# 2016q3 Homework3 (mergesort-concurrent)
contributed by `<vic85821>`
## 預期目標
* 作為 [concurrency](/s/H10MXXoT) 的展示案例
* 學習 POSIX Thread Programming,特別是 [synchronization object](https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19683-01/806-6867/6jfpgdcnd/index.html)
* 為日後效能分析和 scalability 研究建構基礎建設
* 學習程式品質分析和相關的開發工具
## POSIX Thread
先來搞懂posix thread,了解thread 同步的方法機制
* condition variable
* allow threads to synchronize based upon the actual value of data
* always used in conjunction with a mutex lock.
* declare : `pthread_cond_t`
* 使用前必須先初始化
* static: `pthread_cond_t myconvar = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;`
* dynamic: 透過 `pthread_cond_init()`
* example `pthread_cond_init (&count_threshold_cv, NULL);`
* mutex
* implement synchronization by controlling thread access to data
* use `pthread_mutex_lock`, `pthread_mutex_unlock`來達到synchronize
* 當取得資源,使用`pthread_mutex_lock`避免其他thread同時取得
* 結束後,透過`pthread_mutex_unlock`釋放

## Thread Pool
為了讓各個thread可以load-balance,透過thread pool來實作,同樣的,先來弄清楚thread pool的運作
### task
thread pool中的job/task,讓thread知道該做什麼事
```c==
typedef struct {
void (*function)(void *);
void *argument;
} threadpool_task_t;
```
* function pointer : 傳入thread 該做的工作內容
* argument : function所用到的參數
### thread pool
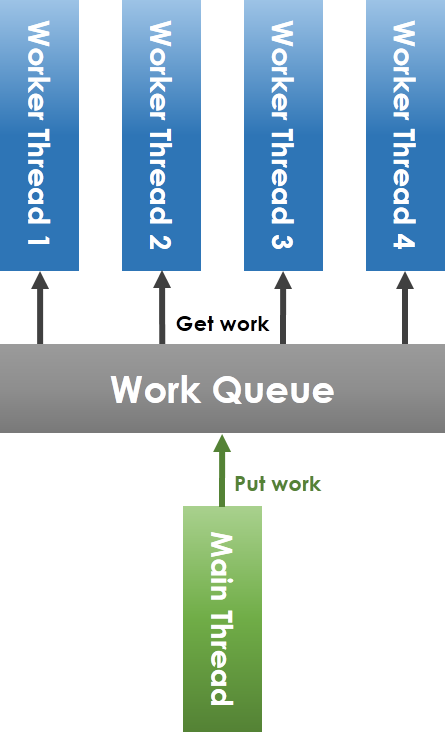
```c==
struct threadpool_t {
pthread_mutex_t lock;
pthread_cond_t notify;
pthread_t *threads;
threadpool_task_t *queue;
int thread_count;
int queue_size;
int head;
int tail;
int count;
int shutdown;
int started;
};
```
* pthread_t : 利用pointer,紀錄所有的thread
* head, tail : pthread array offset
* queue : 存放等待被執行的task
```c==
for(;;) {
/* Lock must be taken to wait on conditional variable */
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
/* Wait on condition variable, check for spurious wakeups.
When returning from `pthread_cond_wait`(), we own the
lock. */
while((pool->count == 0) && (!pool->shutdown)) {
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->notify), &(pool->lock));
}
if((pool->shutdown == immediate_shutdown) ||
((pool->shutdown == graceful_shutdown) &&
(pool->count == 0))) {
break;
}
/* Grab our task */
task.function = pool->queue[pool->head].function;
task.argument = pool->queue[pool->head].argument;
pool->head += 1;
pool->head =
(pool->head == pool->queue_size) ? 0 : pool->head;
pool->count -= 1;
/* Unlock */
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
/* Get to work */
(*(task.function))(task.argument);
}
pool->started--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
pthread_exit(NULL);
return(NULL);
}
```
* thread 一開始先去搶thread pool的mutex,若取得mutex則lock,避免其他thread也取得
* 如果queue沒有task,則一直等到有工作或是thread pool shutdown
* shotdown
* immediate_shutdown : 馬上停止thread pool
* graceful_shutdown : 等到各個thread的工作都結束,task queue是空的才停止thread pool
* 若取得mutex則執行task,執行後釋放mutex
## Lock-free Thread Pool
Lock對效能的影響顯著,因此不希望thread是透過lock來實作。原本的condition variable功能可以透過semaphore來取代。改進方向大致上分為這些
* 避免資源的共享,如此一來就不需要lock
* 各個thread擁有自己的task queue
* main thread 加入task 與 thread 取出task所產生的競爭問題,可以透過**ring buffer**來解決
* condition variable 本質上就是提出來解決執行緒之間的通訊議題,透過semaphore來實作
```c==
sigemptyset(&zeromask);
sigemptyset(&newmask);
sigaddset(&newmask, SIGXX);
sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK, &newmask, &oldmask) ;
while (!CONDITION)
sigsuspend(&zeromask);
sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &oldmask, NULL)
```
>> 是起步慢嗎? [name=jserv]
**需要`#include <signal.h>`**
* `sigemptyset()` : initializes the signal set given by set to empty, with all signals excluded from the set.
* `sigfillset()` : initializes set to full, including all signals.
* `sigaddset()` and `sigdelset()` : add and delete respectively signal signum from set.
* `int sigprocmask(int how, const sigset_t *set, sigset_t *oldset);` : used to fetch and/or change the signal mask of the calling thread.
* `int sigsuspend(const sigset_t *mask);` : wait for a signal
[reference](https://linux.die.net/man/3/sigemptyset)
## Semaphore
假設某段鐵路是單線的,因此,一次只允許一列火車通過;semaphore用於協調同步通過該軌道的火車,火車在進入單一軌道之前必須等待信號燈變為允許通行的狀態,火車進入軌道後,必須改變信號燈狀態,防止其他火車進入該軌道;火車離開這段軌道時,必須再次更改信號燈的狀態,以便允許其他火車進入軌道。
Semaphore可以用於紀錄某一特定資源剩下多少數目可使用;process或thread透過semaphore可以安全的使用共享資源,若特定資源已使用完時,會需要等待資源被釋放。
Semaphore包含兩種:binary semaphore(二進位信號)和counting semaphore(計數信號)。
* binary semaphore
* 只能有0跟1,概念上類似mutex
* mutex有owner的概念,唯有釋放所有權,才能被其他thread存取
* semaphore同樣限制一次只能被一個process/thread存取,但沒有owner的概念限制
* counting semaphore
* 依據semaphore.h的SEM_VALUE_MAX (semvmx)定義。
* 又稱作general semaphore
semaphore有兩種操作方式,為atomic operation(all or nothing)
* V operation
* V()會將semaphore的值加1,signal函數或是sem_post()
* 釋放資源
* P operation
* P()會將semaphore的值減1,wait函數或是sem_wait()
* 獲得資源
* semaphore在減小之前必須為正,確保semaphore值不為負
### 使用
* POSIX semaphore是標準的counting semaphore,使用`sem_post()`執行V opeation,`sem_wait()`執行P operation。
* POSIX semaphore的最大值於limits.h中所定義
* `#define _POSIX_SEM_VALUE_MAX 32767`
* 一個semaphore並非被單一thread所擁有
* thread 執行wait, 另一個thread可以進行signal,但是作業系統在實作時,同一時間點僅能執行其中一個指令,以維持semaphore的一致性。
* 當建立一semaphore時,須設定semaphore的初始值
* Semaphore動作執行成功會回傳0,失敗會回傳 -1
* sem_init():初始化semaphore
* `int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);`
* 第一個參數為semaphore的位址
* 第二個參數為設定semaphore是否可讓不同process使用
* 第三個參數為semaphore初始值
* sem_post():增加semaphore值(加1)
* `int sem_post(sem_t *sem);`
* sem_wait():減少semaphore值(減1)
* `int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);`
* sem_trywait():嘗試減少semaphore值(減1)
* `int sem_trywait(sem_t *sem);`
* sem_destroy():銷毀semaphore
* `int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);`
[reference](http://www.syscom.com.tw/ePaper_Content_EPArticledetail.aspx?id=213&EPID=176&j=5&HeaderName=%E6%8A%80%E8%A1%93%E5%88%86%E4%BA%AB)
## 對Link list 排序
**recursive bubble sort**
```c==
typedef struct list {
int data;
struct list *next;
} LIST;
LIST *sort( LIST *start )
{
if( start == NULL ) return NULL;
start->next = sort(start->next);
if( start->next != NULL && start->data > start->next->data ) {
start = move( start );
}
return start;
}
LIST *move( LIST *x )
{
LIST *n, *p, *ret;
p = x;
n = x->next;
ret = n;
while( n != NULL && x->data > n->data ) {
p = n;
n = n->next;
}
/* we now move the top item between p and n */
p->next = x;
x->next = n;
return ret;
}
```
透過一層一層的呼叫sort,由link list的最後端排列,到整個list都排列完成
[reference](http://faculty.salina.k-state.edu/tim/CMST302/study_guide/topic7/bubble.html)
## 案例分析
### Tools
* **Mutrace**
* `sudo apt-get mutrace`
e.g. : `(for i in {1..8}; do echo $RANDOM; done) | mutrace ./sort 4 8`
```
mutrace: Showing statistics for process sort (pid 6081).
mutrace: 3 mutexes used.
Mutex #0 (0x0x6ad9b0) first referenced by:
/usr/lib/mutrace/libmutrace.so(pthread_mutex_init+0xf2) [0x7fa70f9ea4b2]
./sort(tqueue_init+0x38) [0x401277]
./sort(tpool_init+0x6a) [0x4014cc]
./sort(main+0x161) [0x401c74]
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xf0) [0x7fa70f421830]
Mutex #1 (0x0x7fa70cff0860) first referenced by:
/usr/lib/mutrace/libmutrace.so(pthread_mutex_lock+0x49) [0x7fa70f9ea6b9]
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgcc_s.so.1(_Unwind_Find_FDE+0x2c) [0x7fa70cdecfec]
[(nil)]
Mutex #2 (0x0x603120) first referenced by:
/usr/lib/mutrace/libmutrace.so(pthread_mutex_init+0xf2) [0x7fa70f9ea4b2]
./sort(main+0x11d) [0x401c30]
/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xf0) [0x7fa70f421830]
mutrace: Showing 3 most contended mutexes:
Mutex # Locked Changed Cont. tot.Time[ms] avg.Time[ms] max.Time[ms] Flags
0 76 14 7 0.023 0.000 0.002 Mx.--.
1 20 10 4 0.008 0.000 0.002 M-.--.
2 13 4 0 0.004 0.000 0.000 M-.--.
||||||
/|||||
Object: M = Mutex, W = RWLock /||||
State: x = dead, ! = inconsistent /|||
Use: R = used in realtime thread /||
Mutex Type: r = RECURSIVE, e = ERRRORCHECK, a = ADAPTIVE /|
Mutex Protocol: i = INHERIT, p = PROTECT /
RWLock Kind: r = PREFER_READER, w = PREFER_WRITER, W = PREFER_WRITER_NONREC
mutrace: Note that the flags column R is only valid in --track-rt mode!
mutrace: Total runtime is 1.006 ms.
```
* **GraphViz**
* 依據給定指令的製圖軟體,不過說是繪圖軟體,它能繪的圖並不是一般人想像中的漫畫或 logo,而是數學意義上的 “graph”
* [指令](http://www.graphviz.org/doc/info/shapes.html)
e.g.
```graphviz
digraph {
開始Process[shape="box", style=rounded];
是否為結束Task[shape="diamond"];
結束Process[shape="box", style=rounded];
開始Process->提取Task->是否為結束Task
是否為結束Task->重發結束Task[label="是"]
重發結束Task->結束Process
是否為結束Task->執行Task[label="否"]
執行Task->提取Task;
}
```
### 修改
* 將程式修改成針對string的mergesort
val_t改為char array(大小是根據phonebook的MAX_LAST_NAME_SIZE)
```c==
typedef char val_t[MAX_LAST_NAME_LEN];
```
merge_list()
```c==
while (a->size && b->size) {
llist_t *small = (llist_t *)
((intptr_t) a * (strcmp(a->head->data,b->head->data) < 0 ? 1:0) +
(intptr_t) b * (strcmp(a->head->data,b->head->data) < 0 ? 0:1));
if (current) {
current->next = small->head;
current = current->next;
} else {
_list->head = small->head;
current = _list->head;
}
small->head = small->head->next;
--small->size;
++_list->size;
current->next = NULL;
}
```
* 設計自動化測試
```==
CHECK_CFLAGS = -std=gnu99 -Wall -g -pthread -DTEST
check_right :
$(CC) $(CHECK_CFLAGS) -o list.o -MMD -MF .list.o.d -c list.c
$(CC) $(CHECK_CFLAGS) -o threadpool.o -MMD -MF .threadpool.o.d -c threadpool.c
$(CC) $(CHECK_CFLAGS) -o main.o -MMD -MF .main.o.d -c main.c
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o $@ $(OBJS) -rdynamic
uniq words.txt | sort -R > input.txt
./check_right 4 349900 < input.txt > output.txt
diff words.txt output.txt
```
diff的結果兩個檔案內容一致,可以知道sort的結果正確
* 測試不同thread number的效能
###### tags: `mergesort` `thread pool`
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet