## 状态与副作用
### Fiber 數據結構(中與hook 渲染)相關屬性
- 考虑一个具体的fiber节点如何影响最终的渲染.
- 使用 Hook :控制Fiber屬性
- 二类属性十分关键in fiber object on renders:
```javascript
// packages>react-reconciler>src>ReactInternalTypes
export type Fiber = {
// 1. fiber节点自身状态相关 (state)
// 作用只局限于fiber树构造阶段, 直接影响子节点的生成
pendingProps: any,// passed from ReactElement
memoizedProps: any,// Last render (kept in 內存)
updateQueue: mixed,// 存储update更新对象的队列, 每一次发起更新, 都需要在该队列上创建一个update对象.
memoizedState: any, // 上一次生成子节点之后保持在内存中的局部状态.
// 2. fiber节点副作用(Effect)相关
flags: Flags, // 标志位, 表明该fiber节点有副作用
subtreeFlags: Flags, // v17.0.2未启用
deletions: Array<Fiber> | null, // v17.0.2未启用
nextEffect: Fiber | null,
firstEffect: Fiber | null,
lastEffect: Fiber | null,
};
```
- 状态是一个静态的功能, 它只能为子节点提供数据源,作用于fiber树构造阶段
- 副作用是一个动态功能, 由于它的调用时机是在fiber树渲染阶段, 能获取突变前快照, 突变后的DOM节点等. 甚至通过调用api发起新的一轮fiber树构造, 引发更多的副作用
### 外部 api (外部操作修改到fiber object的方式)
- Class component
```javascript
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
this.state = {a: 1,};// 初始状态
}
changeState = () => {
this.setState({ a: ++this.state.a }); // 进入reconciler流程
};
// 生命周期函数: 状态相关
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState) {...}
shouldComponentUpdate(newProps, newState, nextContext) {...}
// 生命周期函数: 副作用相关 fiber.flags |= ...
componentDidMount() {...} // Update
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState){...}// Snapshot
componentDidUpdate() {...} // Update
// 返回下级ReactElement对象
render() {
return <button onClick={this.changeState}>{this.state.a}</button>;
}
}
```
> class组件会实例化一个instance所以拥有独立的局部状态
- Function component
```javascript
function App() {
// 状态相关: 初始状态
const [a, setA] = useState(1);
// 副作用相关: fiber.flags
useEffect(() => {...}, []); // Passive
useLayoutEffect(() => {...}, []); // Update
// 返回下级ReactElement对象
return <button onClick={changeState}>{a}</button>;
}
```
> function组件不会实例化, 它只是被直接调用, 无法维护一份独立的局部状态;
只能依靠Hook对象间接实现局部状态
[Built-in React Hooks](https://react.dev/reference/react/hooks)
## Hook
### 概览
- Use state and other React features without writing a class.
- Hooks provide a more direct API to the React concepts you already know: props, state, context, refs, and lifecycle.
- Hooks also offer a new powerful way to combine them.
- Solve problems in React (class components)
- Reuse stateful logic between components (easier)
- Complex components become hard to understand
- Classes confuse machines
- hot reloading flaky and unreliable
- encourage unitential patterns
- don't minify very well
> **Hooks are a new addition in React 16.8. at React Conf 2018**
> [Introducing Hooks](https://legacy.reactjs.org/docs/hooks-intro.html) from old React official website
> [Making Sense of React Hooks](https://medium.com/@dan_abramov/making-sense-of-react-hooks-fdbde8803889) Dan Abramov
> [Why Do React Hooks Rely on Call Order?](https://overreacted.io/why-do-hooks-rely-on-call-order/) overreacted
### State Hook / Effect Hook
舊版官网上分为了 2 个类别, 状态Hook(State Hook), 和副作用Hook(Effect Hook).
- State Hook
- 廣義:能实现数据持久化且没有副作用的
Hook,useState, useReducer --> useContext, useRef, useCallback, useMemo
- 得益于`**双缓冲技术(double buffering)**`, 在多次render时, 以fiber为载体, 保证复用同一个Hook对象, 进而实现数据持久化.
- Effect Hook
- 修改`fiber.flags`
- 在performUnitOfWork->completeWork阶段, 所有存在副作用的fiber节点, 都会被添加到父节点的副作用队列后, 最后在commitRoot阶段处理这些副作用节点
- 副作用回調
- Fiber角度
```javascript
export type Fiber = {
// 1. fiber节点自身状态相关 (state)
pendingProps: any,// props
memoizedProps: any,// Last render (內存)
updateQueue: mixed,// queue of state updates and callbacks
memoizedState: any, // state used to create the output
// 2. fiber节点副作用(Effect)相关
flags: Flags, // 标志位, 表明该fiber节点有副作用
subtreeFlags: Flags, // v17.0.2未启用
deletions: Array<Fiber> | null, // v17.0.2未启用
nextEffect: Fiber | null,
firstEffect: Fiber | null,
lastEffect: Fiber | null,
};
```
### Hook 數據結構
- packages/react-reconciler/ReactFiberHooks.js
```javascript
export type Update<S, A> = {
lane: Lane,
revertLane: Lane,
action: A,
hasEagerState: boolean,
eagerState: S | null,
next: Update<S, A>,
};
export type UpdateQueue<S, A> = {
pending: Update<S, A> | null,
lanes: Lanes,
dispatch: (A => mixed) | null,
lastRenderedReducer: ((S, A) => S) | null,
lastRenderedState: S | null,
};
export type Hook = {
memoizedState: any, // current 保持在内存中的局部状态
baseState: any, // baseQueue中所有update对象合并之后的状态
baseQueue: Update<any, any> | null, // 存储update对象的环形链表, 只包括高于本次渲染优先级的update对象
queue: any,// 存储update对象的环形链表, 包括所有优先级的update对象
next: Hook | null, // next指针, 指向链表中的下一个hook
};
```
- Hook是一个链表, 单个Hook拥有自己的状态hook.memoizedState和自己的更新队列hook.queue
### 調用處理函數
hook創建相關位置:react-reconciler 包裡的 [ReactFiberHooks.js](https://github.com/facebook/react/blob/v17.0.2/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.old.js)
調用時間:執行任務回調裡的 beginWork => updateFunctionComponent => renderWithHooks
- state: 樹構造; effect: 樹渲染

#### 1. ReactFiberHooks.js 檔案構造:調用前於頭部設置全局變量:
source code: [ReactFiberHooks.js](https://github.com/facebook/react/blob/v17.0.2/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.old.js#L157C1-L194C49)
```javascript!
let renderLanes: Lanes = NoLanes;// 渲染优先级
// 当前正在构造的fiber, 等同于 workInProgress, 为了和当前hook区分, 所以将其改名
let currentlyRenderingFiber: Fiber = (null: any);
// Hooks被存储在fiber.memoizedState 链表上
let currentHook: Hook | null = null; // currentHook = fiber(current).memoizedState
let workInProgressHook: Hook | null = null; // workInProgressHook = fiber(workInProgress).memoizedState
// 在function的执行过程中, 是否再次发起了更新. 只有function被完全执行之后才会重置.
// 当render异常时, 通过该变量可以决定是否清除render过程中的更新.
let didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate: boolean = false;
// 在本次function的执行过程中, 是否再次发起了更新. 每一次调用function都会被重置
let didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass: boolean = false;
const RE_RENDER_LIMIT = 25;
```
#### 2. renderWithHooks(); 調用hook相關函數 fiber->hook --- **[MOUNT]**
**如果使用了Hook api(如: useEffect, useState), 就会创建一个与之对应的Hook对象**
```javascript!
// ...省略无关代码
export function renderWithHooks<Props, SecondArg>(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: (p: Props, arg: SecondArg) => any,
props: Props,
secondArg: SecondArg,
nextRenderLanes: Lanes,
): any {
// --------------- 1. 设置全局变量 -------------------
renderLanes = nextRenderLanes; // 当前渲染优先级
currentlyRenderingFiber = workInProgress; // 当前fiber节点, 也就是function组件对应的fiber节点
// 清除当前fiber的遗留状态
workInProgress.memoizedState = null;
workInProgress.updateQueue = null;
workInProgress.lanes = NoLanes;
// --------------- 2. 调用function,生成子级ReactElement对象 -------------------
// 指定dispatcher, 区分mount和update
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
current === null || current.memoizedState === null
? HooksDispatcherOnMount
: HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
// 执行function函数, 其中进行分析Hooks的使用
let children = Component(props, secondArg);
// --------------- 3. 重置全局变量,并返回 -------------------
// 执行function之后, 还原被修改的全局变量, 不影响下一次调用
renderLanes = NoLanes;
currentlyRenderingFiber = (null: any);
currentHook = null;
workInProgressHook = null;
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = false;
return children;
}
```
### 创建 Hook
- 初次渲染 mount
- mountState(); mountEffect()->mountEffectImpl()
- 內存結構
- 前
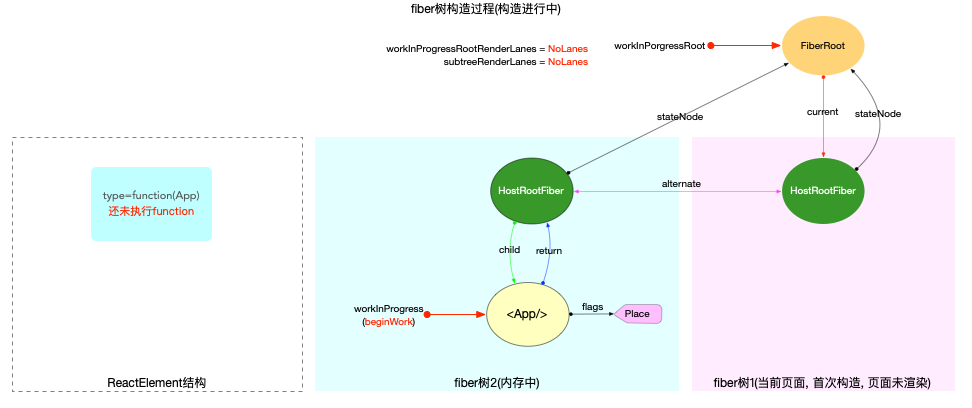
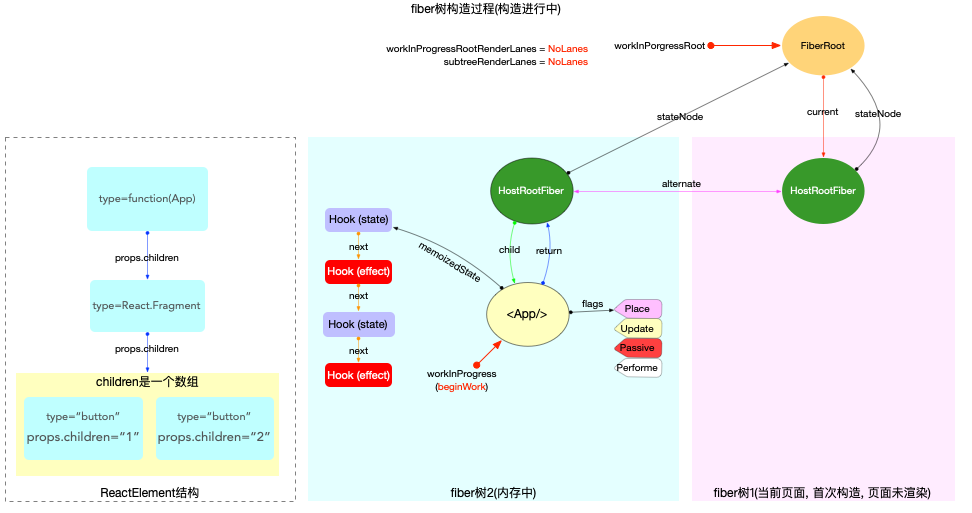
- 後: **创建Hook并挂载到fiber.memoizedState上, 多个Hook以链表结构保存**
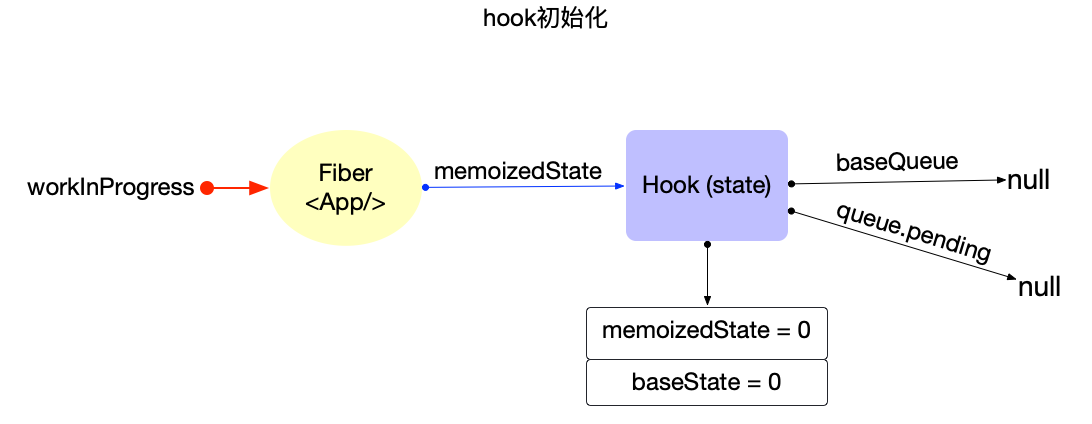
- hook 初始化 (useState()-> **`mountState`** / useEffect()->**`mountEffectImpl`**)
- 在mountState內設置:
- hook.memoizedState
- hook.baseState
- hook.queue
- 回傳: hook.memoizedState, dispatch
> 状态Hook或副作用Hook都按照调用顺序存储在fiber.memoizedState链表中.
- 對比更新 update
- 点击button, 通过dispatch函数进行更新, dispatch实际就是 [dispatchAction](https://github.com/facebook/react/blob/v18.2.0/packages/react-server/src/ReactFizzHooks.js) :
```javascript
function dispatchAction<S, A>(
fiber: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>,
action: A,
) {
// 1. 创建update对象
const eventTime = requestEventTime();
const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber); // Legacy模式返回SyncLane
const update: Update<S, A> = {
lane,
action,
eagerReducer: null,
eagerState: null,
next: (null: any),
};
// 2. 将update对象添加到hook.queue.pending队列
const pending = queue.pending;
if (pending === null) {
// 首个update, 创建一个环形链表
update.next = update;
} else {
update.next = pending.next;
pending.next = update;
}
queue.pending = update;
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
if (
fiber === currentlyRenderingFiber ||
(alternate !== null && alternate === currentlyRenderingFiber)
) {
// 渲染时更新, 做好全局标记
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass =
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = true;
} else {
// ...省略性能优化部分, 下文介绍
// 3. 发起调度更新, 进入`reconciler 运作流程`中的输入阶段.
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);
}
}
```
- mountEffect()->mountEffectImpl()
- 內存結構
- 前
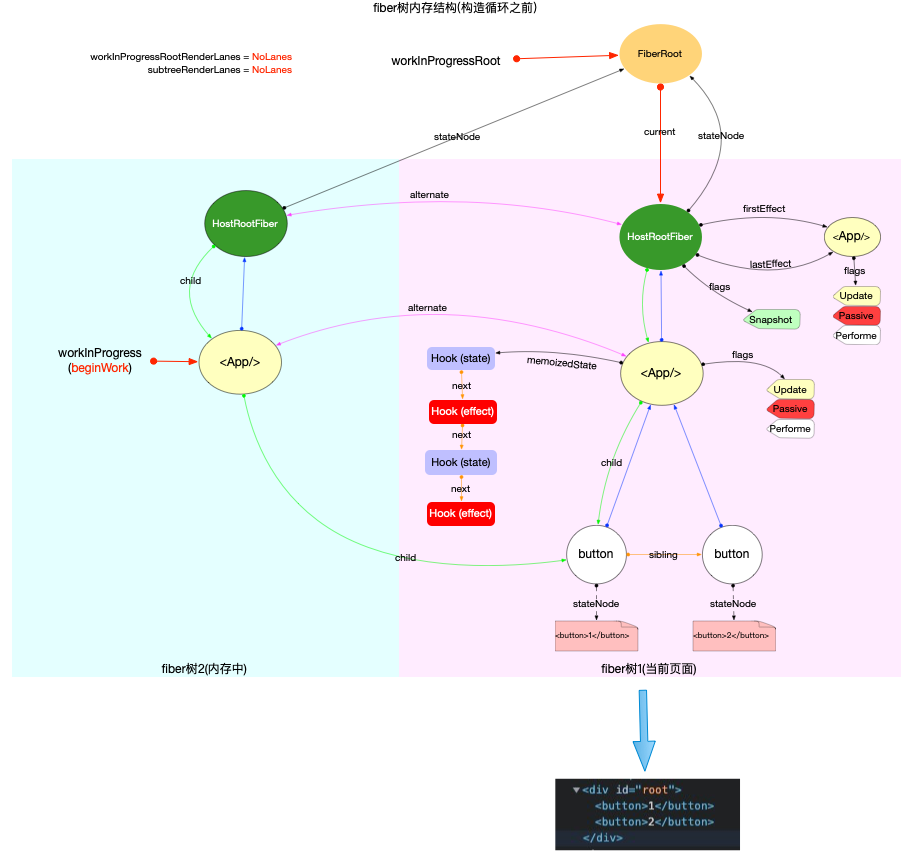
- 後: **创建Hook并挂载到fiber.memoizedState上, 多个Hook以链表结构保存**
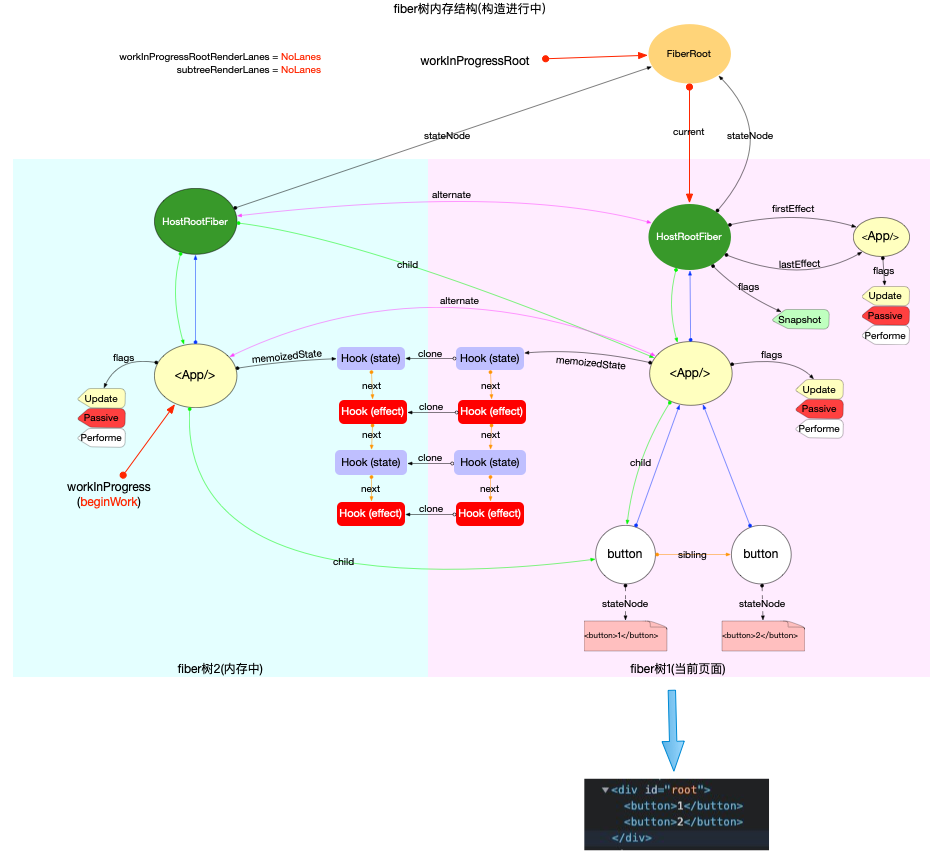
> Referance:
> [Why Do React Hooks Rely on Call Order?](https://overreacted.io/why-do-hooks-rely-on-call-order/) by Dan Abramov
> - Hooks are like functional mixins that let you create and compose your own abstractions.
> - Hooks is that they rely on persistent call index between re-renders.
> -
## useState
### 狀態初始化
在fiber初次构造阶段:
- useState对应源码mountState ; useReducer对应源码mountReducer
- 創建 hook ()
- return [當前状态, dispatch函数]
```javascript!
function mountState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
// 1. 创建hook
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
if (typeof initialState === 'function') {
initialState = initialState();
}
// 2. 初始化hook的属性
// 2.1 设置 hook.memoizedState/hook.baseState
// 2.2 设置 hook.queue
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
const queue = (hook.queue = {
pending: null,
dispatch: null,
// queue.lastRenderedReducer是内置函数
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer,
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any),
});
// 2.3 设置 hook.dispatch
const dispatch: Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>> = (queue.dispatch =
(dispatchAction.bind(null, currentlyRenderingFiber, queue): any));
// 3. 返回[当前状态, dispatch函数]
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
```

### 狀態更新
#### dispatchAction
点击button, 通过dispatch函数进行更新, dispatch实际就是dispatchAction:
- 创建update对象, 其中update.lane代表优先级
- 将update对象添加到hook.queue.pending环形链表
- 发起调度更新: 调用scheduleUpdateOnFiber, 进入reconciler 运作流程中的输入阶段
(進入react-reconciler包 再次調用 ReactFiberHooks.js內提供的 updateState/updateReducer)
```javascript!
function dispatchAction<S, A>(
fiber: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>,
action: A,
) {
// 1. 创建update对象
const eventTime = requestEventTime();
const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber); // Legacy模式返回SyncLane
const update: Update<S, A> = {
lane,
action,
eagerReducer: null,
eagerState: null,
next: (null: any),
};
// 2. 将update对象添加到hook.queue.pending队列
const pending = queue.pending;
if (pending === null) {
// 首个update, 创建一个环形链表
update.next = update;
} else {
update.next = pending.next;
pending.next = update;
}
queue.pending = update;
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
if (
fiber === currentlyRenderingFiber ||
(alternate !== null && alternate === currentlyRenderingFiber)
) {
// 渲染时更新, 做好全局标记
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass =
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = true;
} else {
// ...省略性能优化部分, 下文介绍
// 3. 发起调度更新, 进入`reconciler 运作流程`中的输入阶段.
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);
}
}
```
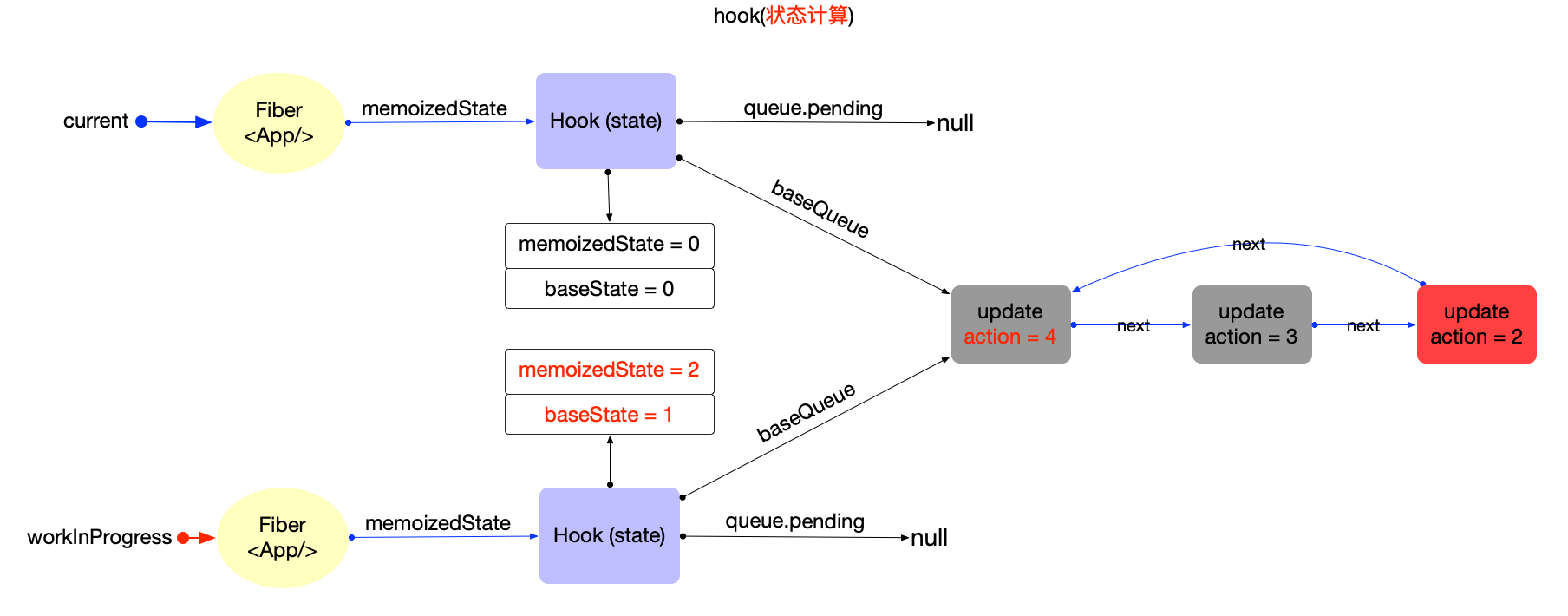
#### updateReducer
- 调用updateWorkInProgressHook获取workInProgressHook对象
- 链表拼接: 将 hook.queue.pending 拼接到 current.baseQueue
- 狀態計算
```javascript
function updateReducer<S, I, A>(
reducer: (S, A) => S,
initialArg: I,
init?: (I) => S,
): [S, Dispatch<A>] {
// 1. 获取workInProgressHook对象
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
// 2. 链表拼接: 将 hook.queue.pending 拼接到 current.baseQueue
const pendingQueue = queue.pending;
// 3. 状态计算
if (baseQueue !== null) {
const first = baseQueue.next;
let newState = current.baseState;
let newBaseState = null;
let newBaseQueueFirst = null;
let newBaseQueueLast = null;
let update = first;
do {
const updateLane = update.lane;
// 3.1 优先级提取update
if (!isSubsetOfLanes(renderLanes, updateLane)) {
// 优先级不够: 加入到baseQueue中, 等待下一次render
const clone: Update<S, A> = {
lane: updateLane,
action: update.action,
eagerReducer: update.eagerReducer,
eagerState: update.eagerState,
next: (null: any),
};
if (newBaseQueueLast === null) {
newBaseQueueFirst = newBaseQueueLast = clone;
newBaseState = newState;
} else {
newBaseQueueLast = newBaseQueueLast.next = clone;
}
currentlyRenderingFiber.lanes = mergeLanes(
currentlyRenderingFiber.lanes,
updateLane,
);
markSkippedUpdateLanes(updateLane);
} else {
// 优先级足够: 状态合并
if (newBaseQueueLast !== null) {
// 更新baseQueue
const clone: Update<S, A> = {
lane: NoLane,
action: update.action,
eagerReducer: update.eagerReducer,
eagerState: update.eagerState,
next: (null: any),
};
newBaseQueueLast = newBaseQueueLast.next = clone;
}
if (update.eagerReducer === reducer) {
// 性能优化: 如果存在 update.eagerReducer, 直接使用update.eagerState.避免重复调用reducer
newState = ((update.eagerState: any): S);
} else {
const action = update.action;
// 调用reducer获取最新状态
newState = reducer(newState, action);
}
}
update = update.next;
} while (update !== null && update !== first);
// 3.2. 更新属性
if (newBaseQueueLast === null) {
newBaseState = newState;
} else {
newBaseQueueLast.next = (newBaseQueueFirst: any);
}
if (!is(newState, hook.memoizedState)) {
markWorkInProgressReceivedUpdate();
}
// 把计算之后的结果更新到workInProgressHook上
hook.memoizedState = newState;
hook.baseState = newBaseState;
hook.baseQueue = newBaseQueueLast;
queue.lastRenderedState = newState;
}
```
- 拼接前後 updateReducer() before & after
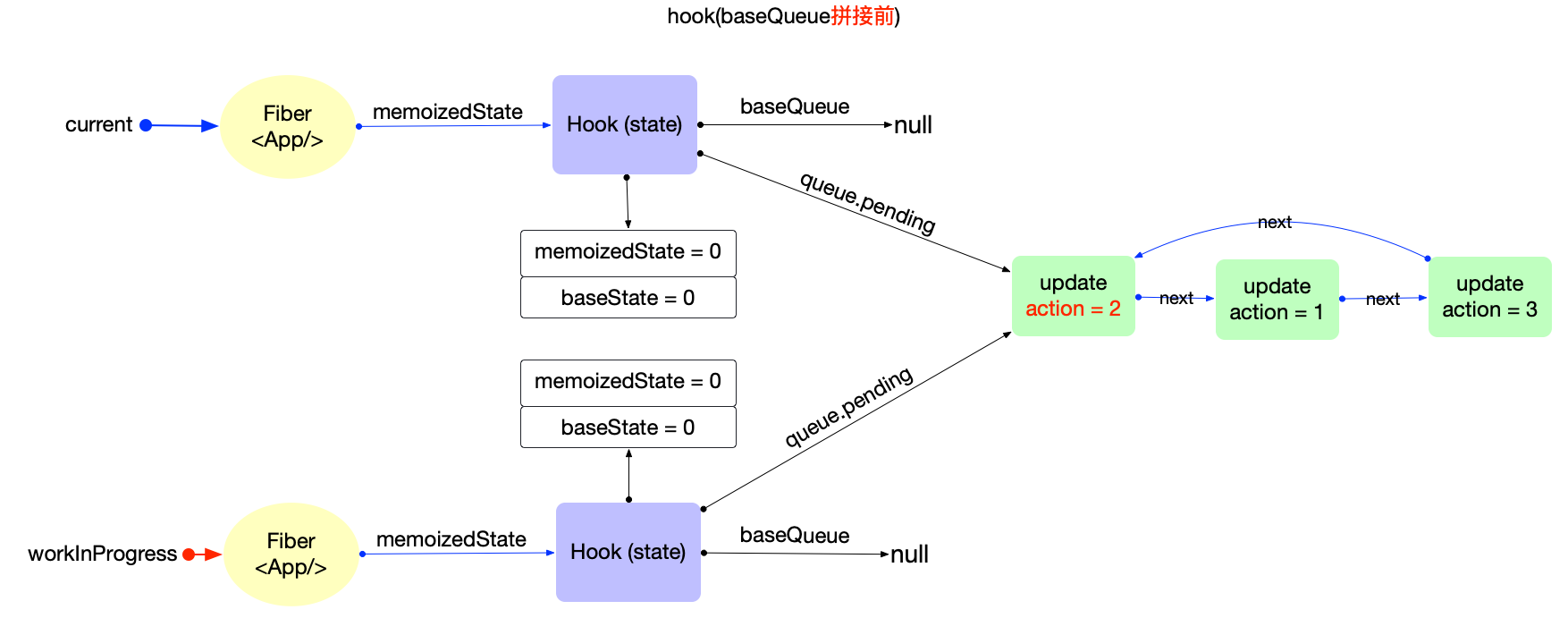
--
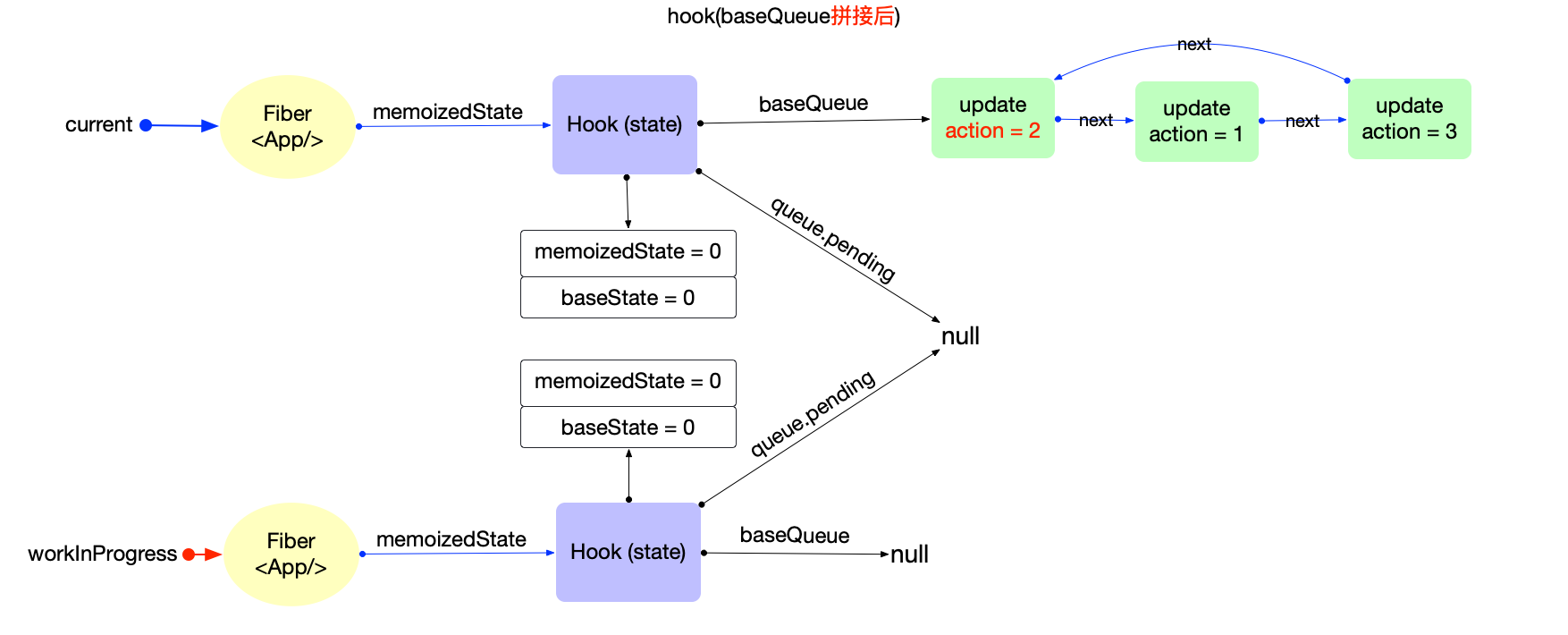
- 状态计算
優先級不夠;加入baseQueue等待下一次render
優先級足夠:狀態合併
[原文](https://7km.top/main/hook-state#%E7%8A%B6%E6%80%81%E6%9B%B4%E6%96%B0)
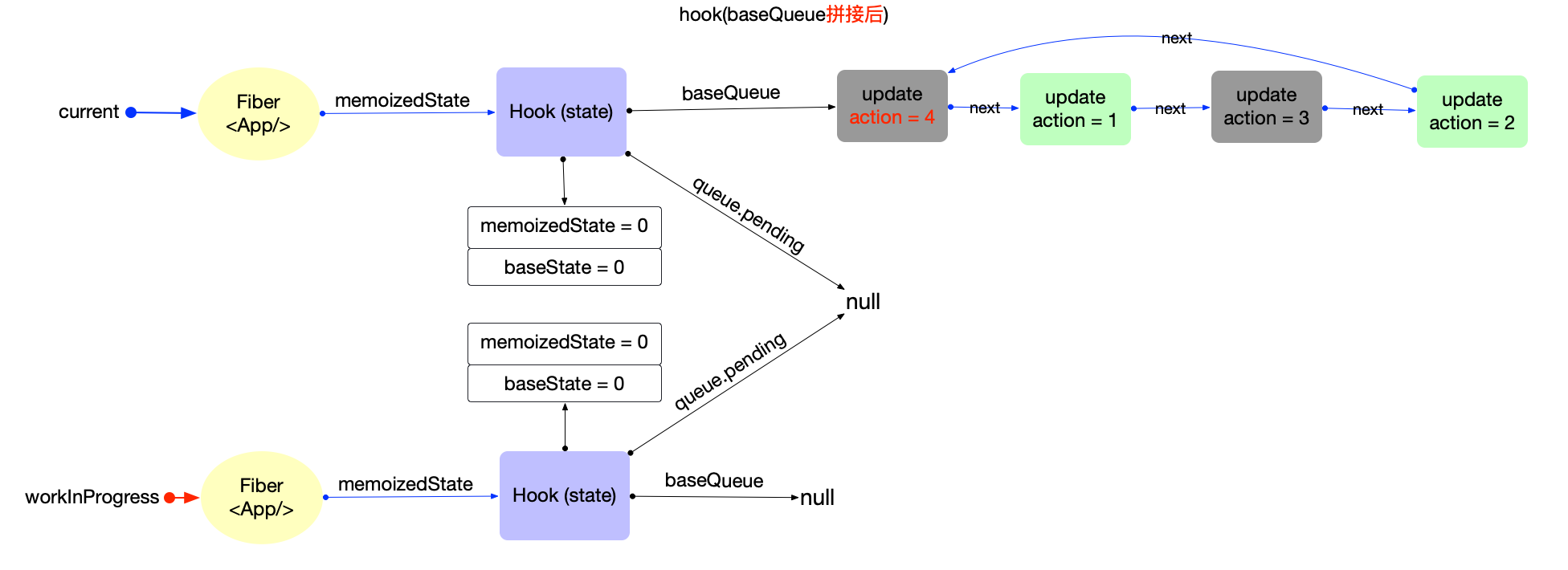
> Referance:
> [How does useState know what to do](https://overreacted.io/how-does-setstate-know-what-to-do/) by Dan Abramov
> [How do useState work](https://jser.dev/2023-06-19-how-does-usestate-work/)
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet