# vuex
{%hackmd BJrTq20hE %}
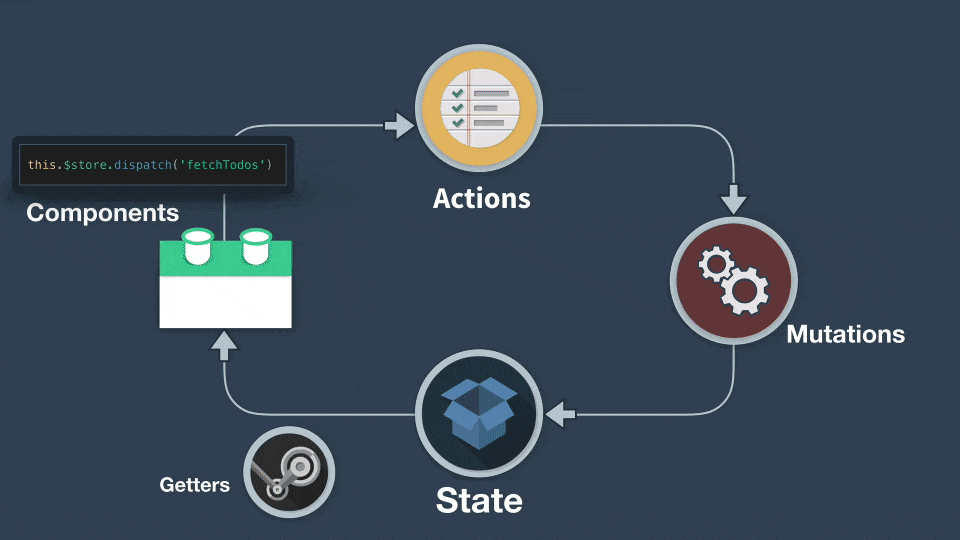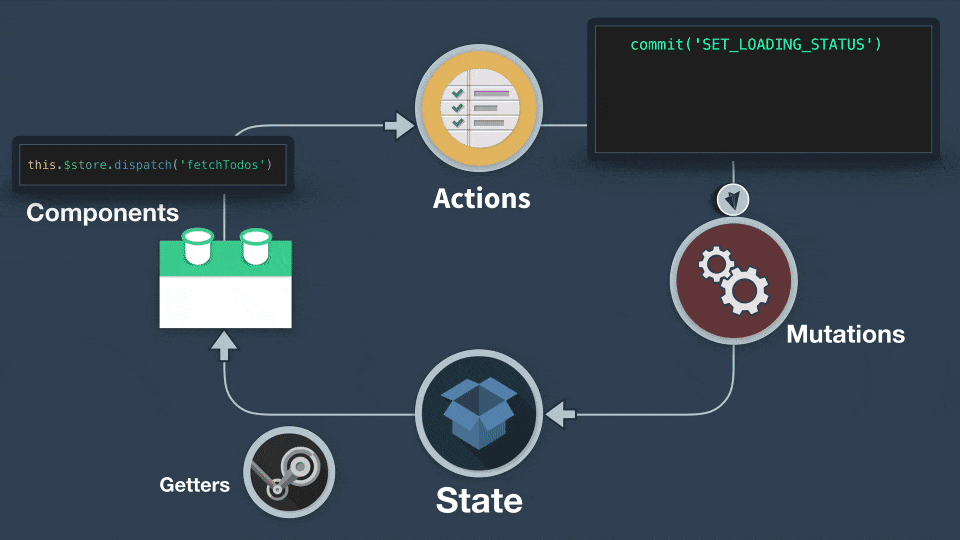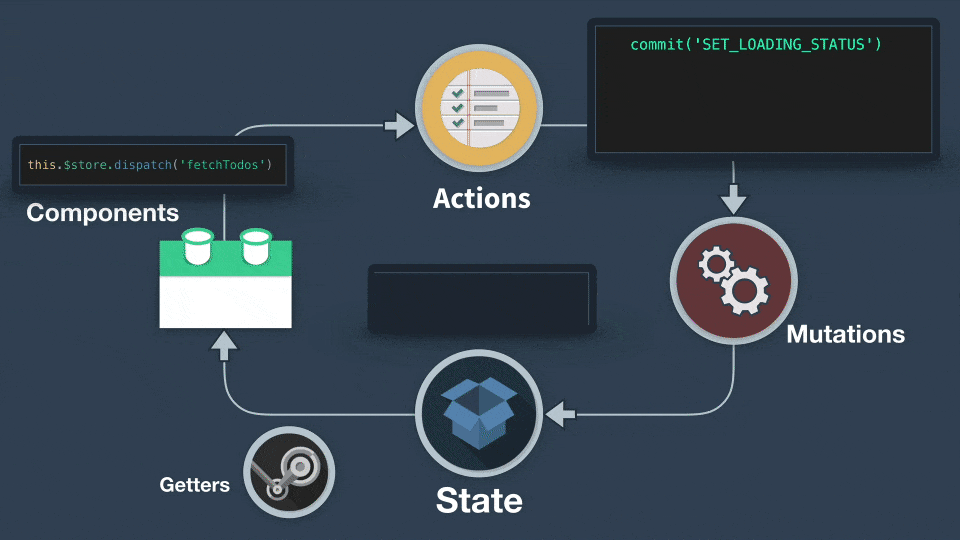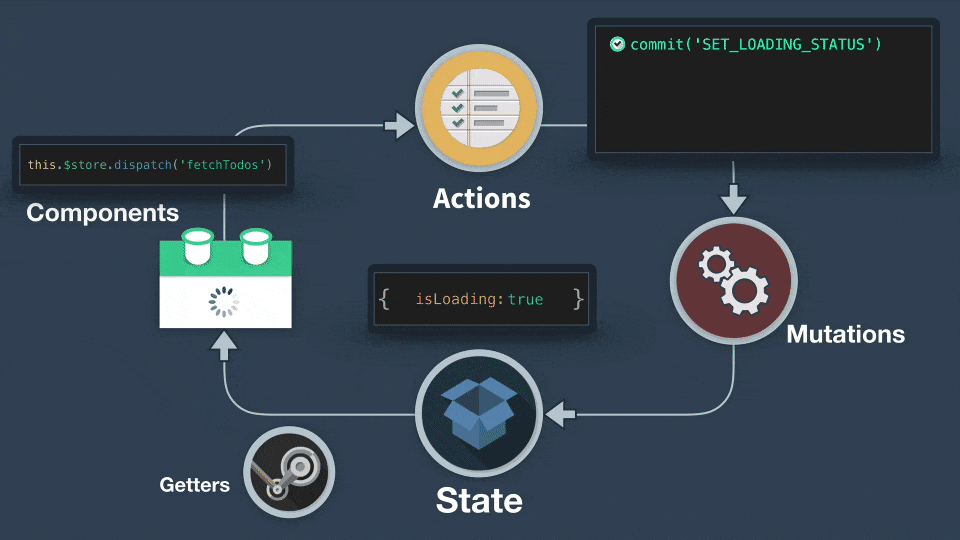
流程:
1. 安裝:
`npm i -S vuex@next`
2. 建立store>index.js
```
|-- src
|-- store
| |-- index.js
```
```javascript=
//store>index.js
import { createStore } from "vuex";
export default createStore({
state: {
//相當於vue的data()
isLoading: false,
clickedTimes: 0,
todos: [
{ id: 1, text: '...', done: true },
{ id: 2, text: '...', done: false }
]
},
mutations: {
//專門用來控制state的methods
//mutation 里面只允许同步的去修改 state 数据。
Loaded(state) {
state.isLoading = !state.isLoading;
},
addTimes(state) {
state.clickedTimes += 1;
},
},
actions: { //相當於vue的methods(只允許異步)
addTimes({ commit }) {
commit('addTimes') //呼叫mutation的addTimes
},
},
getters: { //就是 store 裡面的 computed
doneTodos: state => { //Getter 接受 state 作为其第一个参数
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
}
},
});
```

3. 把store掛到vue上:
```javascript=
//main.js
import { createApp } from "vue";
import store from "../store";
import App from "./App.vue";
const app = createApp(App);
app.use(store);
app.mount("#app");
```
4. 使用
- optonal
```javascript=
<template>
<div>
<p>Loading: {{ isLoading }}</p>
<button @click="reverseLoad(); addTimes()">Reverse</button>
<p>Button Clicked Times: {{ clickedTimes }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "app",
computed: {
ifLoading() {
// 在這邊吐回state裡面的isLoading
return this.$store.state.isLoading;
},
clicked() {
// 抓 state 的 clickedTimes
return this.$store.state.clickedTimes;
}
},
//如果要取得多個state可以用mapState
computed: {
...mapState([
// 需要的state在這邊
'isLoading',
'clickedTimes'
]),
doneTodosCount() { //取得getter資料
return this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount
}
},
methods: {
reverseLoad() {
this.$store.commit("Loaded"); // 在這邊執行store裡面的Loaded這個mutation
},
addTimes() {
this.$store.commit("addTimes");
}
}
};
</script>
```
- composition
```javascript=
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
const store = useStore()
const toDoList = computed(() => store.state.todos)
```
mapState格式可為:(map系列為把store值傳進來)
```javascript=
//可以改用物件來指定state裡面的值
computed: mapState({
ifLoading: "isLoading",
Times: "clickedTimes"
}),
//or函式
computed: mapState({
ifLoading(state) {
return state.isLoading;
},
Times(state) {
return state.clickedTimes;
}
}),
//可簡化為
computed: mapState({
ifLoading: state => state.isLoading,
Times: state => state.clickedTimes
}),
```
通常我們的 computed 裡面,不會只有 mapState,也會有別的 computed 要使用,可以使用 ES6 的 … 來達成:
```javascript=
computed: {
otherfn() {
return "asdf";
},
...mapState({
ifLoading: state => state.isLoading,
Times: state => state.clickedTimes
})
},
```
多個 mutations 也有 mapMutations 可以同理使用:(皆需要import進來)
```javascript=
import { mapState, mapMutations } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "app",
// 陣列、物件指定方法和mapState一樣
methods: mapMutations(["Loaded", "addTimes"])
};
```
多個 actions 也有 mapActions 可以使用
## commit、dispath
- commit 拿來呼叫 mutations
- dispatch 拿來呼叫 actions
actions 不能直接變動 state,只有 mutations 可以更動 state
```javascript=
//store.js
import { createStore } from "vuex";
import axios from "axios";
export default createStore({
state: {
// state 裡面的 Loaded 預設為 false ,在 axios 成功 get 到 user api 的之後,再更改為 true
Loaded: false,
},
actions: {
GetUser(context) {
axios
.get("https://randomuser.me/api/")
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
// context.commit 用來呼叫 mutations,
// context.dispatch 用來呼叫另外一個 actions。
context.commit("MyMutations");
context.dispatch("AnotherActions");
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
},
AnotherActions() {
console.log("Another Actions run!");
},
},
mutations: {
MyMutations(state) {
console.log("MyMutations run!");
// 抓到user之後,將state的loaded改為true
state.Loaded = true;
},
SetFalse(state) {
state.Loaded = false;
},
},
});
```
PS:context可以用 ES6 解構的方法將 context 裡面的 commit, dispatch 解構出來使用:
```javascript=
GetUser({ commit, dispatch }) {
axios.get('https://randomuser.me/api/')
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
// 使用解出來的
commit('MyMutations')
dispatch('AnotherActions')
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
})
},
```
```javascript=
//app.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
// state 的 Loaded
<p>random user api Loaded: {{ userLoaded }}</p>// Reload API
<button @click="Reload">Reload</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "app",
data() {
return {};
},
mounted() {
// 1. 頁面讀取完成時,吃 randomuser API
this.$store.dispatch("GetUser");
},
computed: {
// 2. 將 state 中的 Loaded 用 computed 抓出來給 userLoaded 做使用(取值)
userLoaded() {
return this.$store.state.Loaded;
}
},
methods: {
// 3. Reload 按鈕按下去的時候,把 state 的 Loaded 改回 false,然後再執行一次 GetUser 這個 actions
Reload() {
this.$store.commit("SetFalse");
this.$store.dispatch("GetUser");
}
}
};
</script>
```
actions 跟 mutations 的用法差不多,但是我們要記得 ==**mutations 必須是同步執行**==,而 ==actions 則可以**異步執行**==。
## getters:就是 store 裡面的 computed
Getters 簡單說就是可以把 state 處理過後再丟出去
```javascript=
//store.js
import { createStore } from "vuex";
import axios from "axios";
export default createStore({
state: {
Loaded: false,
clickedTimes: 0,
users: [],
},
actions: {
GetUser({ commit }) {
axios.get("https://randomuser.me/api/?results=5").then(function (res) {
var data = res.data.results;
commit("dataLoaded");
// 把抓回來的data發給mutations
commit("setUserInfo", data);
});
},
ClickedActions({ commit }, payload) {
commit("addTimes", payload);
},
},
mutations: {
dataLoaded(state) {
state.Loaded = true;
},
SetFalse(state) {
state.Loaded = false;
},
addTimes(state, payload) {
state.clickedTimes = state.clickedTimes + payload;
},
// 把拿到的data丟進state裡面
setUserInfo(state, payload) {
state.users = payload;
},
},
getters: {
FemaleNum(state) {
return state.users.filter((item) => item.gender == "female").length;
},
//getters可以帶入三種參數,state、getters、函式
MaleNum(state, getters) {
return state.users.length - getters.FemaleNum;
},
//回傳函式
returnFn(state) {
return function DetectGender(gd) {
if (state.users.filter((item) => item.gender == gd).length > 2)
console.log("There are over 2 " + gd + " in data");
else console.log("No over 2 " + gd + " in data");
};
},
},
});
```
getters 除了帶入 state 之外,總共可以帶入三種參數:
- state
- 其他 getters
- 函式
## map-getters
- optional:
```javascript=
//app.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<p>Loading: {{ Loaded }}</p>
<button @click="Reload(); addTimes()">reload</button>
<p>Button Clicked Times: {{ clickedTimes }}</p>
<p>Female number: {{ FemaleNum }}</p>
<p>Male numner: {{ MaleNum }}</p>
<br />// 資料中有沒有超過兩個女生?
<label>Are there more than 2 women in data?</label>
<button @click="DetectGender('female')">Detect</button>
<br />// 資料中有沒有超過兩個男生?
<label>Are there more than 2 men in data?</label>
<button @click="DetectGender('male')">Detect</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapActions, mapGetters } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "app",
mounted() {
// 1. 頁面讀取完成時,吃 randomuser API
this.$store.dispatch("GetUser");
},
computed: {
...mapState(["Loaded", "clickedTimes", "users"]),
//陣列寫法
...mapGetters(["FemaleNum", "MaleNum"]), //從getter取得資料
},
methods: {
Reload() {
this.$store.commit("SetFalse");
this.$store.dispatch("GetUser");
},
addTimes() {
this.$store.commit("addTimes", 1);
},
DetectGender(gd) {
this.$store.getters.returnFn(gd);
},
}
};
</script>
```
- mapGetters vue3寫法:
https://medium.com/geekculture/mapgetters-with-vue3-vuex4-and-script-setup-5827f83930b4
```javascript=
// assets/js/map-states.js
import { computed } from "vue";
import { useStore } from "vuex";
const mapState = () => {
const store = useStore();
return Object.fromEntries(
Object.keys(store.state).map((key) => [
key,
computed(() => store.state[key]),
])
);
};
const mapGetters = () => {
const store = useStore();
return Object.fromEntries(
Object.keys(store.getters).map((getter) => [
getter,
computed(() => store.getters[getter]),
])
);
};
const mapMutations = () => {
const store = useStore();
return Object.fromEntries(
Object.keys(store._mutations).map((mutation) => [
mutation,
(value) => store.commit(mutation, value),
])
);
};
const mapActions = () => {
const store = useStore();
return Object.fromEntries(
Object.keys(store._actions).map((action) => [
action,
(value) => store.dispatch(action, value),
])
);
};
export { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions };
```
使用:
```javascript=
import { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from '../map-state'
// computed properties
const { count } = mapState()
const { countIsOdd, countIsEvent } = mapGetters()
// commit/dispatch functions
const { countUp, countDown } = mapMutations()
const { getRemoteCount } = mapActions()
```
## Modules
如果專案規模比較龐大,store 裡面的 state 可能會變得越來越肥,可能會有會員資訊、訂單資訊、商品資訊、最新消息…等,所以 Vuex 允許我們使用 **Modules**來解決這個問題,**將 store 中各類的 state 分類管理**。
[教學](https://medium.com/itsems-frontend/vue-vuex4-modules-ddb3eec6b834)
```javascript=
const moduleUser = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const modulePurchase = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
// 在 new Vuex Store 的時候,把modules加進來
const store = new Vuex.Store({ //(vue2寫法)
modules: {
user: moduleUser,
purchase: modulePurchase
}
})
export default createStore({
modules: {
user: moduleUser,
purchase: modulePurchase
}
}
```
## Module — Getters
Module 裡面的 Getters 會有這些參數:`state, getters, rootState, rootGetters` ,前面的 `state, getters` 一樣是 module 自己的 state 跟 getters,`rootState, rootGetters` 則表示回到**根部**(new Vuex.Store 那一層),舉例:
```javascript=
//store.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const moduleUser = {
// 自己的state
state: {
name: "emma",
age: 18
},
getters: {
// 拿自己的state
GetAge(state) {
return state.age
},
// 拿根部的state
GetRealAge(state, getters, rootState) {
return rootState.age
},
// 另一個module的state
GetNextAge(state, getters, rootState) {
return rootState.another.NextyearAge
}
}
}
// 另一個module
const moduleAnother = {
state: {
NextyearAge: 21
},
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 根部的state
state: {
age: 20,
gender: "female"
},
// 註冊modules
modules: {
user: moduleUser,
another: moduleAnother
}
})
export default store;
```
這邊要注意一個小地方,在 moduleUser 裡面的 getters 這邊,假設如範例我要使用 `rootState` 這個參數,前面兩個 `state, getters` 也要帶上去,如果只寫 `rootState` 就會被當成自己的 state,他是依序判斷參數的
- 使用 (此範例有使用 vuex-shared-mutations)
```jsx=
const store = useStore();
const isStudent = computed(() => store.getters["auth/getRole"].isStudent);
```
## Module — Actions
actions 在第二篇說明 actions 的時候有提到他可以帶入的參數,context 原本有 `commit, dispatch, state, getters`,在 modules 裡面,和 getters 一樣也有 `rootState, rootGetters` 可以用
## 區域、全域、namespaced
使用了 module 之後,**module 們的 actions, mutations, getters 都是全域共用的**,全域共用是什麼意思呢?意思就是如果 moduleA 和 moduleB 都有一個 actions 叫做 `sayHi`,那麼我在 component dispatch `sayHi` 的話,兩個 module 的 `sayHi` 都會執行,下面用範例來看看:
```javascript=
const moduleUser = {
namespaced: true, //命名空間
actions: {
sayHi() {
console.log('Hello from moduleUser')
}
}
}
const moduleAnother = {
namespaced: true,
actions: {
sayHi() {
console.log('Hello from moduleAnother')
}
}
}
```
```javascript=
mounted() {
//假設上面沒有設定namespaced,會同時呼叫
this.$store.dispatch("sayHi");
//加上了 namespaced 這個設定之後,在 component 要 dispatch 這個 actions 前面就要加上 module 的名稱
this.$store.dispatch("user/sayHi");
this.$store.dispatch("another/sayHi");
//用 mapGetters 呼叫 moduleUser 的 getters,其他以此類推
...mapGetters({
GetAge: "user/GetAge",
GetRealAge: "user/GetRealAge",
GetNextAge: "user/GetNextAge"
})
},
```
補充:`...mapGetters(["FemaleNum", "MaleNum"])`為原本寫法。
這裡把剛剛 mapGetters 用法從**陣列**轉為**物件**了,因為原本陣列的用法,template 上的名字需要和 getters 一樣,現在因為 namespaced 的關係,getters 的名字前面需要加上 module 的名字,所以就改用物件把 template 的 getters 名稱指定到 module 的 getters。
- 接下來在 store.js 中,在 moduleAnother 的 actions `addYear` commit 會帶上三個參數:`mutations, payload, {root:true}` :
```javascript=
commit('user/addAge', 2, { root: true })
```
第一個參數一樣是要呼叫的別的 module 的 mutations,第二個參數則為 payload,如果不需要 payload,也可以寫 `null` 就好,第三個 `{ root: true }` 表示為**根部**,就是從底部找的意思,**開啟 namespaced 後,module 之間的 actions, getters, mutations 之間要互相呼叫都要記得加上**`{ root: true }`,如果沒有加上這句話,vuex 會當作你還是要呼叫自己的東西,就會錯了
## Module — 使用 mapState, mapMutations, mapActions, mapGetters簡化寫法
在 component 中,如果有很多個 state 要指定,所以也可以將
```javascript=
...mapState({
MyName: state => state.user.name,
gender: state => state.user.gender,
addr: state => state.user.addr
}),
```
改寫為:
```javascript=
...mapState("user", {
MyName: state => state.name,
gender: state => state.gender,
addr: state => state.addr
}),
```
**在 maptState 前面加入一個 module 名的字串**,就可以指定要找的 module 名稱了。
如果 template 上的名稱跟 state 裡面的名稱一樣,改為陣列的話,會更簡短:
```javascript=
...mapState("user", ["name", "gender", "addr"]),
```
### 或是再更精簡一點:
```javascript=
//app.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
// state
<p>hi, I'm {{name}}</p>
<p>I'm a {{gender}}</p>
<p>and I live in {{addr}}</p>
// getters
<p>I'm {{GetAge}} years old.</p>
<p>Just kidding, I'm actually {{GetRealAge}} years old.</p>
<p>And next year I'll be {{GetNextAge}} years old.</p>
</template>
<script>
// import createNamespacedHelpers
import { createNamespacedHelpers } from "vuex";
// 並直接指定使用 user 這個 module,
const { mapState, mapGetters } = createNamespacedHelpers("user");
export default {
name: "App",
computed: {
...mapState(["name", "gender", "addr"]),
...mapGetters(["GetAge", "GetRealAge", "GetNextAge"])
},
};
</script>
```
```javascript=
//store.js
import { createStore } from "vuex";
const moduleUser = {
namespaced: true,
// 自己的state
state: {
name: "emma",
gender: "female",
addr: "Taipei",
age: 18,
},
getters: {
// 拿自己的state
GetAge(state) {
return state.age;
},
// 拿根部的state
GetRealAge(state, getters, rootState) {
return rootState.age;
},
// 另一個module的state
GetNextAge(state, getters, rootState) {
return rootState.another.NextyearAge;
},
},
};
// 另一個module
const moduleAnother = {
state: {
NextyearAge: 21,
},
};
export default createStore({
// 根部的state
state: {
age: 20,
gender: "female",
},
// 註冊modules
modules: {
user: moduleUser,
another: moduleAnother,
},
});
```
## vuex 重整數據丟失解決方案
https://blog.csdn.net/bidepanm/article/details/124686409
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet