# Secure Coding for Web Applications
---
* ### Why is security important?
* ### Common vulnerabilities
* ### NPM packages
---
## Why is security important?
**Service reliability:** software runs *everything*
---
## Why is security important?
**Personal data:** how much of your life is online?
* Usernames, email addresses, passwords
* Real name, home address, phone number
* Private messages, forum posts
* Bank details, medical records
---

---


---

---

---
## What does an attacker want?
* User data (ransom, sell)
* Denial of service (ransom, disrupt)
* Theft (money, sensitive information)
* Control of the machine
* Cyber warfare
---
## Common vulnerabilities in web applications
* SQL injection
* Cross-site scripting
* Cross-site request forgery
* Brute force authentication
* (Distributed) denial-of-service
---
# SQL injection
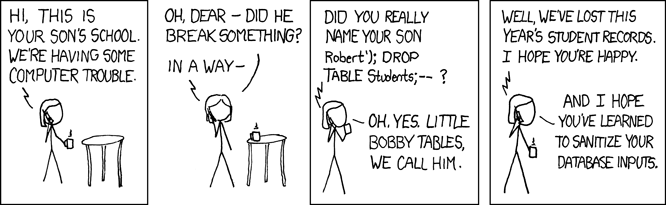
---
Harmless search field? 🤔

---
Get database version 🤨

---
Get usernames and password hashes 😔

---
Read contents of sensitive files 😳

---
Write files to database host ☹️


---
## SQL injection prevention
1. Parameterised queries (prepared statements)
2. Stored procedures
3. Input checked against allowed values
4. Input sanitisation
---
# Cross-site scripting (XSS)
A malicious script is injected into a trusted website
1. Stored XSS attacks
2. Reflected XSS attacks
3. DOM-based XSS attacks
---
## Stored XSS attacks
The malicious script has been stored on the server
Example: *The script is in a product database. A user searches for products and the database query unknowingly returns the malicious script.*
```
<script>alert(document.cookie)</script>
```
---
## Reflected XSS attacks
The malicious script is reflected off the web server
Example: *A user clicks on a URL that contains the malicious script as a search query. The server sends back a page with search results and helpfully displays the original query too.*
```
www.site.com?q=<script>alert(document.cookie)</script>
```
---
## DOM-based XSS attacks
The malicious script is placed in the DOM without the help of the server
Example: *A web page takes options from the URL to construct HTML on the client.*
```
www.site.com?default=<script>alert(document.cookie)</script>
```
---

---
## XSS dangers
* Expose user session cookies
* Modify page content
* Redirect user to malicious website
---
## XSS prevention
`HttpOnly` flag on cookie prevents a client-side script accessing the cookie
---
## XSS prevention
Never insert untrusted data into:
1. Scripts: `<script> NO </script>`
2. Comments: `<!-- DON'T YOU DARE -->`
3. Attributes: `<div absolutelyNot=test />`
4. Tag names: `<NOPE />`
5. Style tags: `<style> HELL NO </style>`
---
## XSS prevention

---
## XSS prevention
React does this automatically through JSX, but be very careful if using...
<iframe src="https://giphy.com/embed/26gR2ktYgH24dGX8A" width="480" height="202" frameBorder="0" class="giphy-embed" allowFullScreen></iframe>
**...`dangerouslySetInnerHTML`**
---
# Cross-site request forgery (CSRF)
Executes actions on a user's behalf on a site they are currently authenticated with, in order to:
* Change the account's email address or password
* Transfer funds
* Make a purchase
---
## CSRF attack
1. User is logged in to facebook.com
2. Attacker tricks user into visiting a malicious site
3. The malicious site sends a request to facebook.com from the user's browser
4. The request from the browser will include the user's session cookies
---
## CSRF prevention
* CSRF tokens
* `SameSite` flag on cookies
* Additional authentication for sensitive actions
---
# Brute force authentication
Trying thousands of passwords for a user account
---
## Brute force authentication dangers
* lists of common passwords
* programs to create lists around a word / theme
* tools to scrape key words from social media, GitHub repos
---
## Brute force authentication prevention
* Account lockout after *X* failed attempts
* Password complexity requirements
* Two-factor authentication
---
# Denial-of-service (DoS)
A server is hit with so many requests it can't respond to them all quickly enough
Distributed means the requests come from a large number of computers, e.g. a botnet
---
# NPM packages

---
## Package security considerations
* Is it kept up-to-date?
* Is there a team working on it?
* Number of weekly downloads?
* Known security flaws?
---
## In summary
<iframe src="https://giphy.com/embed/1b9p0KmGHHih2" width="480" height="258" frameBorder="0" class="giphy-embed" allowFullScreen></iframe>
---
# References
* [WannaCry laid bare the NHS' outdated IT network](https://www.wired.co.uk/article/nhs-cyberattack-it-ransomware)
* [The Malware That Took Down a Power Grid](https://www.wired.com/story/crash-override-malware/)
* [Hackers Gain Direct Access to US Power Grid Controls](https://www.wired.com/story/hackers-gain-switch-flipping-access-to-us-power-systems/)
* [A New Pacemaker Hack Puts Malware Directly on the Device](https://www.wired.com/story/pacemaker-hack-malware-black-hat/)
* [How France's TV5 was almost destroyed by 'Russian hackers'](https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/technology-37590375)
* [How Hackers Slipped by British Airways' Defenses](https://www.wired.com/story/british-airways-hack-details/)
* [Attackers Spill User Data From Cheating Site Ashley Madison](https://www.wired.com/2015/07/hack-brief-attackers-spill-user-data-cheating-site-ashley-madison/)
* [Dating Apps Exposed 845 GB of Explicit Photos, Chats, and More](https://www.wired.com/story/dating-apps-leak-explicit-photos-screenshots/)
* [They Told Their Therapists Everything. Hackers Leaked It All](https://www.wired.com/story/vastaamo-psychotherapy-patients-hack-data-breach/)
* [Hack the Box](https://www.hackthebox.eu/)
{"metaMigratedAt":"2023-06-16T01:16:25.366Z","metaMigratedFrom":"Content","title":"Secure Coding for Web Applications","breaks":true,"contributors":"[{\"id\":\"2b2c8ce5-f4ec-4554-a94c-0397b466cd77\",\"add\":10597,\"del\":4229}]"}