---
tags: ARM 架構, 進階電腦系統理論與實作, NCKU Linux Kernel Internals, 作業系統
---
# 基礎指令和開發環境
contributed by <`RusselCK` >
###### tags: `RusselCK`
## [基礎指令和開發環境](https://youtu.be/yHAdlr4pF30) [(ARM 指令)](https://beta.hackfoldr.org/arm/https%253A%252F%252Fhackmd.io%252Fs%252FBkGRdKmsg)
### ARM 與 MIPS

> 2012年,[MIPS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MIPS_architecture) 被 [Imagination](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Imagination_Technologies) 買走了
> [CoreMarks](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coremark) : a benchmark that measures the performance of central processing units (CPU) used in embedded systems.
- [ ] ==[ARMv8 中文翻譯](http://wiki.csie.ncku.edu.tw/embedded/ARMv8)==
### ARM 的命名方式 (Cortex系列以前) - ARMxyzTDMIEJFS
(在 ARM Cortex-A/R/M之前的 "ARM Classic")
* x: 處理器系列
* y: 記憶體管理單元 (MMU)
* z: cache
* T: 支援 Thumb 指令集
* D: 支援 debugger
* M: 支援快速乘法 ( Multiplier )
* I: 支援 [Embedded ICE](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In-circuit_emulation) (built-in debugger hardware)
* E: 支援增強型 DSP 指令 (Enhanced instruction)
* J: 支援 [Jazelle ](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jazelle)(JVM)
* F: 具備向量浮點單元 VFP ( Floating-point)
* -S: Synthesizible version (source code version for EDA tools)
ps : TDMI 這四項基本功能成了任何新產品的標準配備,於是就不再使用這4個後綴。但是新的後綴不斷加入,包括定義存儲器界面的,定義高速快取的,以及定義"緊耦合存儲器(TCM)"的,於是形成了新一套命名法,這套命名法一直使用至今。
比如ARM1176JZF-S,它實際上預設就支持TDMI功能,除此之外還支持JZF。
這套命名機制在 ARM Cortex-A/R/M 之後,徹底棄置。以 MMU 來說,ARM Cortex-A 系列都有 MMU,而 Cortex-M0/M0+/M3/M4 均缺乏 MMU,僅有選擇性的 MPU。[Cortex-M7](http://www.arm.com/products/processors/cortex-m/cortex-m7-processor.php) 開始提供 **cache 和 TCM**
* ARM7TDMI (armv4)
* 3 stages pipeline (fetch/decode/execute)
* 高密度程式/低功耗
* One of the most used ARM-version (for low-end systems)
* 在 ARM7TDMI 之後版本的所有 ARM cores 都具備 TDMI
* [von Neumann architecture](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Von_Neumann_architecture)
* ARM9TDMI (armv4)
* 與 ARM7
* 5 stages (fetch/decode/execute/**memory/write**)
* Separate instruction and data cache
* modified [Harvard architecture](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Harvard_architecture)
* ARM11
* ARMv6 架構,是Cortex-A的基礎
### ARM 採用 RISC
ARM architecture 從 Berkeley RISC design合併了幾個特點,但也有些並無採用。
* Features used
* a load-store architecture
* 固定長度 32-bit instructions
* 3-address instruction 形式
* Features rejected
* register window
* 主要原因在於 register window是一塊由許多暫存器所佔據的、很大的chip 空間
* delayed branches
* 主要原因在於 delayed branches remove the atomicity of individual instructions.在super-scalar 和 branch prediction mechanisms 無法好好相互配合
* single-cycle execution of all instructions
* 還是有些指令需要超過2個或2個以上的cycle執行
### ARM 的架構
**Data flow**

* Barrel shifter
* MAC = [Multiply–accumulate operation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiply%E2%80%93accumulate_operation)
**Memory**

* CPSR (Current Processor Status Register)
### ARM Register (for ARM classic)
以下是 ARM 的 register,在 User/System Mode 時,可以使用 r0~r15
其中 r13 為 stack pointer,**r14 為 link register**,r15 為 program counter

:::danger
* 上圖不適用於 Cortex-M 系列
* No FIQ
* No CPSR
:::
**IFQ (Fast Interrupt Request) mode**

* Nested Interrupt

### ARM CPSR & Processor modes
**Current Program Status Register(CPSR)**
* 在 user-level 時,用於存取 condition code bits
**Saved Processor Status Register (SPSR)**
* 在中斷時用來自動儲存CPSR的暫存器

* **conditionalized**
N : Negative / Z : Zero / C : Carry / V : oVerflow
* I : Interrupt / F : FIQ / T : Thumb
#### ARM Processor modes
在 ARM 架構中支援了 ( 7+1 ) 種模式 :

#### Instruction sets
裡面有 ARM / Thumb / Jazelle ,下圖為簡單介紹:
(實際上 ARM 的 extension 遠比以下列出的多)

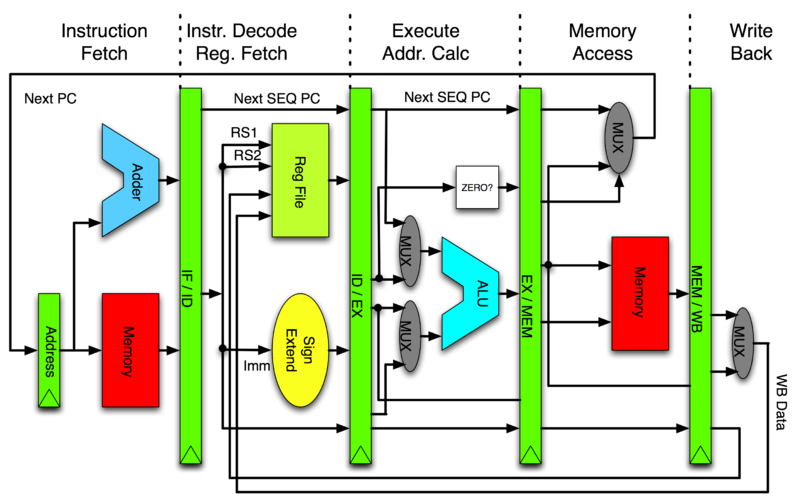
### ARM Pipeline
在執行時, PC 是 8 bytes ahead,也就是說 Pipeline 準備要做 Execute級( 位址是 0x8000)時,要讀取的下一個位置是 ==PC + 8== 的位置(從範例中可清楚看見,即 DCD 指令的位址 0x8008)

他有以下幾點特點:
* 當 Pipeline 在做 branch 或者直接修改 PC 值的話, 會造成 ARM core flush 他的 pipeline
* ARM10 開始使用 branch prediction
* **即使發生中斷,也會將 Pipeline 中所有指令執行完才會去做中斷的事情**
:::warning
- [x] 為何 ARM 的 `PC` 是指向下兩條指令?
* ARM pipeline stages:
* **從 EXE stage 往回看 FETCH stage** : 正在 <u>fetch下兩條指令</u>
* 舊的 MIPS 架構 :
* **fetch 之後, PC = PC + 4, 且一路往下傳遞到接下來的 stages**
- [ ] [关于ARM的PC指针(什么时候PC+8,PC+4,PC-4,PC-8)](https://blog.csdn.net/lee244868149/article/details/49488575)
:::
:::warning
- [x] 如上面所說 PC 指向正在執行的後 2 條指令 (+8),但若某道正在執行指令遇到中斷,這時候的 PC 會如何變化?
* 這個問題要分兩個面向來答覆,一個是 interrupt 的處理機制,另一個則是 PC 的計算方式
* 以 ARM Cortex-M3/M4 來說,不再需要像 ARM7 那樣手動調整返回的 program counter 值,而是以 Cortex-M 硬體給定 `EXC_RETURN` 作為新的 program counter,過程中<u>原有的 pc 值會由硬體重新計算</u>,一旦返回到原有程式時,仍以 +4/+8 (ARM) 作為位移量
- [ ] 《[The Definitive Guide to the ARM Cortex-M3](https://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs373/labs/refs/M3%20Guide.pdf) 》
:::
### Exception / Interrupt / Trap
> 在 ARM 中, Exception = Interrupt = Trap
當發生 exception 或 interrupt 時,會觸發 Interrupt handler,此時,他會尋找 **vector table** 去做中斷時所要處理的 routine.

下圖為中斷定義及其跳躍的起始位址 (for Classic ARM) :

* Software interrupt : 實作 System call
* 唯一可用軟體決定時序的 interrupt
## ARM instruction set
- [ ] ==[ARM Instruction Set](https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cyy/courses/assembly/12fall/lectures/handouts/lec09_ARMisa.pdf)==
### Features
傳統 RISC 都有的特色 :
* Load-store architecture
* [3-address instructions](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Three-address_code)
ARM 獨有的特色 :
* 每個指令都可以做 Conditional execution
* 可以一次 load / store 多個暫存器
* 指令可以結合 shift 和 ALU operations (像是 add, sub)
* Barrier shift : **提升指令的密度**
### 分類
可分成三大項:
1. Data processing
* move
* arithmetic
* logical
* comparison
* multiply
2. Data movement (memory access)
3. Flow control
### 1. Data processing
資料處理指令包含對資料做 移動、算數、邏輯、比較、乘法 的指令,且大部分的 data processing instructions 可以對一個 operand 做 shift :

#### Arithmetic operations
| Mnemonic | Description | Syntax | Result |
|:--------:|:------------------------------ |:---------------- |:----------------------- |
| ADD | simple addition | `ADD r0, r1, r2` | `r0 := r1 + r2` |
| ADC | add with carry | `ADC r0, r1, r2` | `r0 := r1 + r2 + C` |
| SUB | subtract | `SUB r0, r1, r2` | `r0 := r1 - r2` |
| SBC | subtract with carry | `SBC r0, r1, r2` | `r0 := r1 - r2 + C - 1` |
| RSB | reverse subtraction | `RSB r0, r1, r2` | `r0 := r2 - r1` |
| RSC | reverse subtraction with carry | `RSC r0, r1, r2` | `r0 := r2 - r1 + C - 1` |
:::warning
* `( + c - 1 )` = `- !c`

:::
#### Bit-wise logical operations
```c
AND r0, r1, r2 // r0 := r1 and r2
ORR r0, r1, r2 // r0 := r1 or r2
EOR r0, r1, r2 // r0 := r1 xor r2
BIC r0, r1, r2 // r0 := r1 and not r2
```
* BIC : bit clear
#### Register movement operations
* **暫存器間**互相傳送資料
```c
MOV r0, r2 // r0 := r2
NVN r0, r2 // r0 := nor r2
```
#### Comparison operations
只設定在CPSR的 condition code bits (N, Z, C and V)
* `CC` : CPSR 的 **condition code bits**
| Mnemonic | Description | Syntax | Result |
|:--------:|:--------------- |:------------ |:--------------------- |
| CMP | compare | `CMP r1, r2` | set CC on `r1 - r2` |
| CMN | compare negated | `CMN r1, r2` | set CC on `r1 + r2` |
| TST | (bit) test | `TST r1, r2` | set CC on `r1 and r2` |
| TEQ | test equal | `TEQ r1, r2` | set CC on `r1 xor r2` |
#### Immediate operands
* `#1` = (1)~10~
* `#&ff` = `0xff`
```c
ADD r3, r3, #1 // r3 := r3 + 1
AND r8, r7, #&ff // r8 := r7[7:0]
```
#### Shifted register operands
舉例來說 :
```c
ADD r3, r2, r1, LSL #3 // r3 := r2 + ( r1 << 3 )
```

### Barrier shift ( for Classic ARM & ARMv7 )
```c=
mov r0, #8000000F // 將數值 0x8000000F 放入暫存器 r0 中
mov r1, r0, LSL #1 // r0 左移 1 bit 後,將值放入 r1 中
```
`#1` : `r0` = `1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111`
`#2` : `r1` = `0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 1110`
* fast multiply :
```c
mov r1, r0, lsl #2
=> r1 = (int) (r0 << 2)
add r1, r0, r0, lsl #2
=> r1 = (int) (r0 << 2) + r0
=> r1 = r0 * 5
```
* Barrier shift 在 ARMv8 的 A64 之後被去除
> 但 A32 仍可使用 (向下相容)
**Condition flags**
If ==**`S`**== is specified, these instructions update the condition code bits (N, Z, C or V)
```c
ADDS r2, r2, r0 // 32-bit carry out -> C
```
### ARM 如何載入 32-bit 常數 ?
在 r0 暫存器中,存放 `0xDEADBEEF`
> [Hexspeak](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hexspeak)
* 直覺的作法:
```c
mov r0, 0xDEADBEEF
```
:::warning
技術上來說,這是不可能的!為何?
* ARMv7 (含) 之前,所有的指令都是 32 bit (opcode + operand)
* 以 mov 來說,所有的 32 bit 自然包含 **mov 指令本身**、**目標 register**,以及**目標值**
因此,不可能將任意的 32-bit 編碼的值存放到 32 bit 指令中
:::
* MIPS 的作法 : [Loading a 32 bit Immediate](https://courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse378/01au/files/pdf/378-ln8.pdf)
```c
lui $s0, 0xDEAD
ori $s0, $s0, 0xBEEF
```
* ARMv7 之前的作法 :
```c
load_32bit:
ldr r0, [pc #0] // pc 位於目前位址向前 8 bytes 的地方
bx lr // 趕快跳走,不要讓下一行被執行
.word 0xDEADBEEF // 這行不是 ARM 組合語言的指令
```
* 在 ARMv7 後,引入兩個步驟的指令來載入數值: `movw`, `movt`
```c
movw r0, #0xbeef // r0 = 0x0000beef
movt r0, #0xdead // r0 = 0xdeadbeef
```
* GNU as 給予便利的寫法
```c
.equ label, 0xDEADBEEF
movw r0, #:lower16:label
movt r0, #:upper16:label
```
### 3. Flow control instructions
* Determine the instruction to be executed next



### 2. Data transfer instructions
* **暫存器與 memory 間**互相傳遞資料
> Data processing 的 `mov` 指令是**暫存器間**互相傳送資料
三種基本形式:
1. Single register load/store ,也就是對單一暫存器做 load/store
2. Multiple register load/store,可以對多個暫存器做 load/store
3. Single register swap: SWP(B), atomic instruction for semaphore
### Single register load/store


:::warning
* 沒有 **STRSB/STRSH** 是因為 STRB/STRH 儲存 signed/unsigned 到記憶體位置
* 存進去就不管他是有號無號,讀出來才要判別
:::
**Addressing mode**
* Memory 定址可以透過 **暫存器** 和 **offset**
```c
LDR R0, [R1] // mem[R1]
```
**3 ways to specify offsets:**
| Way | Example | Result |
|:------------------ |:--------------------------:|:---------------------------- |
| 1. Immediate | `LDR R0, [R1, #4]` | `// mem[R1+4]` |
| 2. Register | `LDR R0, [R1, R2]` | `// mem[R1 + R2]` |
| 3. Scaled register | `LDR R0, [R1, R2, LSL #2]` | `// mem[ R1 + 4 * R2 ]` |
**三種 Addressing mode:**

| Pre-index | Auto-index | Post-index |
|:------------------------------------:|:------------------------------------:|:------------------------------------:|
|  |  |  |
|  |  |  |
:::warning
* [LDR pseudo-instruction](https://developer.arm.com/documentation/dui0204/j/arm-and-thumb-instructions/pseudo-instructions/ldr-pseudo-instruction)
:::
### Multiple register load/store ( for 32-bit arch. )
* 一次可以存取很多個暫存器的值
```c
LDMIA R0, {R1, R2, R3}
// R1 := mem[R0]
// R2 := mem[R0 + 4]
// R3 := mem[R0 + 8]
```
| Mnemonic | Description | | suffix | meaning |
|:--------:|:------------------------ | --- |:------:| ------- |
| **LDM** | load multiple registers | | **IA** | increase after |
| **STM** | store multiple registers | | **IB** | increase before |
| | | | **DA** | decrease after |
| | | | **DB** | decrease before |
**Addressing mode**

==`!` : 代表要存取後會 register 進行更新==
| `LDMIA Rn, {R1-R3}` | `LDMIB Rn, {R1-R3}` | `LDMDA Rn, {R1-R3}` | `LDMDB Rn, {R1-R3}` |
|:------------------------------------:|:------------------------------------:|:------------------------------------:|:------------------------------------:|
|  |  |  |  |
:::success
學組語的目的,不見得是為了改善效能,而是判斷 optimizing compiler 產生的機械碼是否正確
* gcc 和 clang/llvm 引入大量的最佳化技術,已很難光看原始程式碼,去推知最終生成的機械碼
* 從 Google 搜尋偷到的程式是否有效益 (千萬不要人云亦云,要有判斷能力)
:::
### Copy a block of memory
複製一塊 block 的 memory
* R9: address of the source
* R10: address of the destination
* R11: end address of the source
```c
loop: LDMIA R9!, {R0-R7}
STMIA R10!, {R0-R7}
CMP R9, R11
BNE loop
```

### Stack
* full : pointing to the last used
* ascending : grow towards increasing memory addresses
```c
STMFD R13!, {R2-R9} // used for ATPCS
… // modify R2-R9
LDMFD R13!, {R2-R9}
```


## Introduction to ARM Architecture
> 影片 2:07:00
- [ ] [Introduction to ARM Architecture](https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1cFBRICktpVQAOLzE5eDKD-OM4ckJuncFsn39Wg8aLZI/edit#slide=id.p14)
- [ ] ==[程式練習](https://hackmd.io/s/HkcOofY2x)==
> eabi : 2 進制
> hf : hard floating
**Example 5**
```c
int main(void)
{
int a, b, x, d;
a = 8;
b = 9;
asm("mrs %[result], apsr" : [result] "=r" (x) : );
d = (a ^ b) > 0 ? add(a,b) : subtract(b,a);
printf("a & b is %d\n", d);
printf("Before operation, apsr was %x\n",x);
asm("mrs %[result], apsr" : [result] "=r" (x) : );
printf("After operation, apsr was %x\n",x);
...
```

- [ ] [Cortex --暫存器組](https://www.itread01.com/content/1546802165.html)
---
**`objdump`**
* 可以顯示所有的object file的資訊
* 支援格式非常多: ELF, a.out
* 是 GNU Toolchain 一部分, 可以反組譯
* 使用時要指定架構,如: _arm-linux-gnueabihf-objdump_)
* objdump 和 readelf 相輔相成,可以做到類似的功能,但做法不同(底層library實作不同): BFD
* 可以用兩個不同工具產生的結果來互相對照
* <main> -> C語言的進入點
* 但要有一個人跳進去執行他,所以是從 ELF <start>開始在跳到 <main> => crt (C runtime)
:::warning
- [ ] 不知如何用 `objdump` 得到類似結果? 試了幾種參數感覺跟投影片上都有落差
* 使用 objdump -D 可以得到部份[相似內容](https://embedded2015.hackpad.com/objdump-test-5fD74TMv0Fc)
* -D = disassembler
* 因為可能有最佳化
* -j 看 text section
:::
---
**Versatile Express board**
* Versatile Express 是 ARM 提供的開發硬體(讓客戶廠商的參考硬體),價格較高(19萬~3X萬 NTD),但ARM官方正式支援,而且 QEMU 也支援
:::warning
**QEMU模擬的時間不是 Cycle accurate**
* Cycle accurate : Load、Store、Add、Sub 執行的Cycle數會跟理論上的不一樣
* 所以 Benchmark 會不精確,只能看到趨勢變化
* 需要真正硬體才能得知正確效能
:::
---
**ARMv8 (64-bit) 移除 LD/STR mutiple**
* 有 LD/STR 跟 3 stage pipeline 變成 5 stage pipeline 有關
* 增加了 MEM、WB
* 因為記憶體開銷實在太大
* 一般 LD/STR 2個 Clock cycle
* LD/STR multiple 4個 Clock cycle
* 一次做很多個 LD/STR
* 提升程式碼密度
* 但花的時間可能差不多
* pipeline 設計的好 ,multiple LD/STR 就能發揮效益
* ARMv8 (64-bit) 移除 LD/STR mutiple,因為要考量到 Prediction,一a次失敗會浪費掉太多資源
---
* CPU modes, exception modes, processor modes 對ARM來講都是一模一樣
* 以 ARM 來說,會導致 CPU 變更 execution mode 改變,就是 exception 使然,所以等價,當然,如果我們可用同樣的術語,對簡報陳述較好
* ARM切換不同模式會 exception
---
**為了降低 context switch 成本,ARM降低通用暫存器的數量**
* context switch -> reserve/restore registers (GPR)
* context switch 要保存暫存器
---
- [ ] [Importance of Q(Saturation Flag) in ARM](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/19557338/importance-of-qsaturation-flag-in-arm)
**V 和 Q 差在哪裡??**
* V – Overflow flag
* Q – Sticky overflo
* 簡而言之就是飽和操作如果遇到 overflow 則會讓 Q = 1
---
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet