# DBT
[TOC]
## dbt structures
- validate on column without idx會很慢(吃DB本身效能)
如果要做整張table的test,需要diff
```
Ex: 對沒有original_url的images跑not_null test花了1222秒
```
### [sources](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/sources)
- 命名和描述load到warehouse的data
- test about source data
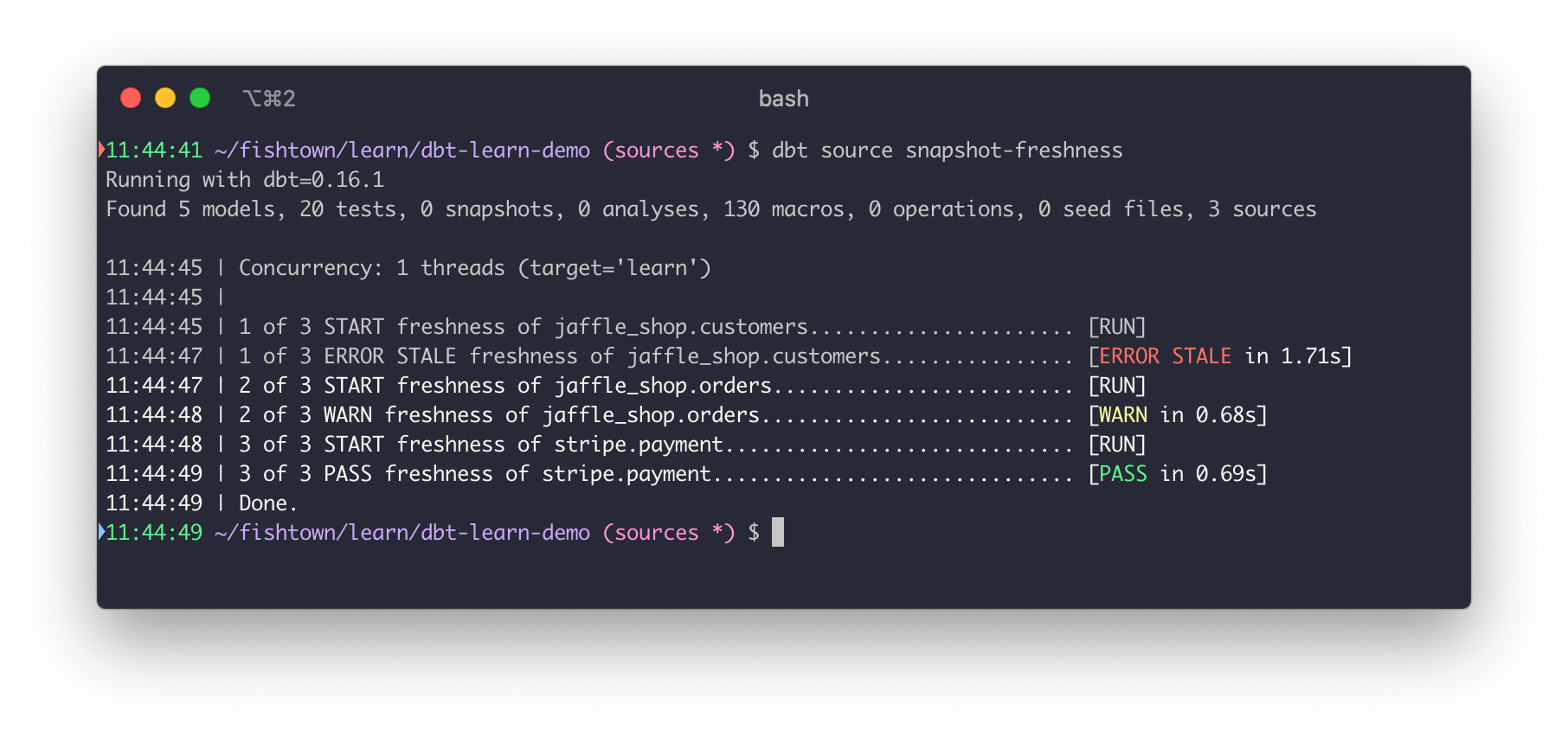
- freshness?
- > if your data pipelines are in a healthy state, and is a critical component of defining SLAs for your warehouse.`
- 看config像是多一個field (`loaded_at_field`) 紀錄timestamp
- [How do I exclude a table from a freshness snapshot?]
- ```sql
-- dbt source freshness
select
max(_etl_loaded_at) as max_loaded_at,
convert_timezone('UTC', current_timestamp()) as snapshotted_at
from raw.jaffle_shop.orders
```
(https://docs.getdbt.com/faqs/project/exclude-table-from-freshness)
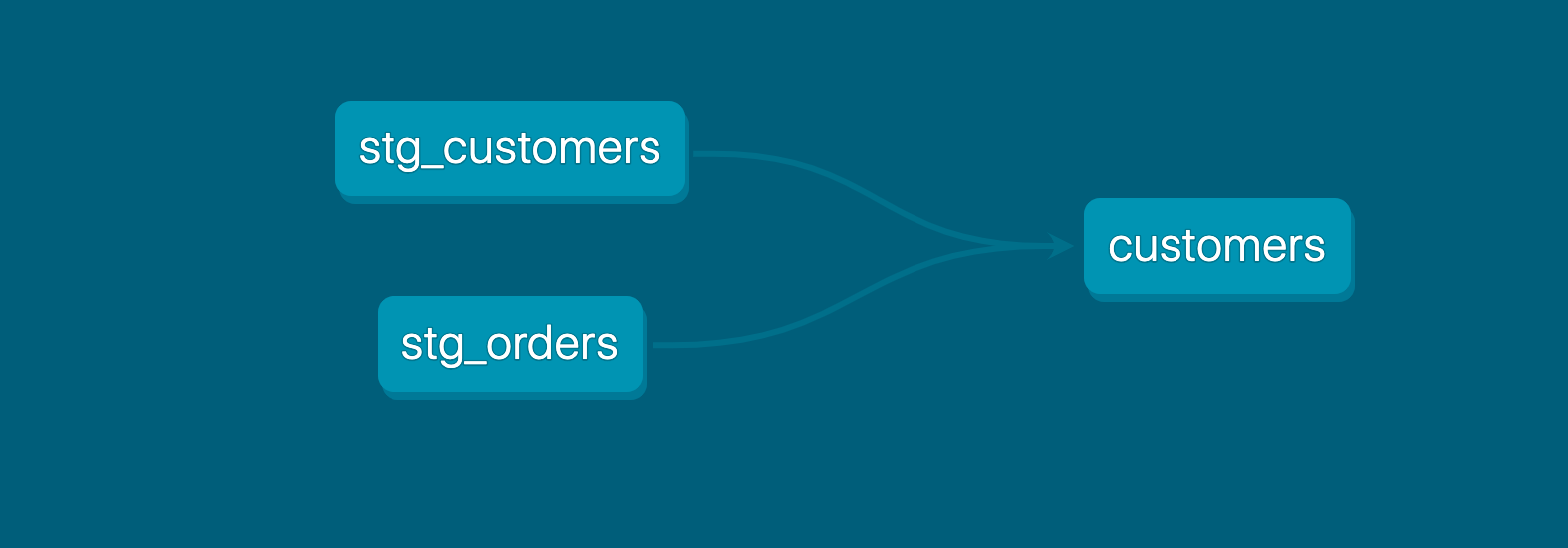
### [models](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/models)
- `select` statement a in `.sql`,一個model一個檔案,檔名即model name
- version 1.3開始有[python model](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/python-models)
- [Materializations](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/materializations)
- table
- view
- incremental
- ephemeral
- dependencies between models
- `{{ ref('dependent_model') }}`
### [seeds](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/seeds)
- CSV files放在seed path底下
- ```sql
-- seeds/country_codes.csv
select * from {{ ref('country_codes') }}
```
> Good use-cases for seeds:
> - A list of mappings of country codes to country names
> - A list of test emails to exclude from analysis
> - A list of employee account IDs
- [seed properties](https://docs.getdbt.com/reference/seed-properties)
### [Snapshots](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/snapshots)
- records changes of table
```
{% snapshot orders_snapshot %}
{{
config(
target_database='analytics',
target_schema='snapshots',
unique_key='id',
strategy='timestamp',
updated_at='updated_at',
)
}}
select * from {{ source('jaffle_shop', 'orders') }}
{% endsnapshot %}
```
- TODO: 確定snapshot觸發時機
### [Metrics](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/metrics)
-
### [Tags](https://docs.getdbt.com/reference/resource-configs/tags)
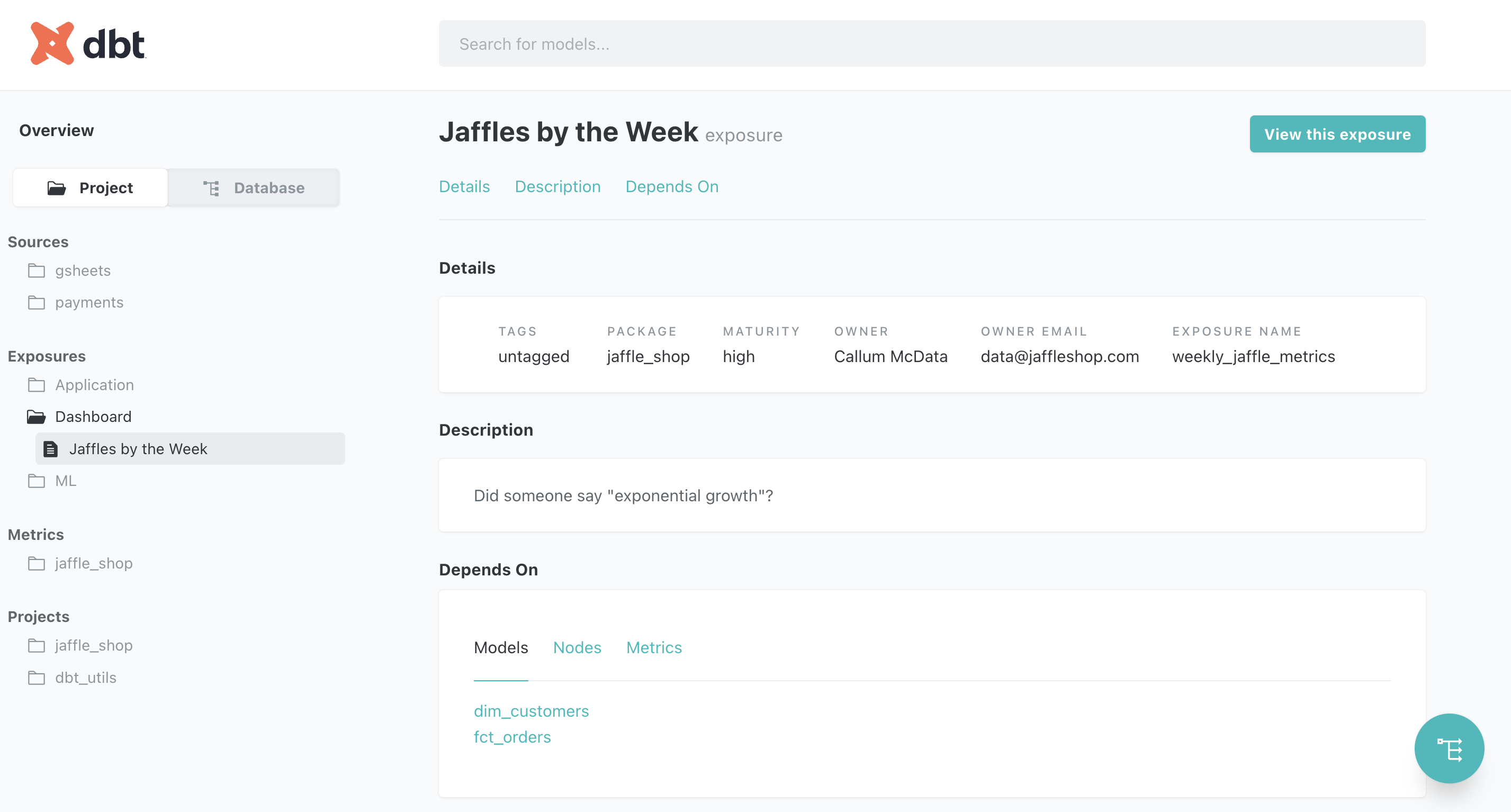
### [Exposures](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/exposures)
- 功能
- 定義給下游的資料
- 可以run, test, list會被餵給下游的resources
- 可以auto-generate documentation site給下游的data consumer
- 範例
```yaml
version: 2
exposures:
- name: weekly_jaffle_metrics
type: dashboard
maturity: high
url: https://bi.tool/dashboards/1
description: >
Did someone say "exponential growth"?
depends_on:
- ref('fct_orders')
- ref('dim_customers')
- source('gsheets', 'goals')
owner:
name: Claire from Data
email: data@jaffleshop.com
```
## Enhance models
### [tests](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/tests)
- singular test
- 放在test path內的sql
- select failure rows
- generic test
- 可以在`.yml`中作為property使用
- parametrized macro
```
{% test not_null(model, column_name) %}
select *
from {{ model }}
where {{ column_name }} is null
{% endtest %}
```
- 內建generic test: `unique`, `not_null`, `accepted_values` and `relationships`
```yml
version: 2
models:
- name: orders
columns:
- name: order_id
tests:
- unique
- not_null
- name: status
tests:
- accepted_values:
values: ['placed', 'shipped', 'completed', 'returned']
- name: customer_id
tests:
- relationships:
to: ref('customers')
field: id
```
- config
- log失敗rows
- 跑command下`--store-failures`
- config `store_failures: true`
- [NOTE] relationship的失敗只有一堆
- [severity](https://docs.getdbt.com/reference/resource-configs/severity)
### [Materializations](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/materializations)
> Materializations are strategies for persisting dbt models in a warehouse. There are four types of materializations built into dbt. They are:
> - table
> - view
> - incremental
> - ephemeral
#### view
- rebulit each run
- always have the latest records
- might be slow to query
- [Best practice] default model, change materialization on condition of performance problems
- [Best practice] models with simple transformation (ex: rename)
#### table
- rebulit each run
- might take a long time to rebuild
- New records are not automatically added to the table
- [Best practice] models needs fast to query
- [Best practice] slow transformations that are used by many downstream models
#### Incremental
- insert or update records into a table since the last time that dbt was run.
- [Best practice] event-style data
#### Ephemeral
- models are not directly built into the database, but still reusable
- keep data warehouse clean by reducing clutter (or use [custom schema](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/custom-schemas))
- cannot select ephemeral models directly
- Operations?
- [Best practice] very light-weight, early transformations with few downstream models and no need to be queried directly
### [Incremental models](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/incremental-models)
- define filter to select new records
```sql
{{
config(
materialized='incremental'
)
}}
select
*,
my_slow_function(my_column)
from raw_app_data.events
{% if is_incremental() %}
-- this filter will only be applied on an incremental run
where event_time > (select max(event_time) from {{ this }})
{% endif %}
```
- set `unique_key` to prevent duplication
```sql
{{
config(
materialized='incremental',
unique_key='date_day'
)
}}
```
- rebuild incremental models and downstream models
```
dbt run --full-refresh --select my_incremental_model+
```
- `on_schema_change`
- (default) `ignore`: ignore removed / added columns
- `fail`: trigger an error message when the source and target schemas diverge
- `append_new_columns`: add new columns without removing missing columns in new schema
- `sync_all_columns`: add new columns and remove missing columns in new schema
- TODO: can test also be incremental?
## Enhance your code
### [Jinja and macros](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/jinja-macros)
- for loop
```jinja
{% set payment_methods = ["bank_transfer", "credit_card", "gift_card"] %}
{% for payment_method in payment_methods %}
...
{% endfor %}
```
- if else
```jinja
{% for payment_method in payment_methods %}
...
{% if not loop.last %},{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
```
- macro
- macro in repo
```jinja
{% macro cents_to_dollars(column_name, precision=2) %}
({{ column_name }} / 100)::numeric(16, {{ precision }})
{% endmacro %}
```
- macro from package
```yaml
# packages.yml
packages:
- package: dbt-labs/metrics
version: [">=1.3.0", "<1.4.0"]
- package: dbt-labs/dbt_utils
version: 1.0.0
```
```sql
select
field_1,
field_2,
field_3,
field_4,
field_5,
count(*)
from my_table
{{ dbt_utils.group_by(5) }}
```
## dbt scheduling
### [Schedule a job](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/get-started/getting-started/building-your-first-project/schedule-a-job) / deploying a project
- periodically rebuild your table to ensure that the data stays up-to-date
- steps
1. Setup `environments`
- Configable `environment` settings
- dbt version
- file repository branch
- TODO: is tag acceptable?
- Deployment Credentials (writeable)
- username
- password
- schema
2. [Optional] Setup `environment variables`
- TODO: survey best practice about environment variables
3. Setup `jobs`
- Configable `job` settings
- `environment` (created previously)
- dbt version (default inherited from selected `environment`)
- [target](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/build/custom-target-names)
- threads
- `environment variables` (created previously)
- Run Timeout (0 is never time out)
- [Defer to a previous run state?](https://docs.getdbt.com/reference/node-selection/defer) (make sure artifacts from other jobs exists)
- Generate docs on run
- Run source freshness
- Commands (list)
- Triggers
- [schedule](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/deploy/job-triggers)
- `* * * * *` (minute, hour, day, month, weekday)
- webhook
- Run on Pull Requests?
- [API](https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/dbt-cloud-apis/overview)
```
POST https://cloud.getdbt.com/api/v2/accounts/{{account_id}}/jobs/{{job_id}}/run/
Headers
{ "Authorization": "Token <your-api-key>" }
Body
{
"cause": "Triggered via API",
}
```
- Accounts on the Team and Enterprise plans can query the dbt Cloud APIs.
1. Access results
- Access data from database (dbt will store data to db)
- Access meta about runs through API (unavailable for free plans)
## Case study
### 確認dbt能否做到validation
- Constraints
- [x] 只有type是mode的attribute才能有parent_id
- [x] source_products連到的attribute type必須為product_name
- 是否先insert再validation? / 是否需要staging table?
- ※建議使用EL工具將各種data source讀取至warehouse後再串dbt
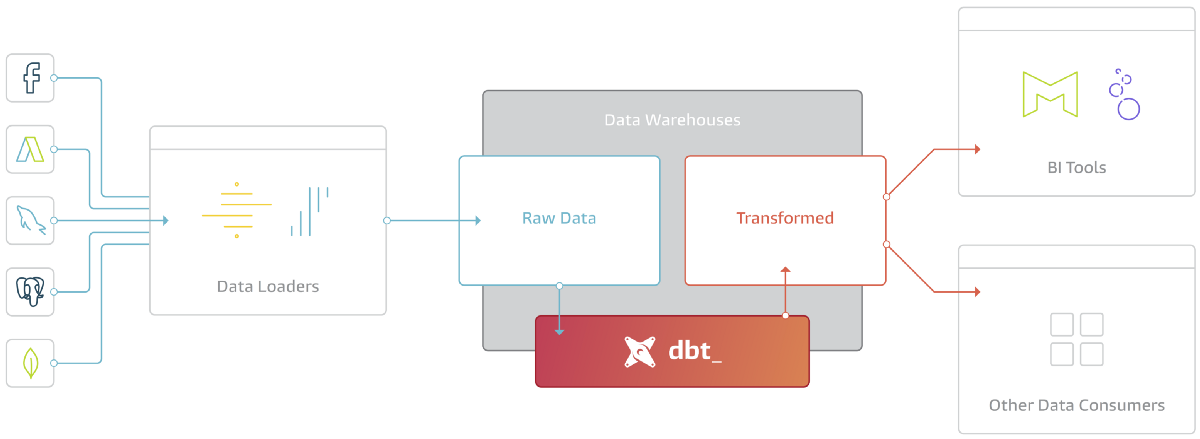
https://www.getdbt.com/blog/what-exactly-is-dbt/
1. raw data insert進warehouse + dbt test (sources)
- 如果失敗,下游的model不會執行transform
1. dbt transform + test (models)
- 如果失敗,model本身會rollback,並且下游的model不會執行transform
- Break constraints時要直接中斷 or warning即可?
- dbt test只能中斷
### 跨source (S3 bucket + DB schema) validation
- 不走API如何同時insert rows & images to bucket
- 後續「row和bucket image是否同時存在」的檢查是否必要or redundent?