---
title: Gen-AI Advanced level
sidebar_label : Gen-AI Advanced level
---
In this article, you will learn about:
- GenAI bot development lifecycle
- OrchLLM and its role in bot development
- Common challenges faced when using Gen AI bots
- How to effectively test Gen AI bots
- Best practices for building a successful Gen AI bot
- Troubleshooting a Gen AI bot for optimal performance
:::note
To request any feature mentioned in this document, please create a ticket or contact the support team.
:::
----------
## GenAI bot development lifecycle
### Guidelines to create an effective GenAI bot
1. **Define target audience and major goals**: Understand the target audience and the bot objectives. Categorize these objectives into static or dynamic flows.
2. **Evaluate each flow and select tools**: Analyze each flow's requirements and choose appropriate tools. Start by testing one major flow with different models to establish an MVP, setting the right expectations early.
3. **Prioritize and manage trade-offs**: For cost-sensitive projects, prioritize critical dynamic flows and be ready to simplify or fallback less important flows to static options or Gen AI.
4. **Leverage GPT-3.5 models for dynamic flows**: Where possible, use GPT-3.5 models for dynamic flows to balance performance and budget.
5. **Play to LLM strengths**: Use large language models for tasks that highlight their strengths. Avoid expecting them to perform tasks where they struggle.
6. **Use Knowledgebase (KB) for Q&A**: If your bot includes question-and-answer capabilities, leverage a Knowledge Base for structured, reliable responses.
7. **Evaluate language constraints early**: Assess language limitations and model capabilities upfront to ensure they align with your bot's requirements.
8. **Customer expectations and education**: Setting the right expectations and educating customers on the capabilities and limitations of LLM-based bots is just as important as the technical aspects.
9. **Focus on iteration and testing**: Building the initial Gen AI flow may be fast, but iterating can be time-consuming. Plan for testing and refinement, and consider launching in phases for complex goals.
10. **Compare models before committing**: Test different model versions against your use case before investing too much time. Expect to make adjustments along the way.

### How to select Gen AI tools
Use the following table to determine the **best Gen AI tool** for your needs:
| **Customer Requirement** | **Suggested Tool/Flow** |
|---------------------------|-------------------------|
| Customer wants to answer from website & documents without hallucination | KB with in-house LLM |
| Customer needs to answer from website & documents with customized persona | KB with GPT |
| Customer has multi-turn conversations and they want flows to be dynamic in handling paths with lower budget | Dynamic flows with GPT-3.5* (comes with tradeoffs) |
| Customer has multi-turn conversations with a lot of API calling, instructions, and wants ability to handle many cases flawlessly | Dynamic flows with GPT-4O, 4, 4 turbo |
| Customer needs specific flows with limited specific input from user’s end | Static flow |
| Customer wants interactive button-based & different visual elements for a specific channel | Pick a static flow(but be clear on limitations) |
| Customer wants interactive button-based visual elements with a mix of handling flexible conversations | Dynamic flows with GPT-4 variants (Currently quick reply rich media available*) OR keep dynamic flows as fallback to static flows |
| Customer needs to search from a structured database (like products) and answer queries | Product search or Database search + entities to autoskip static flows |
| You want to handle one-level prompt with dynamic validations & replies | prompt executor |
| You want to leverage the power of LLM for internal workflows (Non-conversational use case) | LLM integration node / custom API |
| Customer wants better intent identification with low training effort | OrchLLM > NLU |
| Customer wants flexibility in handling fallback based on different cases | OrchLLM for more flexibility or Design flexible static fallback when limited cases |
| Customer wants a specific agent persona and talking style consistently through the bot | OrchLLM persona definition for more flexibility / a mix of custom conversation design vs Gen AI elements (At individual elements, goals can also have persona) |
| Customer wants a multi-lingual bot | Decision based on use case, check KB language list for in-house / For external LLM, check how well LLM works with the language choice |
---------
## Handling Gen AI Knowledgebase
With Gen AI Knowledge Base(KB), you just need to link a website URL or any data source and the bot is automatically creates a customized bot.
> For more information on KB, refer to [this documentation](https://docs.yellow.ai/docs/platform_concepts/studio/kb/overview).
Consider the following points before choosing a Knowledge base(KB) for building Gen AI bots:
| **When to use KB** | **When not to use KB** |
|--------------------|------------------------|
| When knowledge explicitly details out information to form a response | For structured/relational data searches like a database or Excel sheet |
| When you require unstructured data to form a response | For recommending/promotional use cases |
| For dynamic responses from the knowledge base to a user query | When you need very specific keywords used in the answer |
### Data ingestion methods to optimize knowledge base responses
In addition to the quick setup of a [knowledge base](https://docs.yellow.ai/docs/platform_concepts/studio/kb/overview), there are several methods to enhance its performance, improving the tone, complexity, and precision of generated answers:
1. **Web ingestion**: Choose specific subdomains to include or exclude from your domain. You can perform web ingestion using methods such as Sitemap.xml (preferred), in-house crawler, or Bing search engine (add-on).
:::note
- For websites with regularly updated pages, ensure there is a sitemap.xml with mandatory details like [url, lastmod].
- For use cases requiring real-time data (e.g., prices, dates, schedules, event information), avoid web ingestion. Use CMS or custom APIs instead. If the website is managed with a Content Management System (CMS), integrate the KB directly with the CMS.
:::
2. **Add documents**: You can upload documents with a maximum of 25,000 pages per bot (approximately 1,000 files with 25 pages each).
:::note
- OCR support is not available. That is, images and other file or links within the document will not generate any response.
- English and Bahasa languages are benchmarked and supported. Other languages should be tested at scale (200 queries) by pre-sales before committing.
:::
3. **Ingest data from 3rd party sources**:
- Zendesk KB
- Confluence pages
- SharePoint folders
- Amazon S3 buckets
- Salesforce KB
- Google Drive
- ServiceNow KB
4. **Add tags**: Tag knowledge optimally to refine searches based on audience. For example, in an Edtech platform, upload documents tagged for students and parents separately. When a parent queries the bot, it pulls from parent-specific documents, while a student’s query retrieves student-focused content. Use tags like *audience:student* and *audience:parent* to filter responses effectively.
----
## Orch LLM
### What is OrchLLM?
Orchestrator LLM (Large Language Model) is our in-house, fine-tuned conversational AI model designed to enhance chatbot capabilities by orchestrating multiple goals within a single conversation.
OrchLLM acts as the governing system for deciding which tools to use for each user action, ensuring tailored, holistic conversations. It is particularly useful for improving broken or fragmented conversations.
**Benefits of OrchLLM**:
* Enhanced intent identification
* Retains context throughout the conversation window
* Eliminates the need for extensive bot training—just feed simple descriptions
* Enables more human-like, focused small talk

> For more details, refer to [this documentation](https://docs.yellow.ai/docs/platform_concepts/studio/train/orchllm).
### How to use OrchLLM triggers
When adding trigger descriptions, keep the following in mind:
* Your description will be part of a prompt, so ensure it's neither too long nor too short.
* Avoid mentioning example utterances—only include descriptions. Exceptionally, one or two utterances can be added.
* Clearly state when to trigger and when not to trigger.
* You don’t need to include all keywords, but ensure clarity.
* Avoid leaving unused triggers, as this unnecessarily increases prompt length and cost.
**Examples of good and bad triggers**:


### How to test OrchLLM
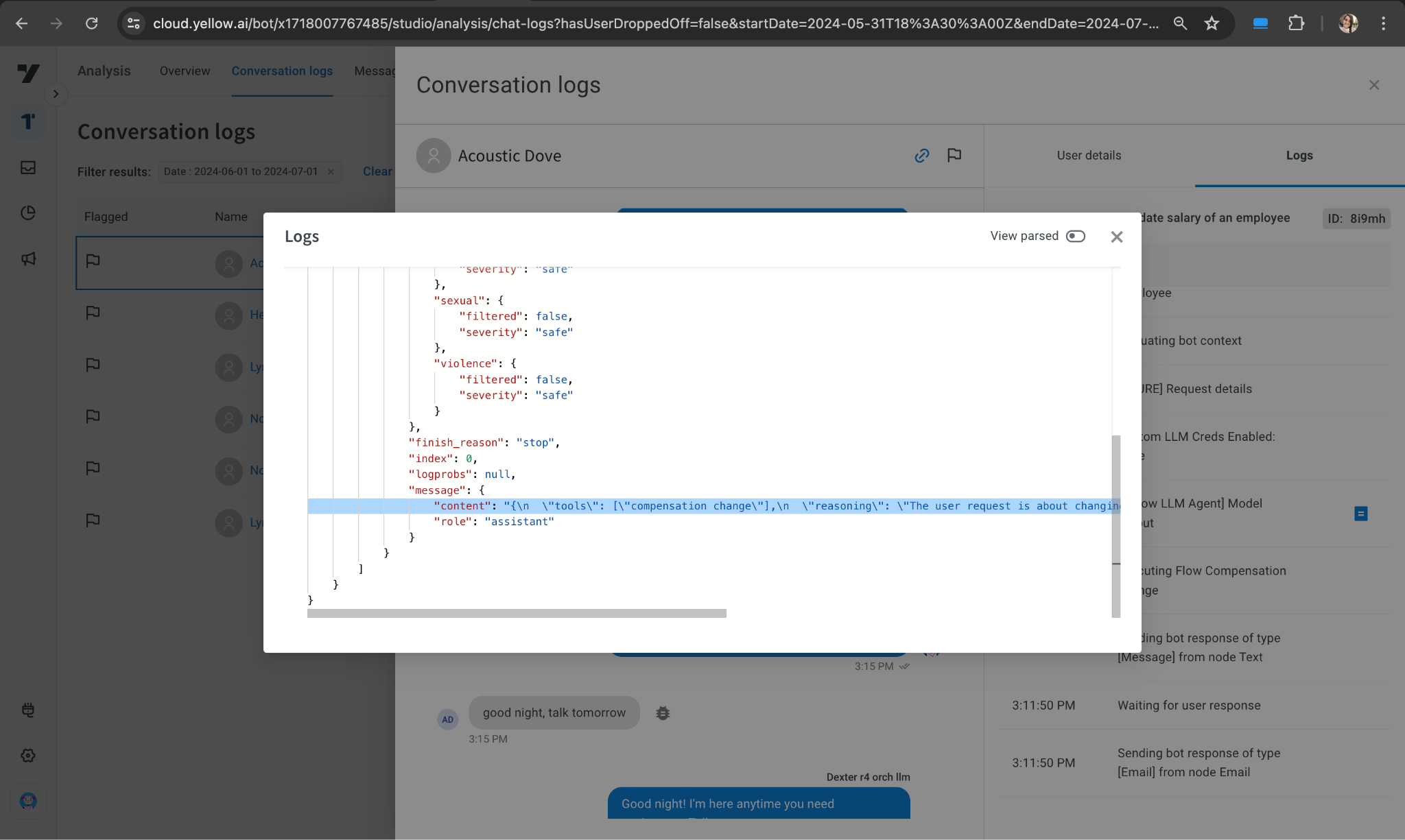
* Review [conversation logs](https://docs.yellow.ai/docs/platform_concepts/analyze/chat-logs) when the bot gives an unexpected response.
* Check the reasoning in the output log (under content) and adjust the description or prompt as needed.
* If hallucinations occur repeatedly, report them.
**Example**: Open the logs and check the tool or reasoning behind the bot's response. If the output is unexpected, review the tool, reasoning, or response (for small talk) and update the trigger descriptions or fine-tune the bot accordingly.
```
"content": "{\n
\"tools\": [\"compensation change\"],\n
\"reasoning\": \"The user request is about changing the compensation of an employee which aligns with the tool 'compensation change'.\",\n
\"response\": \"\"\n}",
```
****
### Things to consider before building an OrchLLM bot
To build tailored conversations, follow these:
* Define your bot’s persona carefully, specifying what it can and cannot do.
* Move FAQs to the knowledge base—avoid adding large numbers of FAQs directly into the OrchLLM prompt.
* OrchLLM works best with 20-30 triggers or flows.
* When migrating intent-based bots to OrchLLM, summarize intents into concise descriptions.
* If you enable OrchLLM in the sandbox environment, remember it will automatically be pushed to higher environments upon publishing.
### Limitations of OrchLLM V1 (GPT-4o/4/3.5)
- Negation of intents won’t work unless explicitly specified in the prompt (e.g., “I don’t want a demo”).
- Contextual questions like "Why do you need my email?" may not be handled and will trigger fallback responses.
- No disambiguation support.
- Conversation history is cleared upon clicking "home" and automatically after 24 hours.
- Incompatible with mother-child Orch bot architecture.
- Currently available only in English.
- **Nodes where OrchLLM doesn’t work**:
- Input to *store comment* node is not considered for switching.
- *QR button* clicks won’t trigger switching if there's an outward connection from the button.
- *Goal nodes* are excluded from switching.
----
## Common challenges of Gen AI bots
Gen AI/LLMs are powerful tools with their own set of advantages and limitations. When not used correctly, they present challenges.
### Challenges with LLMs
- **Citing sources**: LLMs often struggle to cite sources accurately, which can lead to fabricated references.
- **Bias**: LLMs may produce biased responses, reflecting prejudiced or stereotypical views.
- **Hallucinations**: LLMs can confidently generate incorrect or misleading information when they cannot answer a question accurately.
- **Mathematics**: LLMs frequently provide incorrect answers to mathematical questions, as they are primarily trained on text data. However, newer models are improving in logical reasoning.
- **Prompt hacking**: Users can exploit prompt hacking techniques to induce inappropriate or undesirable content from LLMs.
### Dynamic flow challenges
#### Picking the right model by evaluating early
- **GPT-3.5/GPT-3.5 Turbo**: More cost-effective but may exhibit hallucinations, especially with non-specific instructions. They can support 1-2 skills stably, plus a knowledge base skill, but may still show some level of hallucination.
- **GPT-4**: Handles 8-10 skills comfortably and is better for complex cases. Upgrading to newer models when needed can save time and effort.
- **Complex Cases**: GPT-3.5 or older models may struggle with complex scenarios. If issues persist, consider upgrading to a newer model.
- **Dynamic Chat Nodes**: If using GPT-3.5 models, ensure specific points for completion versus continuation. Adding dummy inputs may help manage unexpected exits.
- **Rich Media**: Features like rich media and quick replies are only available for GPT-4. While they can be enabled for lower models, they may not perform as expected.
- **Skill Combination**: Combine skills in a sequence as INPUT → SKILL → OUTPUT. For example, if two APIs need to run sequentially without intermediate data, combine them into a single skill.
:::note
It’s crucial to understand use cases, budgets, and context to select the right model. Higher cost does not always equate to better performance for every use case. GPT-3.5 may not be suitable for complex scenarios with many skills. You can use different models in different nodes within the same bot, but select GPT-3.5 only for very simple use cases or if cost is a significant constraint.
:::
#### Prompt testing and iteration
- **Iterations**: Multiple iterations may be necessary to craft an effective prompt.
- Avoid assuming prompt behavior. Clearly specify what should happen if things deviate from expectations.
- Keep test cases handy for each iteration to ensure thorough testing.
- **Live Performance**: Your prompt might not always perform perfectly in live scenarios.
- Issues may arise if edge cases weren't tested or if there's a mismatch between user expectations and the use case.
- Be prepared to iterate during the initial days of go-live to refine your prompt.
- Gen AI is not infallible but can handle more cases than static flows. Build customer confidence by addressing these issues promptly.
#### Dynamic flows may not be the right tool for your bot/flow
Understand where dynamic flows fit best and select your tools wisely.
> For a detailed understanding of dynamic nodes and their suitability, refer to [this documentation](https://docs.yellow.ai/docs/platform_concepts/studio/dynamicchatnode).
### Knowledgebase challenges
- **JavaScript-rendered Content**: Some web pages use JavaScript to render content, which can be challenging for crawlers like Yellow and Google to access. In these cases, integrating with the source data via CMS or customer APIs is recommended.
- **Selective Indexing**: Only index the necessary web pages from a domain to avoid including irrelevant information. For example, search only specific support pages rather than the entire domain.
- **Crawler Restrictions**: Some domains prevent indexing through services like Cloudflare. Customers need to allowlist Yellow’s IP for data ingestion.
- **No OCR Support**: Images and videos cannot be processed for text extraction.
- **Links in Responses**: Generated responses cannot include clickable links, as LLMs may miss critical characters that break the link.
- **Gated Webpages**: Currently, there is no support for indexing gated webpages. Consider using CMS or API approaches instead.
- **Complex Tables**:
- Tables with merged columns/rows and structured relationships between cell values and headers can be difficult to process.
- Excel-like filters may be needed for effective searching.
- Long entity values (e.g., part numbers) are challenging to search due to their similarity with other parts.
- **Duplicate or Conflicting Knowledge**: Duplicate or conflicting information from the same or different sources can result in cluttered search results.
- **Contextual Relationships**: If a topic’s context is in the title while related paragraphs are placed apart, the system may struggle to establish the connection. We are working on improving this at the parser level to enhance performance.
-------
## Best practices to build a Gen AI bot
You can improve your bot by focusing on **Prompting**, **Designing conversations** and **Model selection**.
### Prompting
- Keep prompts precise and to the point.
- Provide detailed examples to guide the bot (a few short examples are effective).
- Avoid ambiguous or open-ended statements.
- Refrain from repeating the same instructions multiple times.
- Clearly scope the prompt to define its boundaries.
- Include examples of how the output should be formatted.
### Designing conversations
- Focus on one goal per conversation. Use separate goal nodes for multiple goals.
- Limit user inputs to around 5 to avoid confusion.
- Avoid adding too many skills, as this can complicate the goal.
- Provide ample context about the domain and company within the goal.
- Clearly define the bot’s persona.
### Model selection
- Avoid generating facts from the model.
- Set the temperature to a low range (0 - 0.5) for more predictable responses.
- Limit the number of tokens to improve response speed and reduce costs.
- Consider using GPT-4O over GPT-4 for complex use cases due to its lower latency and cost-effectiveness.
--------
## How to effectively test GenAI bots
- **Create Test Cases**: Develop at least 100 test cases to cover various scenarios.
- **Conduct Bulk Testing**: Execute bulk tests for these 100 queries to evaluate overall performance.
- **Evaluate Knowledge Base Performance**: Aim for 80% of queries to be answered correctly if the knowledge base is well-implemented.
- **Manually Test Agent/Conversations**: Perform manual testing for conversational agents to ensure nuanced interactions and accuracy.
----
## GenAI Bots - Troubleshooting
### Accessing platform logs
1. Open **Automation > Build** and **Preview** the bot.
2. Click the debugger icon to open the console logs.
3. Click **Refresh** to view real-time logs.
4. Review all logs. Click the logs icon to read the log files.

### Understanding logs
1. **Verify inputs to the OrchLLM**: Access this log from [OpenAI] Request details.
- Check if the correct user history is passed to the model under messages.
- Verify that model parameters are correct, such as setting a lower temperature for more contained responses.
2. **Verify the response from the model**: Access this log from [Yellow LLM Agent] Model output.
- **Tools**: Identify the model's prediction.
- **Reasoning**: Evaluate why the model chose a particular tool.
- **Response**: Check the final response generated by the model for small talk and general queries.
### Troubleshooting KB issues
Some common KB issues include:
1. A query like “xyz” has information in a file/webpage, but it’s not getting answered.
2. A query like “xyz” was answered previously but is not being answered now, indicating an intermittent error.
3. After publishing, the KB is not working as expected.
4. The sandbox KB response differs from the staging KB response.
For further evaluation, consider the following:
#### Identify if it’s a KB issue
1. **Check Conversation Logs**: Look for the KB Response node.

2. **Verify Query Reach**: Visit **Data Explorer > Knowledge Base report** 30-45 seconds after the query. If the query has reached the KB, you should see a row with the query, search results, and response.
#### Components to check
You must check the input, the search results generated by the KB, and the final response.
**Input**
- Query
- Conversation history (rephrase query)
- Site key (optional, for Bing search websites)
- Tags (optional, for file tags)
- Search confidence (default is 0.5)
- Model type (optional, with InHouse LLM) source
- Knowledge version

**Search**
- Does the answer exist in the KB index?
- Is the relevant paragraph among the top 20 results for that query (check the KB report)?
- Is the paragraph LLM-friendly (e.g., does it contain table data)?
- What is the position of the knowledge?
- Has the knowledge version changed?
- Are there conflicting or similar results?

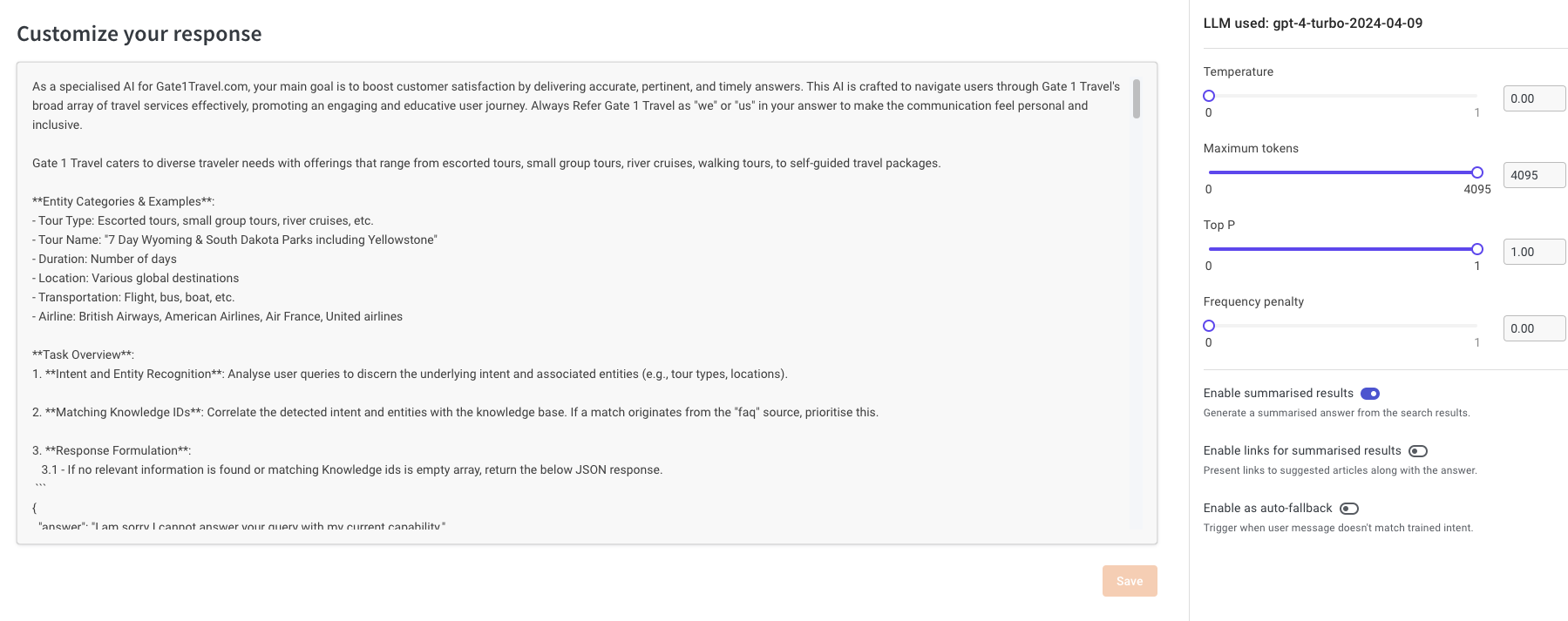
**Response**
- The final output from the response model is shown as the answer.
- Depending on use-cases, you can change the background model and prompt it to follow custom rules. Note: This has implications for cost and hallucination.
- Rules cannot be defined here; it’s a prompt that requires iterations.
> Refer to [this document](https://docs.yellow.ai/docs/platform_concepts/studio/kb/confgure-response) for details.
:::info
**Troubleshooting Reference Docs**
1. [How to use KB report](https://docs.yellow.ai/docs/cookbooks/insights/kbdebugging)
2. [How to write KB prompts](https://docs.yellow.ai/docs/platform_concepts/studio/kb/confgure-response)
3. [What is a sitemap.xml](https://www.semrush.com/blog/website-sitemap/)
:::