# 02.4-WebServic and APIs-Lesson4: Microservices
###### tags: `Udacity`
[ToC]
# 01 Introduction
{%youtube iuOL0IJguCI%}
# 02 MSA
{%youtube M9YlbhAHTzY%}
N-Tier and monolithic applications used to be the de facto standard. In one single binary web artifact, like an EAR or WAR file, there would be a layered architecture with the decomposition of code into more functional components.
* Presentation Layer
* Business Process Layer/Service Layer
* Data Access Layer
There are several disadvantages to the n-tier monolithic application architecture:
* Tight coupling of code which makes changes hard.
* A single deployment with multiple layers that causes long testing, building, and deployment cycles.
* A big monolithic application that makes code reuse and sharing of components difficult.
The Microservices Architecture (MSA) decomposes systems into discrete, individual, standalone components that can communicate amongst themselves, working together or with external systems.
MSA is a more agile framework that fits well with the cloud-based world and lends itself well to web application development and web service development.
**Features**
* MSA is very flexible because it supports any language that can communicate via a RESTful endpoint and leverages REST over HTTP.
* MSA offers agility and systems that are easier to write, test, deploy, and share.
* MSA provides systems that can better scale to load and demand.
* MSA provides systems that are resilient because failures are isolated and don’t cascade through the infrastructure.
# 03 Spring Cloud & Eureka
{%youtube cGKMR-Y_cg0%}
Eureka, created by Netflix, is responsible for the registration and discovery microservices. Spring has incorporated Eureka into [Spring Cloud](https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud), making it even easier to stand up a Eureka server.
Eureka consists of a server and a client-side component. The server component will be the registry in which all the microservices register their availability. The microservices use the Eureka client to register; once the registration is complete, it notifies the server of its existence.
# 04 Case Study: Eureka Server
{%youtube 1dZvq2eAvOc%}
The case study is an online ordering service. There are multiple services that work together to create the system.
* Item Service
* Order Service
* Shipping Service
Each service has its own database. For this case study, instead of building out the entire system, we will focus on the Item Service. The code can be cloned from [GitLab](https://gitlab.com/videolearning/udacity-java/tree/master/Lesson4-microservices).
The project has the following components:
Eureka Module
**Eureka Registry** accessible via http://localhost:8761
Items Microservices Module
* CRUD Repository - ItemRepository.java
* Domain Entity/Model -Item.java
* H2 Database accessible via http://localhost:8080/h2/
* Tomcat Server accessible via http://localhost:8080
* Items Microservice accessible via http://localhost:8080/items
**Troubleshooting**
You may need this additional dependency in your POM file for the Eureka server to load:
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.xml.bind</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-api</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0-b180725.0427</version>
</dependency>
```
==ShannonNote==
如何設定Eureka步驟
> * 加入spring cloud dependency
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
```
> * 加入spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-server,這樣spring cloud就會自動加入eureka server
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
```
> * `application.properties` 設定Eureka server的name and port,eureka-server跟8761是default設定
```xml
spring.application.name=eureka-server
server.port=8761
```
> * 然後針對Eureka client做設定
* 我發現logging.level.com.netflix.eureka會發生錯誤,把ON改成debug就可以了
* 參考: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/62352998/failed-to-bind-properties-under-logging-level-com-netflix-eureka-to-org-spring
```xml
#don't register itself as a client
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false
eureka.client.fetch-registry=false
#新增eureka service logging 還有discovery loggin
logging.level.com.netflix.eureka=ON
logging.level.com.netflix.discovery=ON
```
> * 再main.java的地方新增`@EnableEurekaServer`告訴spring去啟動Eureka server realted configuration
```javascript=
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaApplication.class, args);
}
}
```
> * 設定完成後就可以在網頁輸入 http://localhost:8761
* 裡面Instances currently registered with Eureka是最重要的,會在裡面註冊microservice,你會發現是空的因為還沒有註冊
# 05 Lab I: Build a Dog Microservice
**Lab I: Build a Dog Microservice**
Once again, you'll work with a dog-related API, this time to create a Microservice that returns a list of dogs from an embedded H2 in memory database and registers itself with a Eureka Server. While you may have some code re-use from before, you'll get a chance to see how much you are able to cut out from the earlier REST API in implementing a microservice.
**Eureka**
**In a new module create the Eureka Service:**
* **Step 1**: Create a SpringBoot project that creates a Eureka server.
* Ensure that you use the proper dependencies in the Maven POM file and the necessary annotations.
* Make a note of the service URL and add any other necessary details in `application.properties`.
* **Step 2**: Use a web browser to view the Eureka web console.
# 06 Lab I: Solution
**Solution: Build a Dog Microservice - Eureka**
Below, we'll walk through each step of the lab and look at one potential way to implement the lab. Even if you get stuck, you should always first try to work through the lab without the solution before coming here, so that you can best learn the related skills and be ready for the project at the end of the course.
**Step 1: Create a SpringBoot project that creates a Eureka server.**
* Ensure that you use the proper dependencies in the Maven POM file and the necessary annotations.
* Make a note of the service URL and add any other necessary details in `application.properties`.
First, navigate once again to Spring Initializr. You can add the `Config Client` (for `spring-cloud-starter-config`) and`Eureka Server` (for `spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-server`) dependencies to generate the POM file for this project. Remember that since this is just the Eureka server and not the microservice client you will build later, you won't need dependencies like `H2`.
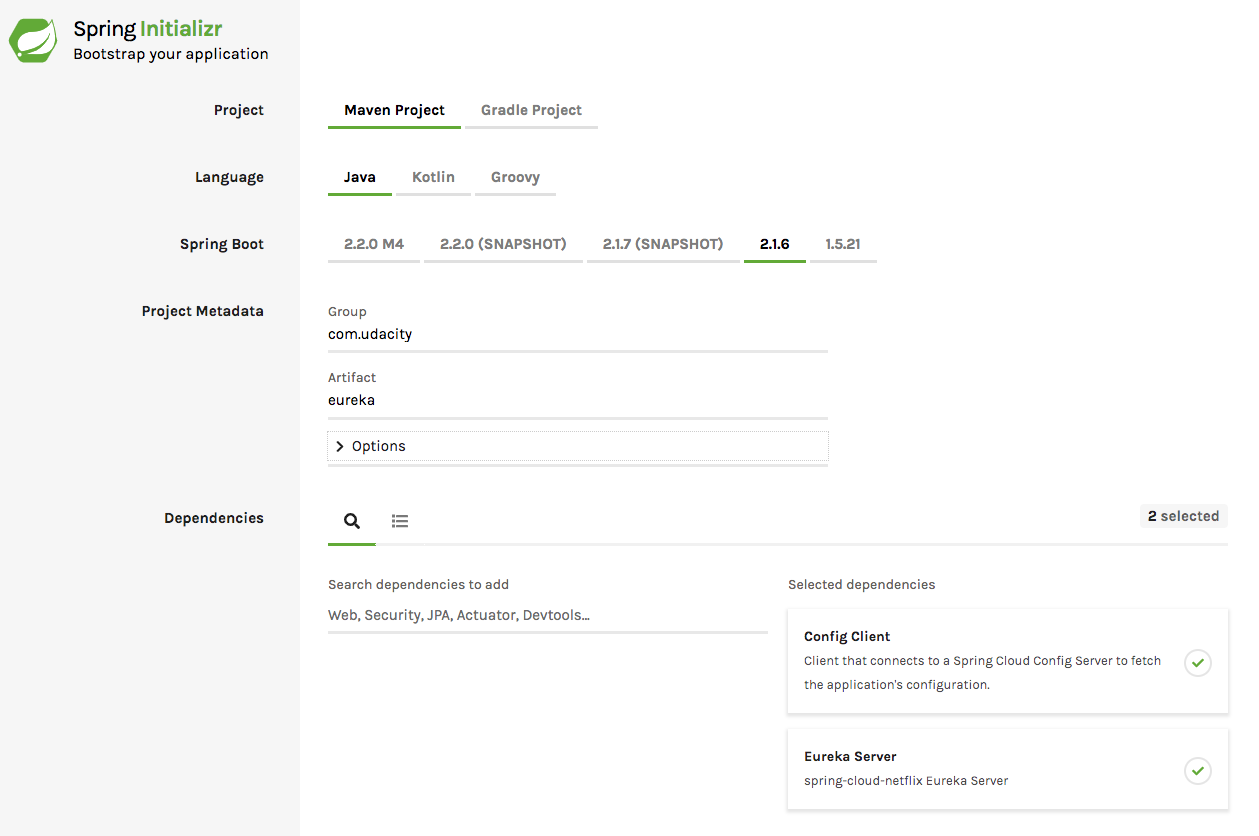
Additionally, I added the below additional dependency to my POM file to get the Eureka server up and running:
==JAXB詳細請見補充01==
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.xml.bind</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-api</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0-b180725.0427</version>
</dependency>
```
From there, navigate to your `application.properties` file to add the application name and server port (`8761` in the case of a Eureka server, typically). Below, I have also added lines to avoid registering the Eureka server itself as a client, as well as adding some additional logging to help with any potential debugging or information needs.
```xml
spring.application.name=eureka-server
server.port=8761
# avoid registering itself as a client
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false
eureka.client.fetch-registry=false
logging.level.com.netflix.eureka=ON
logging.level.com.netflix.discovery=ON
```
You're already almost done! Now, we just need one import and one annotation added to `EurekaApplication.java` - importing `EnableEurekaServer` and adding the related annotation.
```java
package com.udacity.eureka;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaApplication.class, args);
}
}
```
**Step 2: Use a web browser to view the Eureka web console.**
Navigate to http://localhost:8761/ on your computer to view the Eureka web console. Note again that Eureka servers are typically put on port 8761, but if you would have used a different server port in `application.properties`, you would instead navigate to that port.

Supporting Materials: [Eureka](https://video.udacity-data.com/topher/2019/August/5d485584_eureka/eureka.zip)
# 07 Spring Data REST
{%youtube MeHN-SWMjfc%}
[Spring Data REST](https://spring.io/projects/spring-data-rest) makes it easy to expose microservices. Spring Data REST builds on top of Spring Data repositories and automatically exports those as REST resources.
So how does Spring Data Rest work?
1. At application startup, Spring Data Rest finds all of the spring data repositories
2. Then, Spring Data Rest creates an endpoint that matches the entity name
3. Next, Spring Data Rest appends an S to the entity name in the endpoint
4. Lastly, Spring Data Rest exposes CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations as RESTful APIs over HTTP
There is no need to create a controller or service layer!
==ShannonNote==
> * 如果你下載範例檔案,我覺得POM.xml那邊叫加上version如下,否則無法運作
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
<version>2.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
```
> * 然後如果想要使用@Entity又或是CrudRepository
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
```
# 08 Case Study: Spring Data REST
{%youtube EtQe4STbuRA%}
Each service has its own database. For this case study, instead of building out the entire system, we will focus on the Item Service. The code can be cloned from [GitLab](https://gitlab.com/videolearning/udacity-java/tree/master/Lesson4-microservices).
==ShannonNote==
> 我們需要加以下幾個dependency
> * 加入data-jpa才可以使用某些annotation像是@entity
* 參考: https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10229808?sc=rss.qu
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
```
> * 基本的starter-web
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
```
> * H2 database
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
```
> * starter-data-rest
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactId>
</dependency>
```
> * spring cloud跟netflix-erureka 先移除掉,包含main的`@EnableEurekaServer`
# 09 Lab II: Build a Dog Microservice
**Lab II: Build a Dog Microservice**
Now that you have a working Eureka server, you can build out a microservice that provides information about your dogs.
**Spring Data REST**
Steps 1, 2 & 3 below can re-use some of your code from earlier lessons.
**In a new separate module create a Microservice:**
* Step 1: Create an entity called Dog. The dog should have three attributes:
* Name
* Breed
* Origin
* Step 2: Create a repository that extends CrudRepository for creating, reading, updating, and deleting Dog objects.
* Note: This repository will not need to implement anything beyond an interface.
* Step 3: Create a `data.sql` file to create sample dog data in the database.
* Step 4: Create a microservice using Spring Data REST by including the proper dependency in the Maven POM file.
* Step 5: Check that you are able to access your microservice.
# 10 Lab II: Solution
**Solution: Build a Dog Microservice - Spring Data REST**
Below, we'll walk through each step of the lab and look at one potential way to implement the lab. Even if you get stuck, you should always first try to work through the lab without the solution before coming here, so that you can best learn the related skills and be ready for the project at the end of the course.
**Step 0: Create a SpringBoot project/module for an eventual microservice.**
We skipped this step on the original lab page, but it's essentially inferred to get us started. This can either be a new project (in which case you would need the Eureka server running in a separate window) or a new module. Since so far we've been using Spring Initializr as a separate project, I will approach it as such below.
Along with JPA, H2 and Spring Web Starter, you can add `Rest Repositories` (for `spring-boot-starter-data-rest`), `Cloud Config`, and also `Eureka Discovery Client`, which we won't utilize until the last part of the lab in this lesson (you can always update your POM file with this later, if necessary). If you need to debug, you might comment out the Eureka discovery client, as otherwise you'll see a lot of messages being output depending on whether it is connected to your Eureka server yet.
>* 需要的有Spring Data JPA
* H2 Database
* Spring Web Starter
* Rest Repositories
* Eureka Discovery Client
* Config Client

Don't forget to add anything you may need for `H2` to `application.properties` here! I re-used the same lines from the REST API in mine.
* Step 1: Create an entity called Dog.
* The dog should have three attributes:
* Name
* Breed
* Origin
You can re-use your code from the REST API for the `Dog` entity, just make sure to update the package name accordingly!
* Step 2: Create a repository that extends CrudRepository.
* This repository is for creating, reading, updating, and deleting Dog objects.
* Note: This repository will not need to implement anything beyond an interface.
Depending on your implementation, this can be re-used from either the REST API or GraphQL API. In this case, we don't need to add anything within the interface here.
```java
package com.udacity.DogMicroservice.repository;
import com.udacity.DogMicroservice.entity.Dog;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
public interface DogRepository extends CrudRepository<Dog, Long> {
}
```
**Step 3: Create a data.sql file.**
* The file should create sample dog data in the database.
You can either re-use your previous `data.sql` files here or create a new one.
**Step 4: Create a microservice using Spring Data REST.**
* Include the proper dependencies in the Maven POM file.
If you've been following since Step 0, this was actually done by including Rest Repositories within Spring Initializr, but otherwise, you can add the following to your POM file:
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactId>
</dependency>
```
Amazingly, you have now created a microservice to serve up the dogs' information! Spring Data Rest is handling most of the work for you, although since this is a microservice, it is more limited in what it does on its own (we don't have the explicit functionality to just get dog names here, for instance).
Step 5: Check that you are able to access your microservice.
While it might feel like we have hardly coded anything yet, your microservice should now be ready! When I navigated to http://localhost:8080/dogs, I saw the below (with some formatting done by a browser extension).

# 11 Microservice Registration
{%youtube ozWskAAllkw%}
For a `@SpringBootApplication` to be discovery-aware, all that's needed is the Spring Discovery Client (i.e., `spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client` dependency) in the classpath. The next step is to annotate the main Spring application class with the `@EnableEurekaClient` annotation. `@EnableEurekaClient` is optional if the `spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client` dependency is on the classpath.
==ShannonNote==
> 我們目前有entity item去聽取microservice的命令,microservice會使用spring data去implement一個JPA itme repository和spring data REST去提供一個restful介面來存取item 資訊
# 12 Case Study: Registration
{%youtube MMymv5LxfpQ%}
接下來我們要使用Eureka Client註冊microservice,當microservice被註冊之後會造成service表現得像spring discovery client,然後會註冊他自己in Eureka Server去attached to this service
==ShannonNote==
> 1. 設定POM.xml
> * 增加`starter-nextflix-eureka-client` 跟`config`
> * 記得拿掉之前的`starter-nextflix-eureka-server`
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
<version>2.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
<version>2.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
```
> * 增加`dependencyManagement`: spring-cloud-starter-parent
```xml
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>Greenwich.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
```
> 2. 在application main.java那邊增加`@EnableEurekaClient`
> 3. 在`application.properties`設定client相關資訊
* 目的是為了以後可以透過該名字進行查詢`http://item-service/items`
```xml
# 會用這個名字註冊在eureka裡面
spring.application.name=item-service
server.port=8762
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
eureka.client.service-url.default-zone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
instance.preferIpAddress=true
```
> 4. 然後就可以在http://localhost:8761 Spring Eureka看到ITEMS-SERVICE被註冊了
# 13 Lab III: Build a Dog Microservice
**Lab III: Build a Dog Microservice**
Now, you can finish off your Eureka-based microservice! Create a Microservice that returns a list of dogs from an embedded H2 in memory database and registers itself with a Eureka Server.
**Registration**
* Step 1: Turn the microservice into a Eureka client by adding the appropriate annotations and dependencies in the Maven POM file.
* Step 2: Use a web browser to view the Eureka web console to ensure your microservice is registered.
# 14 Lab III: Solution
**Solution: Build a Dog Microservice - Registration**
Below, we'll walk through each step of the lab and look at one potential way to implement the lab. Even if you get stuck, you should always first try to work through the lab without the solution before coming here, so that you can best learn the related skills and be ready for the project at the end of the course.
**Step 1: Turn the microservice into a Eureka client.**
* Add the appropriate annotations and dependencies in the Maven POM file.
If you followed Step 0 in the Lab II solution, you already have the necessary dependencies, but if not, you'll want to add both the Eureka discovery client and cloud config.
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
```
Spring Initializr may have already added the dependency management for you, but if that field does not exist in your POM file, add the following:
```xml
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>Greenwich.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
```
From there, it's just a couple of imports in DogMicroserviceApplication.java (or your similarly named application file) and a single additional annotation.
```java=
package com.udacity.DogMicroservice;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class DogMicroserviceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DogMicroserviceApplication.class, args);
}
}
```
Last is adding the necessary lines to `application.properties`. I decided to add my application `dog-service`, and set to port 8762. You can choose which port to use here, although I will keep it simple by using the very next port after the one for the Eureka server.
```xml
spring.application.name=dog-service
server.port=8762
spring.application.name=dog-servic
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
eureka.client.service-url.default-zone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
eureka.instance.prefer-ip-address=true
```
And that's it! Your microservice is now able to be registered with the Eureka server.
# 15 Recap
{%youtube E54uVaedTY4%}
# 總結
首先我要先架一個Eureka Server,待會給MicroService去註冊用的
## 1. 架Eureka Server步驟
* step1 先設定POM.XML : 必須要有`spring-cloud-starter-config`/ `spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-server` / `spring-cloud-starter-parent`
* 但其實不依定要`jaxb-api`,`starter-parent`
```xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.xml.bind</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-api</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0-b180725.0427</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>Greenwich.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
```
* step2 再來去設定`application.properties`
* ==你會發現`logging.level.com.netflix.eureka=ON`不能用,請改成`DEBUG`==
```xml
spring.application.name=eureka-server
server.port=8761
#don't register itself as a client
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false
eureka.client.fetch-registry=false
logging.level.com.netflix.eureka=DEBUG
logging.level.com.netflix.discovery=DEBUG
```
* step3 在`@SpringBootApplication` 的地方再新增一個`@EnableEurekaServer`
```java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaApplication.class, args);
}
}
```
* step4 嘗試去 http:localhost/8761 去看看有沒有出現Eureka的畫面,如果有就可以進行下一個步驟 建立MicroService
## 2. 架設好Eureka Service之後呢,就可以開始製作MicroService
* step1 先建立基本設定 `POM.xml` :
* 需要有jpa才可以設定@Entity等標示
* 基本的`starter-web`&`starter-test`
* `spring-boot-starter-data-rest`才可以使用`CrueRepository`
* 然後可以存放Entity資料的h2
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactId>
</dependency>
```
* step2: 建立Entity
*==一定要有空的建構值,否則無法顯示dogs內容==
```java
@Entity
public class Dog {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String breed;
private String origin;
//一定要有空的建構值,否則無法顯示http://localhost:8080/dogs的內容
public Dog(){
}
public Dog(Long id, String name, String breed, String origin){
this.id = id;
this.name=name;
this.breed=breed;
this.origin=origin;
}
...
```
* step3: 建立Entity的Repository
```java
public interface DogRepository extends CrudRepository<Dog,Long> {
}
```
* step4: 設定`application.properties`
```xml
logging.level.org.springframework:DEBUG
# H2
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.h2.console.path=/h2
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:items
```
* step5: 嘗試去 http:localhost:8080/items 檢查看看有沒有出現JSON,如果有就可以去下一個步驟
## 3. 開始將microservice自動註冊到eureka service裡面,有幾個步驟,要非常小心!!尤其是POM.xml設置的地方
* step1: 設定 pom.xml 新增一些dependency==注意版本要跟Eureka server一樣,否則會壞掉==
* 下面的`<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>`是參考1-step1的版本`spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-server`一定要一樣!
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
```
* step2: 去`application.properties`設定client的相關設定
* `spring.application.name`: 這是註冊在Eureka Service的名稱
* 在client裡面的`server.port`跟server裡面的`server.port`不一樣,client的可以看到items的JSON,server是用來設定Eureka service的port
* `eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone`: 這是用來設定eureka查看的網址,8761要跟server的`server.port`一樣
```xml
#Eureka
spring.application.name=item-service
server.port=8762
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
eureka.client.service-url.default-zone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
instance.preferIpAddress=true
```
* step3: 去MicroServiceApplication.java增加`@EnableEurekaClient`
```java
@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class MicroservicesApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MicroservicesApplication.class, args);
}
}
```
* step4: 最後執行`microserviceApplication.main`去查看 http://localhost:8761 應該可以進入spring Eureka畫面並且看到 ITEM-SERVICE被註冊了。也可以進入http://localhost:8762 看到相關JSON
> http://localhost:8762

> http://localhost:8761

## 注意: 如果你想要把Server跟Client分開做也可以
* 但是Server需要先架起來,再啟動Client才可以看到microservice被註冊在Eureka上面
==DONE== 機車幹花我兩個晚上找bug
# 補充01: JAXB
全名為Java Architecture for XML Binding
* JAXB提供API和工具去自動mapping java物件跟XML,對開法者來說可以減少code的撰寫也不需要成為xml專家
* 他提供幾個操作
* 將XML解組為java的形式
* 可以存取跟更新java
* 可以將原為xml被解組成的java轉回xml