### What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, and software over the internet ("the cloud").
It allows users to pay only for what they use, scale resources easily, and access services globally.
### Types of Cloud Services
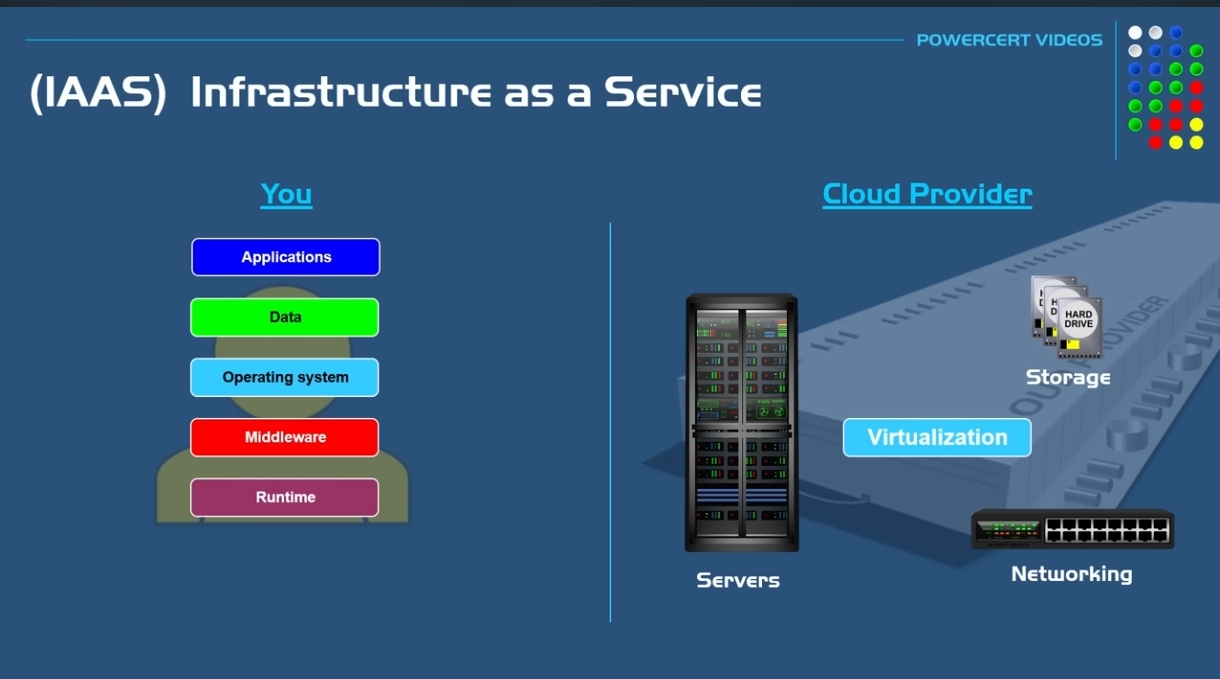
#### 1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet.
##### Example:
AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure.
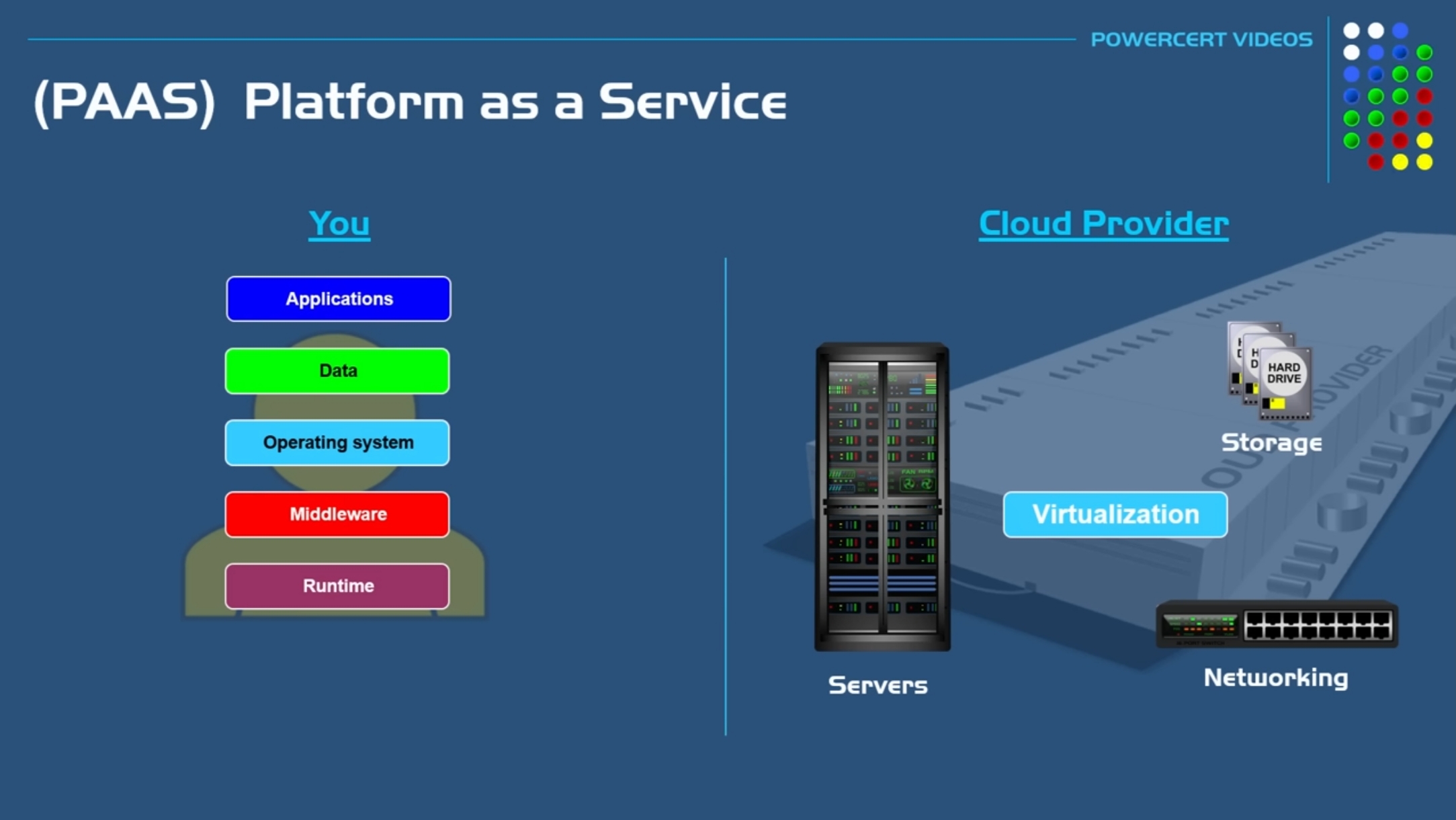
#### 2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Provides tools and frameworks for developers to build applications without managing hardware.
##### Example:
Google App Engine, Heroku.
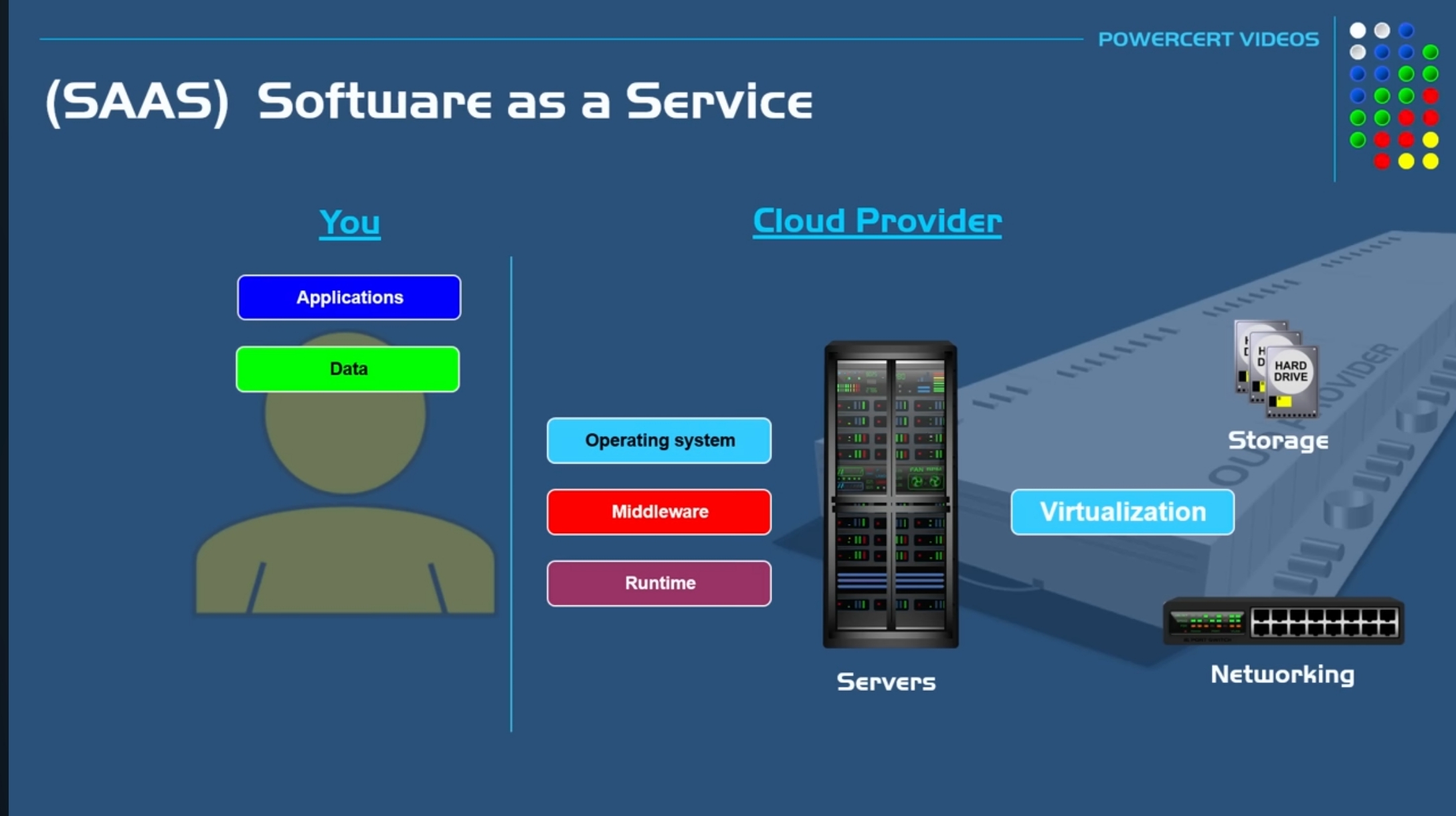
#### 3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
Provides software applications via the cloud, accessible through a browser.
##### Example:
Gmail, Slack, Microsoft 365.
### Deployment Models
#### Public Cloud:
Services offered over the internet and shared among multiple customers (e.g., AWS, Azure).
#### Private Cloud:
Exclusive cloud infrastructure for one organization, offering more control.
#### Hybrid Cloud:
A mix of public and private clouds for flexibility and optimization.
### Advantages of Cloud Computing
**Scalability**: Adjust resources on demand.
**Cost-Efficiency**: Pay-as-you-go model saves costs.
**Accessibility**: Access data and applications from anywhere.
**Disaster Recovery**: Built-in redundancy and backups.
**Collaboration**: Multiple users can work on the same system seamlessly.
### Common Use Cases
1.Hosting websites and applications.
2.Storing and analyzing big data.
3.Machine learning model deployment.
4.Online collaboration tools.
5.Gaming and media streaming services.
### Popular Cloud Providers
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Microsoft Azure
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
IBM Cloud
Oracle Cloud