# Datatypes
---
# Review
----
### What are datatypes?
----
### int?
----
#### Finish last work!
1. Write a `C` code that makes 2 to the power of N(a static number)
```c=
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void){
int N = sizeof(int) * 8;
int target = 2;
/*
* Your core codes should write here
*/
printf("%d\n", target);
}
```
---
# Strings
----
### How does strings store data
----
## ASCII Codes
----
##### ASCII Codes

----
### Any others?
----
## How about Chinese Charactors?
----
## Unicode
----
### Unicodes

---
### Test
----
#### ASCII Codes
```c=
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void){
printf("%d, %c\n", 'A', 'A');
}
```
----
##### Result
```shell=
65, A
```
----
#### Wait
----
##### What is `%d`, `%c`?
----
##### Remember this?

[Reference](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C_data_types)
----
##### Tell the computer what kind of datatype it is
- `%d` -> integer
- `%c` -> charactor
- `%s` -> string
- `%f` -> float
- and so on (just google it)
[Reference](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C_data_types)
----
##### What happened?
- 'A' = 65 in ASCII Code
- 'A' and 65 are actually the same in binary, but different way to present
- `%d` -> 65
- `%c` -> A
----
##### Try it out!
```c=
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void){
printf("%d, %c\n", 'A', 'A');
printf("%d, %c\n", 65, 65);
}
```
###### result
```shell=
65, A
65, A
```
----
###### What is `\n`?
----
##### Try it out!
----
```c=
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void){
printf("%d", '\n');
}
```
###### result
```shell=
10
```
----
##### Compare to ASCII TABLE

LINE FEED (Enter)
---
### What else?
----
#### How many letters are there between 'A' and 'I'?
----
ABCDEFGHI -> 8 letters
----
#### Using Code?
----
#### Cool
```c=
#include<stdio.h>
int main(void){
printf("%d\n", 'I' - 'A');
}
```
---
#### Decode and Encode
----
#### ROT13
ROT13 ("rotate by 13 places", sometimes hyphenated ROT-13) is a simple letter substitution cipher that replaces a letter with the 13th letter after it in the alphabet.
----
#### ROT13
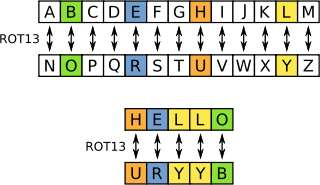
----
```graphviz
digraph {
rankdir=LR;
node [ shape=record ];
struct1 [
label = "<port1>Message";
];
struct2 [
label = "{<port2>Non Sence}";
];
struct3 [
label = "{<port3>Decode Message}"
]
struct1:port1 -> struct2:port2 [ label="ROT13" ];
struct2:port2 -> struct3:port3 [ label="ROT13" ];
}
```
----
#### Try to write a code to decode this!
`LBHNERFBNJRFBZR`
----
#### How about this?
`Lbh_ne3_f0_pb01!`
----
##### Ans
```c=
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(void){
char input[100];
scanf("%s", input);
for(int i = 0; i < strlen(input); i++){
if (input[i] >= 'a' && input[i] <= 'z'){
int tmp = input[i] - 'a';
tmp += 13;
tmp %= 26;
input[i] = tmp + 'a';
}else if (input[i] >= 'A' && input[i] <= 'Z'){
int tmp = input[i] - 'A';
tmp += 13;
tmp %= 26;
input[i] = tmp + 'A';
}
}
printf("%s\n", input);
}
```
---
### That's all for today
----
#### Any questions?
{"metaMigratedAt":"2023-06-16T17:28:14.555Z","metaMigratedFrom":"YAML","title":"Datatypes - Strings","breaks":true,"GA":"UA-208228992-1","slideOptions":"{\"theme\":\"solarized\",\"transition\":\"fade\"}","contributors":"[{\"id\":\"bdcee32f-5dc2-4add-94fa-e418d7247ad0\",\"add\":3791,\"del\":96}]"}