# 2024q1 Homework1 (lab0)
contributed by < `PochariChun` >
## 開發環境
$ gcc -version
gcc (Ubuntu 9.4.0-1ubuntu1~20.04.2) 9.4.0
$ lscpu
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
Address sizes: 39 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
CPU(s): 12
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-11
Thread(s) per core: 2
Core(s) per socket: 6
Socket(s): 1
NUMA node(s): 1
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 158
Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-8700K CPU @ 3.70GHz
Stepping: 10
CPU MHz: 3700.000
CPU max MHz: 4700.0000
CPU min MHz: 800.0000
BogoMIPS: 7399.70
Virtualization: VT-x
L1d cache: 192 KiB
L1i cache: 192 KiB
L2 cache: 1.5 MiB
L3 cache: 12 MiB
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-11
:::danger
不要輕易說「完成」,工程領域是持續的檢討和改進。
:::
<s>## 完成 queue.c</s>
## 指定的佇列操作
<s>由於學習速度不夠快</s>, 才剛理解 [有「品味」的版本 (4 行)](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/c-linked-list#Linked-list-%E5%9C%A8-Linux-%E6%A0%B8%E5%BF%83%E5%8E%9F%E5%A7%8B%E7%A8%8B%E5%BC%8F%E7%A2%BC), 就已經快接近教作業的時刻, <s>決定改變策略, 先完成第一版本的queue 有個對實體的認知</s> , 再根據 [你所不知道的 C 語言: linked list 和非連續記憶體](ttps://hackmd.io/@sysprog/c-linked-list#Linked-list-%E5%9C%A8-Linux-%E6%A0%B8%E5%BF%83%E5%8E%9F%E5%A7%8B%E7%A8%8B%E5%BC%8F%E7%A2%BC) 結構定義 之後的內容來修正
:::danger
誠實面對自己提到,共筆要涵蓋「詳閱第 1 週所有教材」,與其不明究理的說「學習速度不夠快」,不如詳述你的疑惑,寫下來,我們再來討論。通常學員的問題就是賣弄小聰明去「求快」,不踏實的結果就是,用了更多時間、繞了遠路,最終才觸及本來該做的事。
:::
### `q_size`
`q_size` 作為 [lab0 (A)](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/linux2024-lab0/%2F%40sysprog%2Flinux2024-lab0-a#%E7%89%9B%E5%88%80%E5%B0%8F%E8%A9%A6) 提供的範例程式,讓我初探 `queue.c 的操作`,`queue.c 中巨集的使用方式`,以及練習了`用 git 更新程式碼 `以及 `撰寫開發紀錄`的實際流程.
:::danger
- [x] 改進你的漢語表達。
:::
`q_size` 透過**走訪**輸入的結構體,來計算佇列大小。其中走訪藉由`list_for_each` 實現,這個方法可以在 `list.h`和 [The Linux Kernel API](https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/core-api/kernel-api.html) 中找到。
`list_for_each` 這個 **巨集函式** 有兩個參數,分別是:
- 用來 **逐一走訪** 鏈結串列每個節點的指標 `pos`(loop cursor)
- 指向佇列開頭的指標 `head`
:::danger
- [x] traverse (動詞) 和 traversal (名詞)
根據 Dictionary.com 的[解釋](https://www.dictionary.com/browse/traverse
): (作為及物動詞和不及物動詞都有類似的意思,以下列出作為及物動詞的寓意)
* to pass or move over, along, or through.
* to go to and fro over or along.
其實這意思很好懂,就像我們「走過」/「穿越」校園一般,於是 traverse a linked list 就會是「(用某種手段) 存取多個鏈結串列的節點」,但這裡卻沒有必要「所有」的範圍:英語的 "move over/through" 用於某個區域時,根本沒有這樣的隱含意義。如果將 traverse 翻譯為「遍歷」,就會導致「超譯」,也就是跳脫「直譯」和「意譯」。
當我們回頭看 "traverse" 所在的技術描述內容,例如 "traverse every node",若翻譯為「遍歷每個節點」,那麼既然都「遍」(意即「全面」、「到處」),又何來「每個」節點呢?於是,合理的翻譯應改為「逐一走訪每個節點」 —— 差異在哪?在 "traverse every node" 的應用場景中,可能是我們嘗試在鏈結串列尋找特定的節點內含的資料,一旦找到就停止,或者我們要偵測給定的鏈結串列是否包含環狀 (circular) 結構 ,並沒有真的要「遍」(到處/全面)「歷」(意即「經過」) 每個節點。在我們的用語中,要區分「意圖」(intention) 和「實際作用」(reaction),濫用「遍歷」會使得語意不清,從而難以推測英語原文的訴求。
還有個更重要的原因是,「遍歷」這詞已在理工領域存在,且廣泛使用,即「遍歷理論」(Ergodic theory),後者是研究具有不變測度 (invariant measure) 的動力系統及其相關問題的一個數學分支。 遍歷理論研究遍歷變換,由試圖證明統計物理中的遍歷假設 (Ergodic hypothesis) 演進而來。
在統計學中,若單一個物理系統在不同時間內重複相同的實驗 (如丟擲一枚硬幣),其取樣數據所得的統計結果 (如硬幣出現正面的機率) 和極多個完全相同的物理系統的系集 (如丟極多個相同的硬幣) 在同時作相同的實驗取樣數據的統計結果假設為相同時,此種假設即稱為「遍歷性假設」或「遍歷假設」。基於這個假設,對時間平均的統計方式及結果,便可由對系集的平均及統計方式得到。在一般物理系統中,尤其在統計力學範圖中,均採用此遍歷性假設為基本的假設。在流體力學中對亂流的實驗分析,亦是採用此假設。
遍歷 (Ergodic) 源於以下二個希臘詞:
* ergon (對應英語的 work)
* odos (對應英語的 path 或 way)
最初這是由奧地利物理學家波茲曼 ([Ludwig Boltzmann](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ludwig_Boltzmann)) 於統計力學領域 (statistical mechanics) 提出的概念,其一廣為人知的結果是:在經過長時間後,時間平均將會趨近空間平均。此事實在動力系統扮演極重要的角色,在隨機分析領域亦然。
因此,若貿然將 traverse 翻譯為「遍歷」,一來語意不清,二來增加和理工多項領域專業人員的溝通成本,實在得不償失。
$\to$ [資訊科技詞彙翻譯](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/it-vocabulary)
:::
### `q_new`
> [commit 0530b4b](https://github.com/sysprog21/lab0-c/commit/0530b4b6cdf69bf9bedb3ed06116a172d97c0f7a)
為了建立新的「空」佇列,先參考 [HenryChaing ](https://github.com/HenryChaing/lab0-c) 的方法來進行第一次實作,
使用了 list.h 和 [The Linux Kernel API](https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/core-api/kernel-api.html) 中的 `INIT_LIST_HEAD` 來將輸入的 list_head 結構體中的 `next` 和 `prev` 都指向**自己**, 以此初始化節點
> \* This can also be used to initialize a unlinked list node.
但是不了解為何沒這樣做, 就可能會導致 list_del 的結果是未定義的
> \* But the result of a list_del(_init)
> \* on an uninitialized node is undefined
> \* (unrelated memoryis modified, crashes, ...).
:::danger
為何不設計實驗,確認自己的觀點呢?
:::
### 驗證 list_del 帶入 uninitialized node
我的初步想法為, 分別建立 uninitialized node 和 initialized node, 分別帶入 list_del() 之中, 用 lab0 提供的系統工具來檢查 memery 狀況,觀察結果
### `q_free`

`q_free` 的目的是釋放上圖中佇列所佔用的記憶體,
先假設除了鏈結串列的 head 指標本身以外, 還要釋放鏈結串列的**值**和**連續的 char 型態物件**.
:::danger
避免過多的中英文混用,已有明確翻譯詞彙者,例如「鏈結串列」(linked list) 和「佇列」(queue),就使用該中文詞彙,英文則留給變數名稱、人名,或者缺乏通用翻譯詞彙的場景。
:::
於是我先找到佇列所使用的儲存結構 (在 `list.h` 檔案中找到符合描述的儲存結構 `element_t`), 並在 `queue.h` 檔案中找到釋放此儲存結構記憶體的內部 <s>函數</s> **函式** `q_release_element` ,
:::danger
對應到數學公式,function 應翻譯為「函數」,後者就像是台「機器」,它能夠將集合 A 裡面的每個元素「唯一地」對應到集合 B 裡的一個元素。但在 C 語言一類的通用程式語言中,function 未必具備數學函數的意涵,也就是缺乏「唯一對應」的特性,例如對於 [time](https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/time.2.html) 來說,給定同樣的輸入,卻會在不同時間點得到不同的結果,在 C 語言一類的通用程式語言中,甚至可省略傳回值,後者就不符合「函數」的行為。因此,當在通用的程式設計中,function 應翻譯為「函式」,表示「衍生自數學函數的常式 (routine)」。另外,對於更一般的描述,function 會指「功能」一類的意涵,應合適挑選譯詞。
$\to$ [資訊科技詞彙翻譯](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/it-vocabulary)
:::
<s>根據關鍵字 `Iterate` 在 `list.h` 中找到用於迭代佇列中元素的 `list_for_each_entry_safe`, 從敘述得知這可進行迭代的同時確保刪除元素時不會出現記憶體洩漏或損壞. 於是結合這三者來遍歷整個佇列, 並逐一釋放其中元素 `element_t` 。</s>
:::danger
- [x] 以清晰、明確,且流暢的漢語書寫
:::
最後,使用 `free` 函式釋放佇列開頭指標 head ,完成整個佇列的記憶體釋放。
### `q_insert_head`
開始的想法是指派 `element_t` 大小的空間, 並且在分派空間失敗時回傳 `false`,
實際撰寫的時候出現了 **`Memory leak: new [memleak]`**, 才發現結構體 ` element_t *new` 定義完如果不做任何動作, 每呼叫一次 `q_insert_head` 就會多出一個不可參考的 `element_t *new`.
另外我原本是用 `strcpy(new->value, s)` 來作為將字串 s 複製到字元陣列 (char) new->value 中的函數,但發生底下問題:,
```git
wct804@wct804-Z370P-D3:~/Desktop/lab0-c$ git commit -a
Following files need to be cleaned up:
queue.c
Dangerous function detected in /home/wct804/Desktop/lab0-c/queue.c
54: strcpy(new->value, s); /* Copy string s to new->value */
```
參考 [Common vulnerabilities guide for C programmers](https://security.web.cern.ch/recommendations/en/codetools/c.shtml) 其中的strcpy,
> strcpy
The strcpy built-in function does not check buffer lengths and may very well overwrite memory zone contiguous to the intended destination. In fact, the whole family of functions is similarly vulnerable: strcpy, strcat and strcmp.
> *strcpy 內建函數**不會**檢查**緩衝區長度**,並且很可能會覆蓋與預期目標相鄰的記憶體區域。事實上整個函數係列都同樣容易受到攻擊: strcpy、 strcat 和 strcmp*
而網址有提供兩種解決方法, 我採用 strncpy,它可以防止緩衝區溢出, 但不能保證「\0」終止, 所以我的 size 使用 strlen(s) + 1 來包含「\0」.
另外我查閱了 [C99](https://www.open-std.org/jtc1/sc22/wg14/www/docs/n1256.pdf) 其中的 strcpy 和 strncpy 用法:
>**7.21.2.3 The strcpy function**
> #### **Synopsis**
> #include <string.h>
char ***strcpy**(char * restrict **s1**, const char * restrict **s2**);
> #### **Description**
> The strcpy function **copies** the string pointed to by **s2** (including the terminating null
character) **into** the array pointed to by **s1**. If copying takes place between objects that
**overlap**, the behavior is **undefined**.
> #### **Returns**
> The strcpy function returns the **value of s1**.
> **7.21.2.4 The strncpy function**
> #### **Synopsis**
> #include <string.h>
char ***strncpy**(char * restrict **s1**, const char * restrict **s2**, size_t **n**);
> #### **Description**
> The strncpy function copies **not more** than **n characters**
> (characters that follow a null character are not copied) from the array pointed to by s2 to the array pointed to by s1.)
> If copying takes place between objects that **overlap**, the behavior is **undefined**.
If the array pointed to by s2 is a string that is shorter than n characters, null characters
are appended to the copy in the array pointed to by s1, until n characters in all have been
written.
> #### **Returns**
> The strncpy function returns the **value of s1**.
差別真的只有在指定 buffer size size_t. 另外我發現, 沒指定 buffer size 的 **strncpy** 會**騙過 Git hook 在 git commit 時的 Cppcheck**, 但 strncpy 沒有指定 buffer size 效果其實跟 strcpy 一樣, **還是有 **`Memory leak`** 風險**.
### `q_insert_tail`
把 list_add 改成 list_add_tail
### `q_remove_head`
1. 建立一個指標 first_entry, 透過 list_first_entry 函式指向連結串列的開頭元素位置,
2. 透過 list_del_init 函式從連結串列 移除 第一個元素,
3. 如果輸入的 sp 不指向 NULL, 就將取出的元素的值複製到 sp 之中, 再將 sp 的最後一個元素設為 '\0' 代表字串的結尾
4. 回傳開頭元素
### `q_remove_tail`
將 q_remove_head 中第一步的 list_first_entry 函式改成 list_last_entry 函式
第二步改成 移除 最後一個元素
### `q_delete_mid`
[2095. Delete the Middle Node of a Linked List](https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-the-middle-node-of-a-linked-list/description/)
這題我採用快慢指標的方式來實作,
1. 由第一個開頭節點 head->next 開始快慢指標的走訪。由於使用的結構是環狀連結串列,故使用 (fast != head && fast->next != head) 作為快指標遍歷的結束條件。
2. 用暫時指標 mid 指向慢指標,並將慢指標的前一個 next 指標銜接到慢指標的下一個節點。
3. 釋放暫時指標 mid 的空間
:::danger
在中文敘述中,使用全形標點符號,例如該用「,」,而非 ","
:::
### `q_delete_dup`
發現 leetcode 的敘述是要使用排序過的 list, 故先完成 q_sort
```diff
```
### `q_sort`
參考 [Linux 核心風格 Linked List 應用案例](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/c-linked-list#Linux-%E6%A0%B8%E5%BF%83%E9%A2%A8%E6%A0%BC-Linked-List-%E6%87%89%E7%94%A8%E6%A1%88%E4%BE%8B),加入 descend 判斷來改變正序或倒序排序,完成 q_sort。
上傳至 github 時遇到問題 `error: ISO C90 forbids variable length array`,並不是 c99:
```C
queue.c:195:5: error: ISO C90 forbids variable length array ‘begin’ [-Werror=vla]
195 | element_t *begin[max_level], *end[max_level], *result = NULL, *left = NULL,
| ^~~~~~~~~
```
我到 [stackoverflow](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10234288/iso-c90-forbids-variable-length-array) 找到解決方法, 在 makefile 中加入 `CFLAGS += -std=c99`, 結果改成出現 `qtest.c:1172:19: error: ‘CLOCK_MONOTONIC’ undeclared (first use in this function)`,再參考 [stackoverflow](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/40515557/compilation-error-on-clock-gettime-and-clock-monotonic) 發現
> When you use -std=c99, you only get access to the standard C functions in the standard header files. clock_gettime() from time.h is defined by the posix standard, not the C standard.`
故在後方加入
```c
CFLAGS = -g -Wall -std=c99 -D_POSIX_SOURCE -D_GNU_SOURCE
LDFLAGS = -lpthread -lrt
```
結果連結完後還是出現問題 `error: ISO C90 forbids variable length array` , 故查閱
C90 6.7.5.2 Array declarators
```
The expression delimited by [ and ] (which specifies the size of an array) shall be an integral constant expression
that has a value greater than zero
```
必須使用 integral constant expression 作為 array 的 declarators,
### `q_merge`
參考 [Linux 核心的 list_sort 實作](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/c-linked-list) 中的 merge sort 程式碼 [commit b5c56e](https://github.com/torvalds/linux/commit/b5c56e0cdd62979dd538e5363b06be5bdf735a09) 並透過三個任務完成q_sort,
> 1. commit b5c56e0 提及的論文和相關解讀
> 2. 如何撰寫對 cache 友善的程式碼並評估其效益
> 3. 提出合理的排序測試和效能評估機制
Q: 要怎麼評估效能?
A: [Linux 核心的 list_sort 實作](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/c-linked-list) 中有提到 3 個數據,
Execution time (8步驟的變異數分析的手法並搭配 F 分布,目的是不侷限某特定 CPU 硬體平台)
number of comparisons
Cache miss ratio
Execution time
The number of comparisons
Cache miss ratio
:::danger
你如何確保目前的測試程式已涵蓋排序演算法的最差狀況?
:::
### `q_delete_mid`
```diff!
```
## 自動測試程式 qtest, 與追蹤記憶體狀況
使用 DBA 框架 Valgrind, 以及記憶體使用狀況工具 Massif 分析,
> Valgrind 的核心花費大部分的時間在製造、尋找、執行 machine code 和 VEX IR 的轉換, 而 client program 原本的 machine code 都不會跑到。轉換的結果會存在 code cache,再需要時會重新 run 過。
從中文導讀開頭得知,Valgrind 主要負責轉 IR 存在 code cache,
Valgrind 的複雜來自於要把 client 和 tool 壓在同一個 process, 需要用分享的資源 (例如 registers 和 memory), 而且 Valgrind 要小心地確保在 system call、signals、threads 參與的狀況下不會對 client 失去掌控。
(/@sysprog/linux2024-lab0-b)
[Valgrind 運作方式](https://wdv4758h-notes.readthedocs.io/zh-tw/latest/valgrind/dynamic-binary-instrumentation.html#valgrind)
```diff
wct804@wct804-Z370P-D3:~/Desktop/lab0-c$ valgrind -q --leak-check=full ./queue.c
valgrind: ./queue.c: Permission denied
```
嘗試使用 Valgrind 對 queue.c 分析, 得到 Permission denied 但是使用 `ll | grep "queue"` 又是有 rw 權限, 不知道為什麼? 難道 valgrind 使用不同的系統使用者來執行分析嗎?
Invalid memory access => 不會立即造成 segmentation fault, 配置記憶體合法範圍之外的地方進行記憶體操作, 也就是 `**Invalid** write of ___ `
## 在 qtest 新增新的命令 shuffle
```diff
```
## 在 lab0-c 中引入 lib/list_sort.c
```diff
```
## Select 使用方式解釋 和console.c 的實作分析 ,
- 說明其中運用 CS:APP RIO 套件 的原理和考量點。可對照參考 CS:APP 第 10 章重點提示`
```diff
```
---
## 第 1 週教材及作業的啟發和疑惑
### [(一) 改寫自 CMU 電腦系統概論的作業 ](/@sysprog/linux2024-lab0-a)
2024年教材
> "command" 一詞的翻譯是「命令」,常見於終端機裡頭執行的 shell,而 "instruction" 的翻譯是「指令」,特別指在 CPU (central processing unit,中央處理單元) 所執行的 instruction。
[instruction](https://www.dictionary.com/browse/instruction) vs [command](https://www.dictionary.com/browse/command)
`command: to direct with specific authority`
`instruction: information imparted; practice of instructing`
由 web dictionary 的解釋可看出, command 是以 **權限出發來命令**, instruction 是**某資訊的實踐**. 故在專有名詞方面, 可以了解到終端機下的 **命令** 是有階級的概念, 而 CPU 接收的 **指令** 核心思想是就是請 CPU 做某資訊的實踐.
> 在 Ubuntu Linux 20.04-LTS 的 Cppcheck 套件版本較舊,可能會使後文給定的程式碼進行靜態分析時,遇到 false positive,
所以 Git pre-commit / pre-push hook 是會自動執行 Cppcheck 做靜態程式碼分析, 但是我在 [Git hook](https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/git-hooks) 中找不到其中關於 Cppcheck 的設定, 到底是在哪裡設定 Cppcheck 的呢?
> 也就是說,$ make check 將 traces/trace-eg.cmd 檔案內容指派給 qtest,進行以下操作: (僅列出部分)
在 Makefile 中可找到這句的實證, 而 trace-eg.cmd 內全部命令, 其實也是 qtest 的命令.
將多個手動 qtest 測試打包成一個 cmd 實作自動化測試
```diff
check: qtest
./$< -v 3 -f traces/trace-eg.cmd
```
> 另外,lab0-c 專案支援透過 $ make SANITIZER=1 開啟 Address Sanitizer 從而強化執行時期的記憶體檢測,隨後 $ make test 執行過程中會見到類似以下輸出:
>**Clang-format 工具和一致的程式撰寫風格** vs **Git Hooks 進行自動程式碼排版檢查**
- *1. Clang-format 這個工具來調整作業程式的 C 程式撰寫風格*
- *2. Git hook 在 git commit 時會檢查 C/C++ 原始程式碼的風格是否一致,並透過 Cppcheck 進行靜態程式碼檢查。*
**這樣不是重複了嗎? 差別在那可能我要再深入了解.**
> 好的 Git commit message 應符合七條規則
- 針對比較難的 `以祈使句撰寫標題`,
**If applied, this commit will <你的標題>** 這個用來檢查祈使句的簡單句子非常好用
- 針對令一個比較難的 `用內文解釋 what 以及 why vs. how` ,
我目前是嘗試先敘述一次 commit 修改原因 (why), 敘述變動的部份的流程 (what), 以及 what 是如何達成 why (how).
### [(三)](/@sysprog/linux2024-lab0-c)
[(四)](/@sysprog/linux2024-lab0-d)
[(五)](/@sysprog/linux2024-lab0-e)
[(六)](/@sysprog/linux2024-lab0-f)
### [你所不知道的 C 語言: linked list 和非連續記憶體](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/c-linked-list)
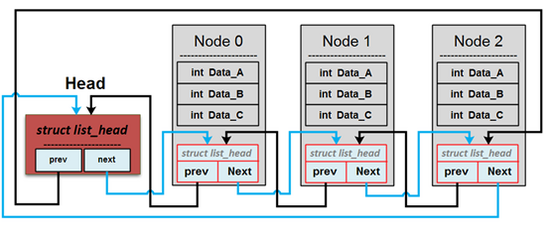
> 有「品味」的版本 (4 行)
> 使用指標的指標 `**indirect` 來代替 `list->head` 和 `head->next`
在原先的程式碼中, 如果 `head` 等於要尋找的目標, 移除目標 (Remove the target)這個動作, 就是將**開頭指標 `list->head`** 這個連結 **跨越 target, 指向 target 的下一個節點位置** `target->next`,
而如果 head 不等於要尋找的目標, 移除目標 (Remove the target)這個動作, 改成將 **target 的前一個節點的指標** `prev->next` 這個連結**跨越 target, 指向 target 的下一個節點位置** `target->next`,
於是可以歸類出底下結論:
- **共同點**:要將 **某個連結** 跨越 target, 指向 target 的下一個節點位置,
- **不同點**:**某個連結** 會因為目標是不是 head 而改變,
於是透過使用 指標的指標 **`**indirect`** 指向 **這個連結** 的位置,
一開始 **這個連結** 儲存 `head` 的位置, 代表 `head` 指標. 在經過 while 的判斷式後, 就能得知 `head` 是不是我們找尋的目標, 也就**同時得知這個連結要不要改變** , 取代原先透過` prev` 是否改變的判斷式, 也省去` prev` 這個指標.
就可以實作 **不用特別撰寫程式碼來處理特例** 的目標
:::info
從「要更新什麼位置的資料」思考,無論是 head 或者非 head,更新的是同一類型的資料,不用特別操作,自然省下額外的處理
:::
#### 暫時節點作法 (dummy point)
暫時節點的 `next` 指向鏈結串列的開頭 `head`,
另外設置用來 **走訪** 鏈結串列的指標 `prev`, 從暫時節點開始走訪鏈結串列
```c
list_entry_t *remove(list_entry_t *head, int value)
{
/* 初始化 list_entry_t 結構體 dummy, 將其 next 指標指向 head */
list_entry_t dummy = {.next = head};
/* 宣告 list_entry_t 指標 prev 指向 dummy,
* prev->next 存在的話,
* prev 就指向 prev->next
*/
for (list_entry_t *prev = &dummy; prev->next; prev = prev->next) {
/* 如果 prev 的`下一個節點`的值, 就是要查找的值 */
if (prev->next->value == value) {
/* 用這句來把 prev 指標指向`下下一個節點`
* 等同繞過`下一個節點`
*/
prev->next = prev->next->next;
break;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
```
#### 作業:使用指標的指標, 改進移走 (remove)
> 因為我們根本不用回傳新的開頭節點,相反的,可將函式原型改為 void remove(list_entry_t **head, int value),藉由間接指標來更動傳入的鏈結串列開頭節點。
使用間接指標 `head` 指向鏈結串列的開頭位置,
並同時用判斷式 (*head)->value != value 來決定使否要更改 `head` 所紀錄的**指標**, 以此 **走訪** 鏈結串列
`ind = &(*ind)->next; ` 是將指標的指標轉移到 `->next` 之上來**走訪**下一個節點
`*ind = (*ind)->next; ` 是等同上一個 `prev->next = prev->next->next;`
```c
void remove(list_entry_t **head, int value)
{
list_entry_t **ind = head;
while ((*ind) && (*ind)->value != value)
ind = &(*ind)->next;
*ind = (*ind)->next;
}
```
這樣發現如果 value 不在鏈結串列之中, 結尾會變成指向 NULL 指標的 next, 造成錯誤.
故加入判斷式 `if (*ind)` 來確保 value 不在鏈結串列之中時, 不做任何動作
```c
void remove(list_entry_t **head, int value)
{
list_entry_t **ind = head;
while ((*ind) && (*ind)->value != value)
ind = &(*ind)->next;
if (*ind)
*ind = (*ind)->next;
}
```
#### 案例探討: LeetCode 21. Merge Two Sorted Lists
Q: L1 跟 L2 分開寫同樣的程式碼,該如何簡化?
A: 可以再使用一個指標的指標來指向 L1 或 L2。
```c
void remove(list_entry_t **head, int value)
{
node = (L1->val < L2->val) ? &L1: &L2;
*ptr = *node;
ptr = &(*ptr)->next;
}
```
依據 C99 規格書 6.5.15 的註腳 ' A conditional expression does not yield an lvalue', node = L1->val < L2->val? &L1: &L2 不能寫成 node = &(L1->val < L2-> val? L1: L2),
#### circular linked list
用「龜兔賽跑」(Floyd's Cycle detection)來偵測是否有 cycle 產生。
#### `list_head`
自行定義一個結構來用 `list_head` 實作 `queue` , 可以使用 `typeof` 定義, 其中 `struct list_head list` 就已經代表雙向鏈結串列;
```graphviz
digraph list {
rankdir=LR;
node[shape=record, style=bold];
subgraph cluster_0 {
node [shape=record];
value [label="{value}"];
head [label="{<prev>prev|<next>next}"];
style=bold;
label=my_data
}
}
```
下方標註了在`typeof element_t` 中定義的type
```graphviz
digraph list {
rankdir=LR;
node[shape=record, style=bold];
subgraph cluster_0 {
node [shape=record];
value [label="{char *|value}"];
head [label="{list_head *head|<prev>prev|<next>next}"];
style=bold;
label=my_data
}
}
```
> 乍看之下,若將 WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, new) 替換成 prev->next = new,兩者一樣嗎?
WRITE_ONCE 定義在 linux/tools/include/linux/compiler.h 路徑下,我們可以從註解中對其作用進行理解:
:::info
比對程式碼作法:
1. 找不同
2. 假設: 不同處是否可以更換?
3. 驗證: 不同處的定義與可達成的事( spec 如同 C99, linux API spec), 使用的技巧, 了解目的
:::
### Git
> [Why is Git always asking for my password? ](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/getting-started-with-git/why-is-git-always-asking-for-my-password)
遇到問題:
之中的 [linux 額外設定](https://github.com/git-ecosystem/git-credential-manager/blob/release/docs/credstores.md), 透過 設定讓 GCM 憑證助手(Git Credential Manager)使用 GPG 來加密包含儲存在檔案系統中的憑證的檔案, 我不知道 `pass init <gpg-id>` 這個步驟的 `<gpg-id>` 為何, 無法完成設定.
解決方式:
執行 `pass init <gpg-id>` 之前先執行 `gpg --gen-key`, 照步驟進行, 只有 password 需要輸入, 取得的 `sec rsa3072 2024-03-02 [SC] [expires: 2026-03-02]
3....D` 的 3....D 就是要輸入的 `gpg-id`, 每次 git push 只須輸入本地存取 GPG 憑證的 password 即可完成 git push.
#### list.h
##### `__LIST_HAVE_TYPEOF`
```diff
#if defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__)
#define __LIST_HAVE_TYPEOF 1
#endif
```
檢查編譯器是否為 GCC 或 Clang,如果是的話,就定義了 `__LIST_HAVE_TYPEOF` 這個巨集 <s>變數</s>
#### `container_of`
[Linux 核心原始程式碼巨集: container_of](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/linux-macro-containerof)
```diff
*/
#ifndef container_of
#ifdef __LIST_HAVE_TYPEOF
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) \
__extension__({ \
const __typeof__(((type *) 0)->member) *__pmember = (ptr); \
(type *) ((char *) __pmember - offsetof(type, member)); \
})
#else
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) \
((type *) ((char *) (ptr) -offsetof(type, member)))
#endif
#endif
```
container_of() 是此專案由 Linux 核心抽離出的關鍵程式碼:
提供了兩種不同的實作方式,根據巨集變數 `__LIST_HAVE_TYPEOF` 是否被定義 (是否為 GCC 或 Clang) 來選擇不同的實作, 其中的 `__extension__` 在 [你所不知道的 C 語言:技巧篇](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/c-trick) 中有詳細介紹, 因為程式使用到非 ANSI C 標準的語句, 是一個用來防止 gcc 編譯器產生警告的修飾字,
> 在 `container_of` 巨集出現前,程式設計的思維往往是:
給定結構體起始地址
求出結構體特定成員的記憶體內容
傳回結構體成員的地址,作日後存取使用
> `container_of` 巨集則逆轉流程,從 struct list_head 這個公開介面,「反向」去存取到自行定義的結構體開頭地址。
由 `container_of`() 更了解 struct 的記憶體配置,
:::warning
留意出現在行文間的 `__` 和 `_` 字元,這些可能會影響 HackMD 的排版,應適度用額外的標示處理。
:::
### 面試
提到兩個演算法要能快速做比較
### 排除問題怎麼排除
把所有問題記錄下來,逐個擊破
紀錄下哪裡遇到問題,正在怎麼解決,例如閱讀什麼資料,衍生的問題都記錄下來,不能空想
課程提到使用 GDB, 了解 gdb
搞定限制(最差最優,記憶體,使用場合),變化,做法
e.g. inplace 其一是為了在 kernal
寫出自己程式碼的比較次數
### 為什麼要考慮 in place
可以確保在kernal的程式在指定的內容完成
### FREE RTOS
可以查詢
表達任務用 link list
### git tree
是什麼?
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet