻都在變化的程式 (game、FB...)
* **LITTLE** : 執行沒什麼變化的程式 (e-mail、打電話...)


:::warning
如何分辨這個程式要用 **big** or **LITTEL** ?
* Machine Learninig
:::
- [ ] [Energy-Aware Scheduling (EAS) Project](https://www.linaro.org/blog/energy-aware-scheduling-eas-project/)
## [架構和指令集](https://youtu.be/SwqKJVhWZmA)
ARM 的獲利模式 : 賣 IP,矽智財
到目前為止,ARM 共 8 種 ISA 版本,也就是 ARMv1 ~ ARMv8。其中 ARMv1 和 ARMv2 位址範圍只到 26 bits,自 ARMv3 開始則採用了 32 bits 位址範圍
### GPRS
ARM 處理器具有 16 個 32 bit 長度的暫存器
* 其中有 13 個為 **通用暫存器 (General Purpose Registers, GPRs)**
* R13-R15 則有其他用途。

**R13** 通常會被用來當作**堆疊指標 (Stack Pointer, SP)**,在實際使用中,一般會在記憶體分配一些空間作為堆疊,系統初始化時將這一塊堆疊的底部位址儲存到 R13 。
* [ARM Application Procedure Call Standard (AAPCS)](https://www.crifan.com/files/doc/docbook/uboot_starts_analysis/release/htmls/arm_reg_name_apcs.html)
**R14** 為 連結暫存器 (Link register, LR) ,用來存放副程式的返回地址,比如我們在組語中呼叫到了 BL、BLX 等指令時,會將 PC 的數值複製到 R14 中,作為反還 (return) 的位址,具體範例如下。
**R15** 則是程式計數器(Program Counter, PC),用來存放下一道指令的位址,根據 [ARM7TDMI Technical Reference Manual](http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.ddi0210c/ch02s06s01.html)
* R15 在 ARM 或是 Thumb 模式下狀況不同
* ARM 模式 (ARM state)
* bits [1:0] 未定義且會被忽略, bits [31:2] 保留了 PC 數值
* Thumb 模式 (Thumb state)
* bit [0] 未定義且被忽略, bits [31:1] 保留了 PC 數值
各個不同的 ARM 版本對應的擴充指令集架構資訊如下:

而這些 ISA 擴充架構則又可以分為兩組:
* 通用暫存器 (General Purpose Registers, GPRs)
* **FP (Floating Point)** 和 **Advanced SIMD (NEON)**
### SIMD
> Intel 的 [MMX](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/MMX)、[SSE](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/SSE)、[AVX](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/AVX指令集) ...
> * [MMX、SSE、AVX指令集](https://www.itread01.com/content/1547290202.html)
我們先來看 SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) extension, 他其實是透過通用暫存器 (General Purpose Registers, GPRs) ,也就是 R0 ~ R12 這 13 個 32-bit 暫存器所組成,這項擴展自 [ARMv6](http://lars.nocrew.org/computers/processors/ARM/ARMv6.pdf) 引入 ,但是由於效能提昇有限,自 ARMv7 後被 Advanced SIMD, 也就是我們說的 NEON 所替代掉。
> 在 ARMv8 之後仍繼續演化~
### VFP
早期的 ARM 處理器並沒有負責處理浮點數運算的功能,因此浮點數的運算就必須透過 CPU 來進行處理,對於越來越多的浮點數要求 (影像處理、音訊、遊戲等等) 若沒有額外的計算輔助,則 CPU 會耗費非常多的時間進行浮點數的運算,為了解決這個問題,ARM 加入了 VFP (Vector Floating Point) 這種透過協同處理器來輔助計算浮點數的應用。
VFP (Vector Floating Point) 指令集擴充可以分兩個部份來討論
* 自 ARMv5 引入的 VFPv1/VFPv2
* 自 ARMv6 引入的 VFPv3/VFPv4。

> 因應 IEEE 754 的改版 及 加入新的浮點數操作 (e.g. [FMA instruction set](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FMA_instruction_set))
#### VFPv1/v2
VFPv1/v2 自 ARMv5 引入,**具有 32 個 VFP 暫存器**,並可分成**四個暫存器庫區(Register Banks)**,每一區具有 8 個 VFP 暫存器,如下圖

從上圖我們可以看到,在 VFPv1/v2 中,
* 第一個暫存器庫區 (Register Banks) 存放了純量 (Scalar) 運算元
* 剩下的三區則是存放向量 (Vector) 運算元。
和 SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) 不同的是,**向量是依序 (sequential) 處理**,而不是像 SIMD 那樣同步進行。

#### VFPv3/v4
如同名稱一樣,VFPv3/v4 是 VFPv1/v2 的延伸,自 ARMv6 開始引入。
和 VFPv1/v2 不同的是:
* VFPv3/v4 的 **VFP 暫存器變成 64 bit 暫存器**
* **增加了一些指令協助 FX (Fixed Point) 與 FP (Floating Point) 之間的轉換**。
### NEON (Adv. SIMD)
NEON 指令集自 ARMv7 引入,為 64/128-bit SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) extension。NEON 指令集被設計用來補足日益興盛的影像編碼/解碼、2D/3D 圖像處理、遊戲、影像處理等功能。
* [VP9](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/VP9) (Google)
> Google 為了不要給 [MPEG LA](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/MPEG_LA) 大量的授權金,改買下 [On2 Tecnology](https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-tw/On2_Technologies)
為何這類用途需要額外的指令集去處理?
以影像處理為例,影像的處理其實就是透過遮罩(mask)去對2維影像陣列進行 **捲積(convolution)** 的運算
- [ ] [Performing Convolution Operations](https://developer.apple.com/library/prerelease/content/documentation/Performance/Conceptual/vImage/ConvolutionOperations/ConvolutionOperations.html) (apple developer)

對於這種運算,我們是可以同時對陣列(vector)的各個元素進行處理的,也就是這些運算可以平行處理(parallel),可以加快運算速度。
順道一題,[SIMD](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SIMD) (Single Instruction Multiple Data) 這種運算模式也是費林分類法([Flynn’s Taxonomy](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flynn%27s_taxonomy)) 中的一種運算結構。

若以 NEON 指令集的命令來看,`VADD.I16 Q0, Q1, Q2` 這樣的指令,會執行一個平行的陣列加法,將 **Q1** 以及 **Q2** 各元素的運算結果存放到 Q0 中。
- [ ] [What is NEON ?](http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.dht0002a/BABIIFHA.html) (ARM developer)


* Registers are considered as **vectors** of **elements** of the same **data type**
* Data types can be: signed/unsigned 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit, 64-bit, single precision [floating point](http://www.arm.com/products/processors/technologies/vector-floating-point.php)
* Instructions perform the same **operation** in all **lanes**
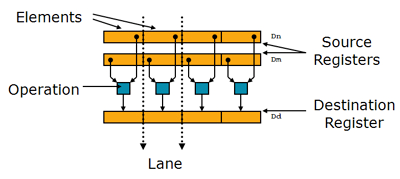
Register :
* 16 x 32-bit general purpose ARM registers (R0-R15).
* 32 x 64-bit NEON registers (D0-D31) OR viewed as 16 x 128-bit registers (Q0-Q15).
### ARM NEON 案例分析
**目前實作的程式碼**:[embedded-summer2015 / RGBAtoBW](https://github.com/charles620016/embedded-summer2015/tree/master/RGBAtoBW)
> 個別函式在 [bmp.c](https://github.com/charles620016/embedded-summer2015/blob/master/RGBAtoBW/bmp.c)
給定每個像素 (pixel) 為 32-bit 的 RGBA 的位元圖 (bitmap),其轉換為灰階影像 (gray scale) 的函式 :
```c
void rgba_to_bw(uint32_t *bitmap, int width, int height, long stride) {
int row, col;
uint32_t pixel, r, g, b, a, bw;
for (row = 0; row < height; row++) {
for (col = 0; col < width; col++) {
pixel = bitmap[col + row * stride / 4];
a = (pixel >> 24) & 0xff; // alpha : 透明度
r = (pixel >> 16) & 0xff; // red
g = (pixel >> 8) & 0xff; // green
b = pixel & 0xff; // blue
bw = (uint32_t) (r * 0.299 + g * 0.587 + b * 0.114);
// 77/256 151/256 28/256
bitmap[col + row * stride / 4] = (a << 24) + (bw << 16) + (bw << 8) + (bw);
}
}
}
```
- [ ] [我們的眼睛是如何 看見光 與 分辨顏色的?](http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/demolab/html.php?html=everydayPhysics/color)
眼吸收綠色比其他顏色敏感,也可說人眼最容易捕捉到綠色,所以當影像變成灰階時,僅僅將紅色、綠色、藍色加總取平均,不足以反映出人眼所見。常見的方法是將 $Red \times 77, Green \times 151, Blue \times 28$,這三個除數的總和為 `256` (即 $2^8$)
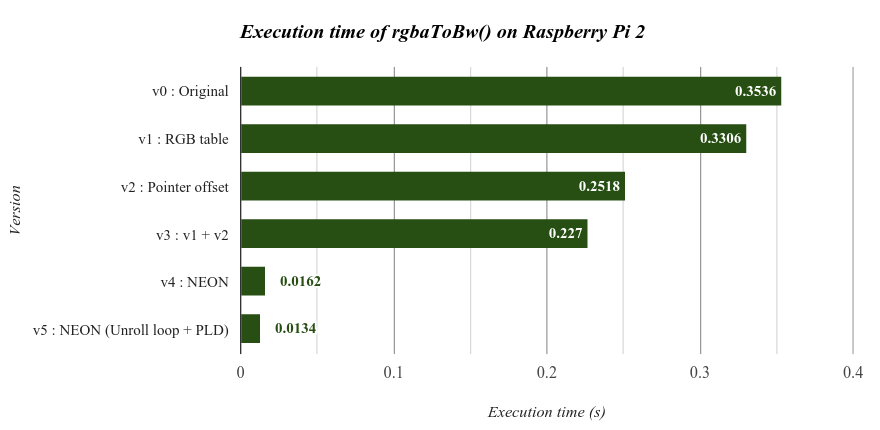
#### v1: 查表
RGB 分別都是 8 bit,可以建立三個大小為 256 bytes 的 table,這樣就不用在每次轉 bw 過程中進行浮點數運算。
* 原本 :
```c
bw = (uint32_t) (r * 0.299 + g * 0.587 + b * 0.114);
```
* 查表 :
```c
bw = (uint32_t) (table_R[r] + table_G[g] + table_B[b]);
```
#### v2: Pointer offset
使用 pointer 的 offset 取代原本的繁雜的 bitwise operation。
* 原本 :
```c
pixel = bitmap[col + row * stride / 4];
a = (pixel >> 24) & 0xff; // alpha : 透明度
r = (pixel >> 16) & 0xff; // red
g = (pixel >> 8) & 0xff; // green
b = pixel & 0xff; // blue
```
* Pointer offset
```c
uint32_t *pixel = bmp->data;
r = (BYTE *) pixel + 2;
g = (BYTE *) pixel + 1;
b = (BYTE *) pixel;
```
#### v4 : NEON
1. 將 RGB 三色的 weight 存入 r3 - r5。
2. **`vdup.8` (Vector Duplicate)**,分別複製到大小為 8 bit 的 NEON register d0 - d2
```cpp
mov r3, #77
mov r4, #151
mov r5, #28
vdup.8 d0, r3
vdup.8 d1, r4
vdup.8 d2, r5
```
3. **`vld4.8` (Vector Load)**,載入 pixel 的資料到 4 個 8-bit 的 NEON register d4-d7,其中那個 `4` 為 interleave,因為我們有 ARGB,所以 gap = 4。
4. 再來就是計算 weighted average。
**[`vmull.u8` (Vector Multiply)](https://developer.arm.com/architectures/instruction-sets/simd-isas/neon/intrinsics?search=vmull_u8)** 和 **[`vmlal.u8` (Vector Multiply Accumulate)](https://developer.arm.com/architectures/instruction-sets/simd-isas/neon/intrinsics?search=vmlal_u8)**
```cpp
@ (alpha,R,G,B) = (d7,d6,d5,d4)
vld4.8 {d4-d7}, [r0]!
vmull.u8 q10, d6, d0
vmlal.u8 q10, d5, d1
vmlal.u8 q10, d4, d2
```
5. 將值除以 256 就是我們要的灰階值。
**`vrshrn` (Vector Shift Right by immediate value)**
```c
vrshrn.u16 d4, q10, #8
```
6. 最後儲存結果。
**`vst` (Vector Store)**
```c
vst4.8 {d4-d7}, [r3]!
```
#### v5 : Unroll loop + PLD
### ARMv8

- [ ] [A64 - ARM - WikiChip](https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/arm/a64)
* 32-bit instruction encodeings
* 48-bit virtual addresses
> [[64-bit data model]](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/64-bit_computing#64-bit_data_models)
> 
ARMv8 的實作
- [ ] [Introducing Cortex-A32: ARM’s smallest, lowest power ARMv8-A processor](https://community.arm.com/developer/ip-products/processors/b/processors-ip-blog/posts/introducing-cortex-a32-arm-s-smallest-lowest-power-armv8-a-processor-for-next-generation-32-bit-embedded-applications)

> A35 + A53 可以搭配成 big.LITTLE

* [jserv/armv8-hello](https://github.com/jserv/armv8-hello) - Hello World for bare metal ARMv8 using QEMU
* [QEMU](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/QEMU) - hardware virtualization VMM
[**[`boot.S`]**](https://github.com/jserv/armv8-hello/blob/master/boot.S)
```c=6
_start:
/* init UART (38400 8N1) */
ldr x4, =UART_BASE // UART base
mov w5, #0x10 // IBRD
str w5, [x4, #0x24]
mov w5, #0xc300
orr w5, w5, #0x0001 // CR
str w5, [x4, #0x30]
/* check CPU ID */
mrs x0, mpidr_el1
tst x0, #15
b.ne other_cpu
```


### Jazelle
除了上面的基礎 ISA 外,ARM 根據不同的狀況增加了許多種 ISA 的擴充,比如在 Java 很火紅的年代,為了提昇 JVM 執行的效率,而引入了 [Jazelle 指令集](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jazelle) ,用來加速 Sun Microsystems 定義的 Java bytecode 執行。不過 Android 的 Dalvik/ART 不採用 Java bytecode (stack-based),而是使用自行定義的 register-based 指令,這使得 Jazelle 指令集對 Dalvik/ART 的加速沒有任何效果,自然形同雞肋。
### TrustZone / Crypto


* [OP-TEE Documentation](https://optee.readthedocs.io/en/latest/#op-tee-documentation)
* [Digital rights management, DRM](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/数字版权管理)
## 4. Overview of ARM's Processor lines

### ARMv1 ~ ARMv3

### ARMv4 ~ ARMv6 (ARM11 / ARM11 MPcore)

* [Digital](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/迪吉多)
* 1998年被[康柏電腦(Compaq)](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/康柏)收購
* 2002年康柏公司被[惠普公司(hp)](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/惠普)收購
* [StrongARM](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/StrongARM)
* Digital 和 ARM 合作改造的 233 MHz CPU
> 省電、高效
* 1997年,作為訴訟的和解條件之一,Digital 將 StrongARM 出售給[英特爾(intel)](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/英特爾)
* 2000年,英特爾公司推出 XScale,作為它的下一代產品。
* [Xscale](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/XScale)
* 2006年11月,[Marvell](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/美滿電子科技) 以 6 億美元整體收購英特爾 XScale 手機及手持設備晶片業務。


關於第一隻智慧型手機:
- [ ] [从GHz到多核 移动处理器核变简史 - 高通MSM7000系列](https://m.mydrivers.com/newsview.aspx?id=223488&cid=1&p=4) ([wiki](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/MSM7000))
MSM7000 系列晶片有兩種核心:
1. Applications processor : [ARM1136EJ-S](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARM11) (ARMv6 高效能)
* running Windows Mobile / Android / GNU/Linux / etc.
> ARM1136EJ-S 沒有浮點數運算功能
3. Baseband processor : [ARM9](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARM9) (ARMv5 低功耗)
* running a real-time OS and the **GSM stack**
* 軟體架構採用 AMSS (Advanced Mobile Subscriber Software)
* 其底層為 [L4 microkernel](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/L4_microkernel_family)
> 裡面有 jserv 老師的貢獻
- [ ] [高通平臺android開發總結 MSM平臺上的AMSS](https://www.itread01.com/content/1548716795.html)
- [ ] [qualcomm amss 文件结构以及编译流程分析](https://blog.csdn.net/ZhongGuoRenMei/article/details/109399825)


XScale 開啟了 高效能、複雜電源管理 的時代
#### ARM11


> simultaneous 同時
* Single issue : one instruction, one clock cycle
> Cortexx-A15 : Out of order processor

#### ARM11 MPcore

* [MESI protocol](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MESI_protocol)

* 4 個 CPU 且有各自的 L1 cache
* 但沒有 L2 cache
* [Interrupt Ditributor](https://developer.arm.com/documentation/ddi0360/f/mpcore-distributed-interrupt-controller/interrupt-distributor)
* interrupt request 該分配給哪個 CPU
- [ ] [Linux 多核下绑定硬件中断到不同 CPU(IRQ Affinity)](https://www.vpsee.com/2010/07/load-balancing-with-irq-smp-affinity/)
> 最好直接去找 linux documentation 看最快
> 但事先要搞懂 : ==C 語言、架構 (Architecture)、英文==
* [Snoop Control Unit (SCU)](https://developer.arm.com/documentation/100486/0401/snoop-control-unit)
* Maintain data cache coherency
> Cache Coherent Interconnect, CCI : 有 L2 cache 後的考量
> * [CoreLink Cache Coherent Interconnect Family](https://developer.arm.com/ip-products/system-ip/corelink-interconnect/corelink-cache-coherent-interconnect-family)
### ARMv7 ~ ARMv8

ARMv8:
* 32-bit 編碼
* 48-bit 記憶體
* 64-bit data bus


* [Arm SecurCore SC300](https://developer.arm.com/ip-products/processors/securcore/sc300-processor)
* [Evaluation Assurance Level](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evaluation_Assurance_Level)
* EAL7: Formally Verified Design and Tested
- [ ] [形式化驗證 (Formal Verification)](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/H1xxp3pF0?type=view)

> R 系列 : for 車廠

> jserv : 強烈建議讀完 [ARMv8 的整理筆記](http://wiki.csie.ncku.edu.tw/embedded/ARMv8)
## 5. Overview of ARM's Cortex-A series

Cortex-A8 : 唯一不支援 multiprocessor 的產品
* 但至今仍還有在賣
* AM335x (航空業使用)、[RTmux](https://elinux.org/images/a/a4/Huang--rtmux_a_thin_multiplexer_to_provide_hard_realtime_applications_for_linux.pdf)



* Out-of-Oder、dual issue : 高效能高功耗的開始

> Cortex-A72 : 地表最強
寫軟體的思考:
* 盡量在低功耗的 processor 完成任務
* 盡量減少 big / LITTLE 之間的轉換,成本很高

* [Texas Instruments - AM5728](https://www.ti.com/product/AM5728?utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=epd-null-null-gpn_en-cpc-pf-google-tw&utm_content=am5728&ds_k=%257b_dssearchterm%257d&DCM=yes&gclid=Cj0KCQiA8dH-BRD_ARIsAC24umboV1R_xgCHt2MjZPDv_CPKl8F31QGoTwBJVKEgud_b8SJI7tbMBMMaArVsEALw_wcB&gclsrc=aw.ds)
* CCI (Cache Coherent Interconnect) 決定 多核的可用性/效能
> * [CoreLink Cache Coherent Interconnect Family](https://developer.arm.com/ip-products/system-ip/corelink-interconnect/corelink-cache-coherent-interconnect-family)
* [Mali (GPU)](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mali_(GPU))
* [Generic Interrupt Controllers, GIC](https://developer.arm.com/ip-products/system-ip/system-controllers/interrupt-controllers)
* [input–output memory management unit, IOMMU](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/输入输出内存管理单元)
* [AMBA (Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture)](https://developer.arm.com/architectures/system-architectures/amba)



> jserv : 給自己 2 年的時間學習 ARM 架構,如果效果不錯,接著可以去想要成為哪個部份的專家,能夠解決那些 "實際" 的問題,想好切入點 ...
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet