---
title: 案例教學 - 使用 MLflow 追蹤 NVIDIA FLARE 實驗
description: OneAI 文件
---
[OneAI 文件](/s/xKNcU3O5D)
# 案例教學 - (NVIDIA FLARE with MLflow)
## 說明
**AI Maker(搶鮮版)** 整合的 **MLflow** 服務結合 **OneAI** 的權限管理、專案管理及資源控管等功能,使用 **AI Maker(搶鮮版)、筆記本服務、容器服務** 所建立與機器學習相關的作業,都可透過 **MLflow 追蹤** 記錄及比較模型訓練過程的參數、指標和結果,並透過 **MLflow 模型** 管理模型版本及模型生命週期。
MLflow 追蹤 可記錄每一次執行聯合學習時的參數、程式碼版本、指標和產出文件,並將結果視覺化,追蹤聯合學習實驗並監視執行計量,可以強化AI模型建立。
本教學將指導你如何記錄從各個 FL client 訓練參數與各項指標,AI 研究員將可以在oneai 提供的線上 MLflow 服務上視覺化的進行聯合訓練結果分析。

## 教學範例規劃
本教學將分兩個階段展示,分別是聯合學習訓練中記錄到MLflow與訓練後上傳訓練結果到MLflow。在聯合學習訓練中階段將示範如何
將各個 client 的訓練參數與各項指標記錄傳送到oneai 的 ML flow,最後研究員可以透過MLflow進行分析,本教學範例在MLflow的記錄結果如下圖所示:

參數的部份將會記錄每個 client 的 epochs, lr(learning rate) , number of rounds

Metrics 的部份將記錄各個client 的train loss rate/rounds, validation accuracy/rounds

Tags 的部份將記錄 nvflare 發動的job id 與 name
在聯合學習訓練後階段, 將使用job2mlflow.py 範例程式將訓練後資料上傳到 mlflow Artiface, 使用model2mlflow.py 範例程式上傳 global model 到 mlflow artiface, 結果如下圖所示:

## 環境設定
### 1. 準備工作
* 確認已在OneAI完成 NVflare 部署,部署教學請參考部署文件。
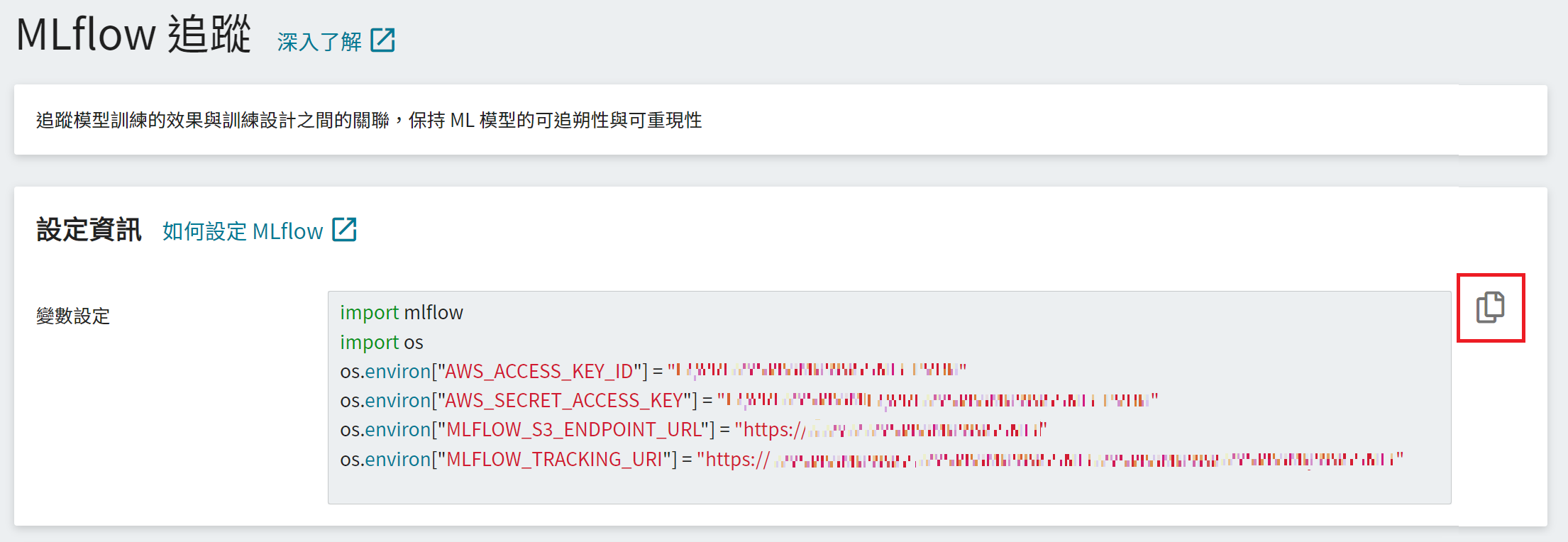
### 2. 取得 **MLflow** 設定資訊
* 從 OneAI 服務列表選擇「**AI Maker(搶鮮版)**」,再點擊「**MLflow 追蹤**」。
* 進入「**MLflow 追蹤**」頁面後可看到 MLflow 的設定資訊,此為與 **MLflow** 串接的必要資訊,包括:MLflow SDK、S3 連線資訊及 MLflow 追蹤端點。
* 點擊右側的 **複製** 圖示,複製「**變數設定**」欄位中的內容並添加至MLAnalyticsReceiver 程式。
### 3. 安裝 MLflow 套件
使用 MLflow 前在需要使用MLflow的node 上安裝MLflow 套件安裝 MLflow 套件,為避免版本衝突導致不可預期的結果,建議安裝 **MLflow 1.24** 版,亦可將 MLflow 套件寫入 **requirements.txt**,更多資訊請參考 [**筆記本服務 > 安裝其他 Python 套件**](/s/Z8LdmjL9M#安裝其他-Python-套件) 說明文件。
本教學預計在FL Server 與 Admin 上使用MLflow,請到FL server 與 Admin 的終端機上執行以下命令:
```python
pip install --upgrade mlflow==1.24
```
### 4. 安裝 TensorBoard 套件
本教學使用 Hello PyTorch with Tensorboard Streaming範例,需要安裝TensorBoard套件,請在FL Server 與 各Client 執行以下命令:
```python
pip install tensorboard
```
## 修改nvflare範例 Hello PyTorch with Tensorboard Streaming
### Hello PyTorch with TensorBoard 範例說明
[Hello PyTorch with TensorBoard](https://github.com/NVIDIA/NVFlare/tree/2.1.3/examples/hello-pt-tb)是nvflare 其中一個範例,它展示了從客戶端到服務器的 TensorBoard 流功能。

上圖實線的部份是此範例的示意架構圖
在client方面,在每個client 端有個 AnalyticsSender,它的功用跟 TensorBoard 的SummaryWriter一樣。原本SummaryWriter 會將log 寫到 TB 格式檔案,AnalyticsSender 實際上是將 log 產生 analytix_log_stats 型態的 NVFLARE events。NVFLARE 內部的 ConvertToFedEvent widget 會再把 analytix_log_stats 轉成 fed.analytix_log_stats,之後就會被送到 Server 端。
在 Server 端,TBAnalyticsReceiver 負責收來自各 client 送過來的fed.analytix_log_stats events,然後寫到 TensorBoard 資料檔去。(內建會放在 server端的/[job ID]/tb_events)
### 建立 ml_analytics_receiver.py
本範例將參考 NVflare TBAnalyticsReceiver 新開發 ml_analytics_receiver.py程式,這隻程式會將 fed.analytix_log_stats events 寫到TB 檔案,同時也會透過MLflow API 寫到 MLflow 追蹤,如圖虛線的部份,程式修改內容有以下說明:
#### 1. 加入 MLflow 設定資訊
在MLAnalyticsReceiver程式中加入所取得的 [**MLflow 設定資訊**](#取得-MLflow-設定資訊),包括滙入套件、S3 連線資訊及 MLflow Tracking Server URI。

#### 2. 設定 Experiment Name
設定 Experiment Name,若 Experiment Name 不存在會自動建立。
```python
os.environ["MLFLOW_EXPERIMENT_NAME"] = "Your Experiment"
mlflow.set_experiment(os.environ["MLFLOW_EXPERIMENT_NAME"])
```
#### 3. 記錄訓練資料
透過 MLflow 提供的 Tracking API 記錄每一次訓練的程式碼版本、超參數、指標及結果,詳細資訊請參閱 [**MLflow Logging functions**](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/tracking.html#logging-functions)。
```python=
...
# Log parameter and metrics to MLflow
with mlflow.start_run(run_id=self.restore_run(fl_ctx.get_job_id())):
if isinstance(analytic_data.kwargs, dict):
#self.log_info (fl_ctx, f"save tag {analytic_data.kwargs}", fire_event=False,)
if ("type", "param") in analytic_data.kwargs.items():
mlflow.log_param(tag_name, v)
else:
mlflow.log_metric(tag_name, v)
else:
mlflow.log_metric(tag_name, v)
...
```
完整MLAnalyticsReceiver如下:
:::spoiler **完整範例程式碼**
```python=1
# Copyright (c) 2021-2022, NVIDIA CORPORATION. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import os
'''---導入mlflow--'''
import mlflow
from typing import List, Optional
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
from nvflare.apis.analytix import AnalyticsData, AnalyticsDataType
from nvflare.apis.dxo import from_shareable
from nvflare.apis.fl_context import FLContext
from nvflare.apis.shareable import Shareable
from nvflare.app_common.widgets.streaming import AnalyticsReceiver
FUNCTION_MAPPING = {
AnalyticsDataType.SCALAR: "add_scalar",
AnalyticsDataType.TEXT: "add_text",
AnalyticsDataType.IMAGE: "add_image",
AnalyticsDataType.SCALARS: "add_scalars",
}
'''---導入必備資訊---'''
os.environ["AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"] = "1CN9TN9I275E4V3ECZTDTX4Z"
os.environ["AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY"] = "J6y3IzXUlPfp1zvCrQarURs9kuSyEhZm2wHll0qU"
os.environ["MLFLOW_S3_ENDPOINT_URL"] = "https://cloudstorage.oneai.twcc.ai"
os.environ["MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI"] = "https://mlflow-token:eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VySWQiOiJlNWJmOTFkNy1kN2U2LTQ2MDAtOTcwYS0xZTkzOWNmYzM2YTkiLCJ1c2VyTmFtZSI6Im1sZmxvdy10b2tlbiIsInByb2plY3RJZCI6IjQzODQzOWNmLTg1ZTAtNGQ0Zi1iZjcyLWM5MGFkNDg5N2E2MCIsImlzcyI6Im1sZmxvdy1tYW5hZ2VtZW50IiwiaWF0IjoxNjUxMTQwMjEyMDAwfQ.O57pHhfD92cww6a7MgVVPT7bb4TtkOZ4u246h1FAETY@mlops.oneai.twcc.ai/mlflow/sdk/projects/438439cf-85e0-4d4f-bf72-c90ad4897a60/"
'''---定義 MLflow 追蹤實驗名稱---'''
os.environ["MLFLOW_EXPERIMENT_NAME"] = "nvflare-tutorial"
mlflow.set_experiment(os.environ["MLFLOW_EXPERIMENT_NAME"])
class TBAnalyticsReceiver(AnalyticsReceiver):
def __init__(self, tb_folder="tb_events", events: Optional[List[str]] = None):
"""Receives analytic data and saved as TensorBoard.
Folder structure::
inside run_XX folder
- workspace
- run_01 (already created):
- output_dir (default: tb_events):
- peer_name_1:
- peer_name_2:
- run_02 (already created):
- output_dir (default: tb_events):
- peer_name_1:
- peer_name_2:
Args:
tb_folder (str): the folder to store tensorboard files.
events (optional, List[str]): A list of events to be handled by this receiver.
"""
super().__init__(events=events)
self.writers_table = {}
self.tb_folder = tb_folder
self.root_log_dir = None
def initialize(self, fl_ctx: FLContext):
workspace = fl_ctx.get_engine().get_workspace()
run_dir = workspace.get_run_dir(fl_ctx.get_job_id())
root_log_dir = os.path.join(run_dir, self.tb_folder)
os.makedirs(root_log_dir, exist_ok=True)
self.root_log_dir = root_log_dir
'''---啟動 MLflow 追蹤實驗名稱,以job id 當作每一次的實驗--'''
with mlflow.start_run(run_name=fl_ctx.get_job_id()):
'''---將 job id 與 名稱 寫入MLflow 追蹤,當作 tag 方便日後查詢 --'''
mlflow.set_tag("job.id", fl_ctx.get_job_id())
mlflow.set_tag("job.name", fl_ctx.get_identity_name())
'''---新增 restore_run,用 job id 找回mlflow run id --'''
def restore_run(self, name: str):
histories = mlflow.search_runs(filter_string=f"tags.mlflow.runName = '{name}'")
if len(histories["run_id"]) > 1:
raise NotImplementedError("to many run_id with the same runName.")
elif len(histories["run_id"]) == 1:
run_id = histories["run_id"][0]
else:
run_id = None
return run_id
def save(self, fl_ctx: FLContext, shareable: Shareable, record_origin):
dxo = from_shareable(shareable)
analytic_data = AnalyticsData.from_dxo(dxo)
writer = self.writers_table.get(record_origin)
if writer is None:
peer_log_dir = os.path.join(self.root_log_dir, record_origin)
writer = SummaryWriter(log_dir=peer_log_dir)
self.writers_table[record_origin] = writer
# depend on the type in dxo do different things
for k, v in dxo.data.items():
'''---tag name 新加 record_origin 用以記錄來自那個 client, 例如 site-1_train_loss_0,site-1 --'''
'''---例如 site-1_train_loss_0, record_origin: site-1, k: train_loss_0 --'''
tag_name = f"{record_origin}_{k}"
#mlflow.log_param ("num_round", fl_ctx.get_prop(AppConstants.NUM_ROUNDS))
self.log_info (
fl_ctx,
f"Save item {tag_name} and value {v} ",
fire_event=False,
)
func_name = FUNCTION_MAPPING.get(analytic_data.data_type, None)
if func_name is None:
self.log_error(fl_ctx, f"The data_type {analytic_data.data_type} is not supported.", fire_event=False)
continue
'''---將記錄資訊寫入MLflow追蹤與Tensorflow---'''
with mlflow.start_run(run_id=self.restore_run(fl_ctx.get_job_id())):
if isinstance(analytic_data.kwargs, dict):
#self.log_info (fl_ctx, f"save tag {analytic_data.kwargs}", fire_event=False,)
if ("type", "param") in analytic_data.kwargs.items():
mlflow.log_param(tag_name, v)
else:
mlflow.log_metric(tag_name, v)
else:
mlflow.log_metric(tag_name, v)
def finalize(self, fl_ctx: FLContext):
for writer in self.writers_table.values():
writer.flush()
writer.close()
```
:::
#### 4. 將ml_analytics_receiver.py放置到 custom 目錄
ml_analytics_receiver.py 完成後將它放到 hello-pt-tb/custom/
#### 5. 修改 config_fed_server.json
接著我們需要修改 config_fed_server.json 告訴 nvflare 執行 ml_analytics_receiver.py
將以下設定
```
{
"id": "tb_analytics_receiver",
"name": "TBAnalyticsReceiver",
"args": {"events": ["fed.analytix_log_stats"]}
}
```
改成以下設定
```
{
"id": "ml_analytics_receiver",
"path": "ml_analytics_receiver.MLAnalyticsReceiver",
"args": {"events": ["fed.analytix_log_stats"]}
}
```
### 修改訓練程式 pt_learner.py
hello-pt-tb 的範例主要的訓練程式都放在 pt_learner.py 檔案裡,讓我們修改它使訓練過程中可以記錄更多的參數與記錄到MLflow。您可以參考本教學修改的方式,日後依需求客製自己的訓練程式。
#### 6.1 新增 current_round 變數
我們在def __init__() 新增current_round 的變數,用來存放現在FL Server正在跑第幾round。
```
def __init__(...)
...
...
...
self.current_round = 0
```
#### 6.2 記錄 client 的 learning rate 、epochs 與 round number 參數
接著在def train()裡新增以下的code到#Convert weights to tensor之前,用以把 client 的 learning rate 、epochs 與 round number 參數型態記錄到 MLFlow.
為了將參數寫到 Tensorboard 與 MLFlow, 其中 self.writer.add_scalar () 的第三個欄位需要填入type="param",此參數為了讓MLAnalyticsReceiver判斷參數是否寫到MLFlow
```
def train(self, data: Shareable, fl_ctx: FLContext, abort_signal: Signal) -> Shareable:
...
...
...
self.writer.add_scalar("lr", self.lr,None,type="param")
self.writer.add_scalar("epochs", self.epochs * 1.0, None, type="param")
self.writer.add_scalar("num_rounds", get_header(AppConstants.NUM_ROUNDS) * 1.0,None,type="param")
self.current_round = data.get_header(AppConstants.CURRENT_ROUND)
# Convert weights to tensor. Run training
torch_weights = {k: torch.as_tensor(v) for k, v in dxo.data.items()}
...
...
```
#### 6.3 記錄 client 的 lose rate 與 validation accuracy 的 matrix
接著我們要將訓練過程lose rate 與 validation accuracy 的 matrix 寫到MLFlow 與 Tensorboard,我們這裡會將matrix 的tag 加上current_round,讓我們日後在MLFlow分析時能在每個 round 做比較。
請在def local_train()裡修改以下程式碼
在 # Stream training loss at each step 的程式碼裡,我們將tag字串 "train_loss" 加上 current_round的數字,例如 變成 "train_loss_2"
而if i % 50 == 0: 是為了不讓 train_loss 寫的太過頻煩。
```
# Stream training loss at each step
current_step = len(self.train_loader) * epoch + i
self.writer.add_scalar("train_loss", cost.item(), current_step)
```
改成如下程式碼
```
# Stream training loss at each step
if i % 50 == 0:
current_step = len(self.train_loader) * epoch + i
self.writer.add_scalar(f"train_loss_{self.current_round}", cost.item(), current_step)
```
如上做法,在 # Stream training loss at each step 的程式碼裡,我們將tag字串 "validation_accuracy" 加上 current_round的數字,例如 變成 "validation_accuracy_2"
```
# Stream validation accuracy at the end of each epoch
metric = self.local_validate(abort_signal)
self.writer.add_scalar("validation_accuracy", metric, epoch)
```
改成如下:
```
# Stream validation accuracy at the end of each epoch
metric = self.local_validate(abort_signal)
self.writer.add_scalar(f"validation_accuracy_{self.current_round}", metric, epoch)
```
#### 6.4 修改後完整 pt_learner.py 程式
完整 pt_learner.py 如下:
:::spoiler **完整範例程式碼**
```
# Copyright (c) 2021-2022, NVIDIA CORPORATION. All rights reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import os.path
import torch
from pt_constants import PTConstants
from simple_network import SimpleNetwork
from torch import nn
from torch.optim import SGD
from torch.utils.data.dataloader import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
from torchvision.datasets import CIFAR10
from torchvision.transforms import Compose, Normalize, ToTensor
from nvflare.apis.dxo import DXO, DataKind, MetaKey, from_shareable
from nvflare.apis.fl_constant import FLContextKey, ReservedKey, ReturnCode
from nvflare.apis.fl_context import FLContext
from nvflare.apis.shareable import Shareable, make_reply
from nvflare.apis.signal import Signal
from nvflare.app_common.abstract.learner_spec import Learner
from nvflare.app_common.abstract.model import (
ModelLearnable,
ModelLearnableKey,
make_model_learnable,
model_learnable_to_dxo,
)
from nvflare.app_common.app_constant import AppConstants
from nvflare.app_common.pt.pt_fed_utils import PTModelPersistenceFormatManager
class PTLearner(Learner):
def __init__(self, data_path="~/data", lr=0.01, epochs=5, exclude_vars=None, analytic_sender_id="analytic_sender"):
"""Simple PyTorch Learner that trains and validates a simple network on the CIFAR10 dataset.
Args:
lr (float, optional): Learning rate. Defaults to 0.01
epochs (int, optional): Epochs. Defaults to 5
exclude_vars (list): List of variables to exclude during model loading.
analytic_sender_id: id of `AnalyticsSender` if configured as a client component.
If configured, TensorBoard events will be fired. Defaults to "analytic_sender".
"""
super().__init__()
self.writer = None
self.persistence_manager = None
self.default_train_conf = None
self.test_loader = None
self.test_data = None
self.n_iterations = None
self.train_loader = None
self.train_dataset = None
self.optimizer = None
self.loss = None
self.device = None
self.model = None
self.data_path = data_path
self.lr = lr
self.epochs = epochs
self.exclude_vars = exclude_vars
self.analytic_sender_id = analytic_sender_id
self.current_round = 0
def initialize(self, parts: dict, fl_ctx: FLContext):
# Training setup
self.model = SimpleNetwork()
self.device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
self.model.to(self.device)
self.loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
self.optimizer = SGD(self.model.parameters(), lr=self.lr, momentum=0.9)
# Create CIFAR10 dataset for training.
transforms = Compose(
[
ToTensor(),
Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)),
]
)
self.train_dataset = CIFAR10(root=self.data_path, transform=transforms, download=True, train=True)
self.train_loader = DataLoader(self.train_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
self.n_iterations = len(self.train_loader)
# Create CIFAR10 dataset for validation.
self.test_data = CIFAR10(root=self.data_path, train=False, transform=transforms)
self.test_loader = DataLoader(self.test_data, batch_size=32, shuffle=False)
# Set up the persistence manager to save PT model.
# The default training configuration is used by persistence manager in case no initial model is found.
self.default_train_conf = {"train": {"model": type(self.model).__name__}}
self.persistence_manager = PTModelPersistenceFormatManager(
data=self.model.state_dict(), default_train_conf=self.default_train_conf
)
# Tensorboard streaming setup
self.writer = parts.get(self.analytic_sender_id) # user configuration from config_fed_client.json
if not self.writer: # else use local TensorBoard writer only
self.writer = SummaryWriter(fl_ctx.get_prop(FLContextKey.APP_ROOT))
def train(self, data: Shareable, fl_ctx: FLContext, abort_signal: Signal) -> Shareable:
# Get model weights
try:
dxo = from_shareable(data)
except:
self.log_error(fl_ctx, "Unable to extract dxo from shareable.")
return make_reply(ReturnCode.BAD_TASK_DATA)
# Ensure data kind is weights.
if not dxo.data_kind == DataKind.WEIGHTS:
self.log_error(fl_ctx, f"data_kind expected WEIGHTS but got {dxo.data_kind} instead.")
return make_reply(ReturnCode.BAD_TASK_DATA)
# Convert weights to tensor. Run training
torch_weights = {k: torch.as_tensor(v) for k, v in dxo.data.items()}
# Set the model weights
self.model.load_state_dict(state_dict=torch_weights)
self.local_train(fl_ctx, abort_signal)
# Check the abort_signal after training.
# local_train returns early if abort_signal is triggered.
if abort_signal.triggered:
return make_reply(ReturnCode.TASK_ABORTED)
self.writer.add_scalar("lr", self.lr,None,type="param")
self.writer.add_scalar("epochs", self.epochs * 1.0, None, type="param")
self.num_rounds = data.get_header(AppConstants.NUM_ROUNDS)
self.writer.add_scalar("num_rounds", self.num_rounds * 1.0,None,type="param")
self.current_round = data.get_header(AppConstants.CURRENT_ROUND)
# Save the local model after training.
self.save_local_model(fl_ctx)
# Get the new state dict and send as weights
new_weights = self.model.state_dict()
new_weights = {k: v.cpu().numpy() for k, v in new_weights.items()}
outgoing_dxo = DXO(
data_kind=DataKind.WEIGHTS, data=new_weights, meta={MetaKey.NUM_STEPS_CURRENT_ROUND: self.n_iterations}
)
return outgoing_dxo.to_shareable()
def local_train(self, fl_ctx, abort_signal):
# Basic training
for epoch in range(self.epochs):
self.model.train()
running_loss = 0.0
for i, batch in enumerate(self.train_loader):
if abort_signal.triggered:
return
images, labels = batch[0].to(self.device), batch[1].to(self.device)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
predictions = self.model(images)
cost = self.loss(predictions, labels)
cost.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
running_loss += cost.cpu().detach().numpy() / images.size()[0]
if i % 3000 == 0:
self.log_info(
fl_ctx, f"Epoch: {epoch}/{self.epochs}, Iteration: {i}, " f"Loss: {running_loss/3000}"
)
running_loss = 0.0
# Stream training loss at each step
current_step = len(self.train_loader) * epoch + i
self.writer.add_scalar("train_loss", cost.item(), current_step)
# Stream validation accuracy at the end of each epoch
metric = self.local_validate(abort_signal)
self.writer.add_scalar("validation_accuracy", metric, epoch)
def get_model_for_validation(self, model_name: str, fl_ctx: FLContext) -> Shareable:
run_dir = fl_ctx.get_engine().get_workspace().get_run_dir(fl_ctx.get_job_id())
models_dir = os.path.join(run_dir, PTConstants.PTModelsDir)
if not os.path.exists(models_dir):
return None
model_path = os.path.join(models_dir, PTConstants.PTLocalModelName)
self.persistence_manager = PTModelPersistenceFormatManager(
data=torch.load(model_path), default_train_conf=self.default_train_conf
)
ml = self.persistence_manager.to_model_learnable(exclude_vars=self.exclude_vars)
# Get the model parameters and create dxo from it
dxo = model_learnable_to_dxo(ml)
return dxo.to_shareable()
def validate(self, data: Shareable, fl_ctx: FLContext, abort_signal: Signal) -> Shareable:
model_owner = "?"
try:
try:
dxo = from_shareable(data)
except:
self.log_error(fl_ctx, "Error in extracting dxo from shareable.")
return make_reply(ReturnCode.BAD_TASK_DATA)
# Ensure data_kind is weights.
if not dxo.data_kind == DataKind.WEIGHTS:
self.log_exception(fl_ctx, f"DXO is of type {dxo.data_kind} but expected type WEIGHTS.")
return make_reply(ReturnCode.BAD_TASK_DATA)
if isinstance(dxo.data, ModelLearnable):
dxo.data = dxo.data[ModelLearnableKey.WEIGHTS]
# Extract weights and ensure they are tensor.
model_owner = data.get_header(AppConstants.MODEL_OWNER, "?")
weights = {k: torch.as_tensor(v, device=self.device) for k, v in dxo.data.items()}
self.model.load_state_dict(weights)
# Get validation accuracy
val_accuracy = self.local_validate(abort_signal)
if abort_signal.triggered:
return make_reply(ReturnCode.TASK_ABORTED)
self.log_info(
fl_ctx,
f"Accuracy when validating {model_owner}'s model on"
f" {fl_ctx.get_identity_name()}"
f"s data: {val_accuracy}",
)
dxo = DXO(data_kind=DataKind.METRICS, data={"val_acc": val_accuracy})
return dxo.to_shareable()
except:
self.log_exception(fl_ctx, f"Exception in validating model from {model_owner}")
return make_reply(ReturnCode.EXECUTION_EXCEPTION)
def local_validate(self, abort_signal):
self.model.eval()
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(self.test_loader):
if abort_signal.triggered:
return 0
images, labels = images.to(self.device), labels.to(self.device)
output = self.model(images)
_, pred_label = torch.max(output, 1)
correct += (pred_label == labels).sum().item()
total += images.size()[0]
metric = correct / float(total)
return metric
def save_local_model(self, fl_ctx: FLContext):
run_dir = fl_ctx.get_engine().get_workspace().get_run_dir(fl_ctx.get_prop(ReservedKey.RUN_NUM))
models_dir = os.path.join(run_dir, PTConstants.PTModelsDir)
if not os.path.exists(models_dir):
os.makedirs(models_dir)
model_path = os.path.join(models_dir, PTConstants.PTLocalModelName)
ml = make_model_learnable(self.model.state_dict(), {})
self.persistence_manager.update(ml)
torch.save(self.persistence_manager.to_persistence_dict(), model_path)
```
:::
#### 6.5 執行訓練
依以上步驟修改完後您可以登入 admin 下submit_job hello-pt-tb 開始您的聯合訓練
#### 6.6 檢閱MLFlow追蹤
最後您可以參考[MLFlow追蹤結果](https://hackmd.io/YwZ1pHrgRqqjYpx3lDKRGg#%E6%AA%A2%E8%A6%96-MLflow-%E8%BF%BD%E8%B9%A4%E7%B5%90%E6%9E%9C)步驟前往MLFlow追蹤分析您的AI實驗結果
## 將nvflare job訓練後資料上傳到 MLflow artifact
每個 nvflare job 訓練完成後,可以透過admin command 下 download <job id> 得到job worksace 的資料,你可以把它上傳到MLflow articfact。
### 上傳訓練結果資料
這個步驟將指導如何上傳job workspace 資料。
請 copy 以下檔案job2mlflow.py 到 job workspace 所在地方,並且在程式裡修改成你的環境定義,完整程式如下:
:::spoiler **完整範例程式碼**
import os
import mlflow
import sys, getopt
os.environ["AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"] = "1CN9TN9I275E4V3ECZTDTX4Z"
os.environ["AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY"] = "J6y3IzXUlPfp1zvCrQarURs9kuSyEhZm2wHll0qU"
os.environ["MLFLOW_S3_ENDPOINT_URL"] = "https://cloudstorage.oneai.twcc.ai"
os.environ["MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI"] = "https://mlflow-token:eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VySWQiOiJlNWJmOTFkNy1kN2U2LTQ2MDAtOTcwYS0xZTkzOWNmYzM2YTkiLCJ1c2VyTmFtZSI6Im1sZmxvdy10b2tlbiIsInByb2plY3RJZCI6IjQzODQzOWNmLTg1ZTAtNGQ0Zi1iZjcyLWM5MGFkNDg5N2E2MCIsImlzcyI6Im1sZmxvdy1tYW5hZ2VtZW50IiwiaWF0IjoxNjUxMTQwMjEyMDAwfQ.O57pHhfD92cww6a7MgVVPT7bb4TtkOZ4u246h1FAETY@mlops.oneai.twcc.ai/mlflow/sdk/projects/438439cf-85e0-4d4f-bf72-c90ad4897a60/"
def restore_run(name: str):
histories = mlflow.search_runs(filter_string=f"tags.mlflow.runName = '{name}'")
if len(histories["run_id"]) > 1:
raise NotImplementedError("to many run_id with the same runName.")
elif len(histories["run_id"]) == 1:
run_id = histories["run_id"][0]
else:
run_id = None
return run_id
def main(argv):
#job_id = argv[0]
job_id = "d985fbda-deeb-49cc-9c1d-bddf79184e2c"
print (job_id)
mlflow.set_experiment("nvflare-1")
with mlflow.start_run(run_id=restore_run(job_id)):
mlflow.log_artifacts(argv[0])
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(sys.argv[1:])
:::
完成修改後請下以下命令:
`python3 job2mlflow.py <job id>`
## 記錄 MLflow 模型
你也可以將global model 記錄到 MLflow 模型,本教學將參考hello-pt-tb/custom/pt_learner.py 的model建立程式建立 model2mlflow.py,然後下以下命令將 global model 上傳到 MLflow 模型
```
python3 model2mlflow.py
```
model2mlflow.py 完整程式與說明如下,你可以參考它並根據你的model修改成你的程式。
:::spoiler **完整範例程式碼**
import os
import sys, getopt
import torch
import mlflow
import mlflow.pytorch
import importlib.util
from nvflare.app_common.abstract.model import (
ModelLearnable,
ModelLearnableKey,
make_model_learnable,
model_learnable_to_dxo,
)
from nvflare.app_common.pt.pt_fed_utils import PTModelPersistenceFormatManager
os.environ["AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"] = "1CN9TN9I275E4V3ECZTDTX4Z"
os.environ["AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY"] = "J6y3IzXUlPfp1zvCrQarURs9kuSyEhZm2wHll0qU"
os.environ["MLFLOW_S3_ENDPOINT_URL"] = "https://cloudstorage.oneai.twcc.ai"
os.environ["MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI"] = "https://mlflow-token:eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VySWQiOiJlNWJmOTFkNy1kN2U2LTQ2MDAtOTcwYS0xZTkzOWNmYzM2YTkiLCJ1c2VyTmFtZSI6Im1sZmxvdy10b2tlbiIsInByb2plY3RJZCI6IjQzODQzOWNmLTg1ZTAtNGQ0Zi1iZjcyLWM5MGFkNDg5N2E2MCIsImlzcyI6Im1sZmxvdy1tYW5hZ2VtZW50IiwiaWF0IjoxNjUxMTQwMjEyMDAwfQ.O57pHhfD92cww6a7MgVVPT7bb4TtkOZ4u246h1FAETY@mlops.oneai.twcc.ai/mlflow/sdk/projects/438439cf-85e0-4d4f-bf72-c90ad4897a60/"
def restore_run(name: str):
histories = mlflow.search_runs(filter_string=f"tags.mlflow.runName = '{name}'")
if len(histories["run_id"]) > 1:
raise NotImplementedError("to many run_id with the same runName.")
elif len(histories["run_id"]) == 1:
run_id = histories["run_id"][0]
else:
run_id = None
return run_id
def main(argv):
#job_id = argv[0]
job_id = "d985fbda-deeb-49cc-9c1d-bddf79184e2c"
print ("start push model ...")
sys.path.append ('hello-pt-tb/custom/')
import simple_network
from simple_network import SimpleNetwork
#spec = importlib.util.spec_from_file_location("module.name", "/path/to/file.py")
#foo = importlib.util.module_from_spec(spec)
#sys.modules["module.name"] = foo
#spec.loader.exec_module(foo)
model = SimpleNetwork()
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
train_conf = {"train": {"model": type(model).__name__}}
persistence_manager = PTModelPersistenceFormatManager(
data=torch.load(f"/home/asusceph/mlflow/poc/admin/transfer/54622420-e1f4-4ee8-b022-c9c15946560b/workspace/app_server/FL_global_model.pt"), default_train_conf=train_conf
)
ml = persistence_manager.to_model_learnable(exclude_vars=None)
dxo = model_learnable_to_dxo(ml)
weights = {k: torch.as_tensor(v, device=device) for k, v in dxo.data.items()}
model.load_state_dict(weights)
print ("create persistence manger pass")
mlflow.set_experiment("nvflare-1")
with mlflow.start_run(run_id=restore_run(job_id)):
# model = mlflow.pytorch.load_model (f"/home/asusceph/mlflow/poc/admin/transfer/54622420-e1f4-4ee8-b022-c9c15946560b/workspace/app_server/FL_global_model.pt")
model_path = "my_model"
mlflow.pytorch.log_model(model, model_path)
print ("push model finish...")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(sys.argv[1:])
:::
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet