---
GA: UA-7042909-2
---
# Red Team Infrastructure
[TOC]
> ## How to learn from slidedecks?
> Slidedecks tend to be the most condensed way to present and transfer information, they assume some (often a lot) prior knowledge - and a presenter that supplies the narrative and the context needed to understand a slidedeck. Thus when trying to learn from a slide deck, make sure you understand the big picture presented, and every detail mentioned in the slide. Don't be content with just explaining to yourself - spin up a VM and try to redo what's presented in the slide (if possible).
>
> To make your learning expierence easier this document tries to include the presentaion video with each slidedeck, in addition to tutorials and reading material to fill in the required prior knowledge.
>
> To get the most of this document - always start with the slidedeck (when availalble), if you don't understand go over the linked documents and then watch the presentation video (if not available - re-read the slidedeck).
>
## Overview
The Advanced Persistent Threat
(or Informationized Force Operations)
> A short presentation examining APT concepts - from the days before APTs been all the rage. With simpler day & age afford for a clear explanation that age well.
>
{%pdf https://www.usenix.org/legacy/events/lisa09/tech/slides/daly.pdf %}
[An Introduction to Privacy & Anonymity](https://www.ivpn.net/privacy-guides/an-introduction-to-privacy-anonymity)
[Adversaries and Anonymity Systems: The Basics](https://www.ivpn.net/privacy-guides/adversaries-and-anonymity-systems-the-basics)
> Provides a good overview & taxonomy of anonymity related definitions, concerns and technologies, As well as lays a framework useful for analyzing adversaries.
> In this document we'll deal with the building of a covert infrastructure for red team engagements - for this end we'll leverage many of the same privacy & anonymity preserving technologies and use the above mentioned framework to analyse the dangers presented by the blue.
>
:::info
Internet Annonymity 2011
> A leaked NSA presentation from 2011 that gives an overview of anonymising technologies as viewed by an apex adversary.
>
{%pdf https://edwardsnowden.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/media-35540.pdf %}
:::
### Red Team Infrastructure
> We now opt for a quick overview of important topics, consideration and techniques for building covert red team infrastructure. We do so by reviewing seminal work by [@armitagehacker](https://twitter.com/armitagehacker), [@bluescreenofjeff](https://twitter.com/bluscreenofjeff), [@424f424f](https://twitter.com/424f424f) & [@curi0usJack](https://twitter.com/curi0usJack).
> Later on we'll deep dive into each one of the presented concept.
{%speakerdeck bluscreenofjeff/building-a-better-moat-designing-an-effective-covert-red-team-attack-infrastructure %}
:thought_balloon: [Designing Effective Covert Red Team Attack Infrastructure](https://bluescreenofjeff.com/2017-12-05-designing-effective-covert-red-team-attack-infrastructure/)
:::info
##### A Methodical Note
Many of the following linked articles talk in the term of Meterpreter, Beacon & Team Server - those term refer to an industry standard post-exploitation implant, the long haul implant from the Cobalt Strike toolkit and the Cobalt Strike toolkit C2 framework. Fear not - the concepts discussed within are generic, and while the implementation details (when discussed) will vary - might be applied to the implant or tool of your choice.
Also note, that some times post-exploitation & staging servers would be called "Short Haul".
:::
:thought_balloon: [Infrastructure for Ongoing Red Team Operations](https://blog.cobaltstrike.com/2014/09/09/infrastructure-for-ongoing-red-team-operations/)
> A discussion of consideration for long haul infrastructure
#### C&C
#### Redirectors
A redirector is a system that proxies all traffic from your target’s network to a team server system. Redirectors give you IP diversity.

#### Domains
#### Infrastructure Deployment & Management
## Internet Infrastructure
* Transit
* Peering
* CDN
* IXP
* Submarine cables - https://www2.telegeography.com/submarine-cable-faqs-frequently-asked-questions
* https://www.submarinecablemap.com/#/
* https://blog.telegeography.com/international-internet-capacity-growth-just-accelerated-for-the-first-time-since-2015
* https://www.itu.int/itu-d/tnd-map-public/
## Networking
### Linux Networking
#### Namespaces & Containers
{%slideshare jpetazzo/anatomy-of-a-container-namespaces-cgroups-some-filesystem-magic-linuxcon %}
:::spoiler Namespaces and cgroups - the basis of Linux containers
{%slideshare kerneltlv/namespaces-and-cgroups-the-basis-of-linux-containers %}
{%youtube zMJD8PJKoYQ %}
:::
##### Network namespaces
* [Introducing Linux Network Namespaces](https://blog.scottlowe.org/2013/09/04/introducing-linux-network-namespaces/)
* [Network namespaces](https://blogs.igalia.com/dpino/2016/04/10/network-namespaces/)
> Linux namespaces are a relatively new kernel feature which is essential for implementation of containers. A namespace wraps a global system resource into an abstraction which will be bound only to processes within the namespace, providing resource isolation. In this article I discuss network namespace and show a practical example.
* :thought_balloon: [Using network namespaces and a virtual switch to isolate servers](https://ops.tips/blog/using-network-namespaces-and-bridge-to-isolate-servers/)
> How to create a virtual network that connects network namespaces using a bridge, veth pairs and iptables.
* :thought_balloon: [Namespaces in operation, part 1: namespaces overview](https://lwn.net/Articles/531114/)
#### Netfilter
[Introduction to Netfilter](https://home.regit.org/netfilter-en/netfilter/)
> A primer focusing on the internals of implementing NAT using in modern linux
>

##### iptables
{%slideshare kerneltlv/netfilter-and-iptables %}
[An In-Depth Guide to iptables, the Linux Firewall](https://www.booleanworld.com/depth-guide-iptables-linux-firewall/)
> The Linux kernel comes with a packet filtering framework named netfilter. It allows you to allow, drop and modify traffic leaving in and out of a system. A tool, iptables builds upon this functionality to provide a powerful firewall, which you can configure by adding rules. In addition, other programs such as fail2ban also use iptables to block attackers.
>
> In this article, we’re going to take a look at how iptables works. We’re also going to look at a few examples, which will help you write your own rules.
>
:::spoiler Advanced usage & best practices
* [Best practices: iptables](https://major.io/2010/04/12/best-practices-iptables/)
* [Advanced Features of netfilter/iptables](https://linuxgazette.net/108/odonovan.html)
:::
:::spoiler iptables vs nftables
* [What is nftables, and how is it different from IPtables?](https://ungleich.ch/en-us/cms/blog/2018/08/18/iptables-vs-nftables/)
* [iptables vs nftables: What’s the Difference?](https://linuxhandbook.com/iptables-vs-nftables/)
:::
#### eBPF
[https://blogs.igalia.com/dpino/2019/01/07/introduction-to-xdp-and-ebpf/](https://blogs.igalia.com/dpino/2019/01/07/introduction-to-xdp-and-ebpf/)
> Continuing with the XDP series, in this post I briefly introduce this new technology. Then I focus on BPF and eBPF, which are fundamental to understand XDP
>
{%slideshare lcplcp1/introduction-to-ebpf-and-xdp %}
{%slideshare brendangregg/linux-bpf-superpowers %}
[BPF, eBPF, XDP and Bpfilter… What are These Things and What do They Mean for the Enterprise?](https://www.netronome.com/blog/bpf-ebpf-xdp-and-bpfilter-what-are-these-things-and-what-do-they-mean-enterprise/)
> You may have been following the development of the extended Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF) in the kernel community since 3.15, or you may still associate the Berkeley Packet Filter with the work Van Jacobson did in 1992. You may have used BPF for years with tcpdump, or you may have started to plumb it in your data plane already! This blog aims to describe, at very high level, the key developments from a performance networking point of view and why now this is becoming important to the network operator, sysadmin and enterprise solution provider in the same way that it has been relevant since its inception for the large scale data center operator.
>
[An overview of some eBPF use cases by Cloudflare](https://blog.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-architecture-and-how-bpf-eats-the-world/)
>:::spoiler Slides
>{%speakerdeck majek04/linux-at-cloudflare %}
> :::
[BPFILTER: the next-generation Linux firewall](https://linux-audit.com/bpfilter-next-generation-linux-firewall/)
> The Linux community has a continuous drive to enhance the GNU/Linux kernel. When we look at network traffic filtering, we moved from ipchains to iptables. More recently we saw the introduction of nftables. Next in line is BPFILTER, part of the development work for the Linux 4.18 kernel.
:::spoiler eBPF Tutorials
:::info
* [bcc Tutorial](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/docs/tutorial.md)
> This tutorial covers how to use bcc tools to quickly solve performance, troubleshooting, and networking issues.
* [The art of writing eBPF programs: a primer](https://sysdig.com/blog/the-art-of-writing-ebpf-programs-a-primer/)
> An example driven overview of writing eBPF programs used to intercept syscall data - aimed at creating an uderstanding of how the different parts of the eBPF VM work together.
* [bcc Python Developer Tutorial](https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/blob/master/docs/tutorial_bcc_python_developer.md)
> This tutorial is about developing bcc tools and programs using the Python interface. There are two parts: observability then networking.
* :thought_balloon: [Learn eBPF Tracing: Tutorial and Examples](http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2019-01-01/learn-ebpf-tracing.html)
:::
:::spoiler Even more eBPF
:::info
[Why is the kernel community replacing iptables with BPF?](https://cilium.io/blog/2018/04/17/why-is-the-kernel-community-replacing-iptables/)
> The Linux kernel community recently announced bpfilter, which will replace the long-standing in-kernel implementation of iptables with high-performance network filtering powered by Linux BPF, all while guaranteeing a non-disruptive transition for Linux users.
>
[Awesome eEBPF](https://github.com/zoidbergwill/awesome-ebpf)
> BPF, as in Berkeley Packet Filter, is an in-kernel virtual machine running programs passed from user space. Initially implemented on BSD, then Linux, the (now legacy) "classic BPF" or cBPF machine would be used with tools like tcpdump for filtering packets in the kernel to avoid useless copies to user space. More recently, the BPF infrastructure in Linux has been completely reworked and gave life to the "extended BPF", or eBPF, which gained new features (safety and termination checks, JIT-compiling for programs, persistent maps, a standard library, hardware offload support, etc.) and is now used for many tasks. Processing packets at a very low level (XDP), tracing and monitoring events on the system, or enforcing access control over cgroups are but a few examples to which eBPF brings performance, programmability and flexibility.
:::
#### Protocol multiplexing
:::info
[sshttp](https://github.com/stealth/sshttp)
> SSH/HTTP(S) multiplexer. Run a webserver and a sshd on the same port w/o changes
:::
### SSH
{%youtube VXgBYDzHBL4 %}
#### OpenSSH WikiBook
> The OpenSSH suite provides secure remote access and file transfer. Since its initial release, it has grown to become the most widely used implementation of the SSH protocol. During the first ten years of its existence, SSH has largely replaced older corresponding unencrypted tools and protocols. The OpenSSH client is included by default in most operating system distributions, including OS X, Linux, BSD, and Solaris. Any day you use the Internet, you are using and relying on hundreds if not thousands of machines operated and maintained using OpenSSH. A survey in 2008 showed that of the SSH servers found running, just over 80% were OpenSSH. Even with the advent of the Internet of Things and the increased use of IPv6, a cursory search of Shodan [3] for SSH-2.0 services on port 22 in April 2017 showed 56% of responding IPv4 addresses running OpenSSH.
>
> OpenSSH was first released towards the end of 1999. It is the latest step in a very long and useful history of networked computing, remote access, and telecommuting.
* [Overview](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/OpenSSH/Overview)
* [Multiplexing](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/OpenSSH/Cookbook/Multiplexing)
* [Load Balancing](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/OpenSSH/Cookbook/Load_Balancing)
* [Remote Processes](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/OpenSSH/Cookbook/Remote_Processes)
:::spoiler Some more OpenSSH tips & tricks
{%vimeo 54505525 %}
> * Can be used for remote port forwarding. Port from local machine will be exposed as port on remote machine so that all connections make on that remote machine port will be forwarded to your local machine. e.g. expose local Apache port to remote machine through ssh tunnel for testing non-deployed web apps. Share tmux session with many user with 0 configuration.
> * You can change ssh settings of a live connection through the ssh console without having to reconnect.
> * Can also do local port forwarding. i.e. connect to remote port through a local port. e.g. initiate VNC connection on a server which does not expose the VNC port to the outside world.
> * Can do dynamic port forwarding. Creates a SOCKS 5 proxy on your local machine. Makes all your network connections tunnel through ssh and go outbound from a remote machine. e.g. Use Netflix as if you are from another geographic location.
> * X11 forwarding
> * Agent forwarding. Forwards your private key to remote machine so that any connections made from the remote machine can authenticate you using your credentials on your local machine. e.g. ssh to remote machine, push code from there to your github using the credentials on the local machine.
> * Run a remote command (rather than a shell). Pipe data from the remote command through the ssh connection. e.g. use it in local scripts.
> * Can force remote command to execute for particular user when ssh connection created with the authorization_keys file.
> * Make your favorite options the default on a per server address basis.
> * Create host aliases. e.g. ssh mygit connects to git.myserver.com
> * ProxyCommand: configure how remote stdin/stdout is connect. e.g. automatically have an ssh connection to remote server connect to another ssh server on an internal private network that is not accessible from the outside.
> * Mutliplex connection: have multiple ssh connections all go through a single TCP/IP connection.
> * Compress data going through ssh connection
> * keepalive
> * SSHFS. Mount remote directories as if they were filesystems.
:thought_balloon: [ssh tricks - the usual and beyond ](http://www.jedi.be/blog/2010/08/27/ssh-tricks-the-usual-and-beyond/)
> SSH is an amazing beast. I nearly use it everyday and I'm amazed every time I learn something new. The following is a list of my tricks in the bag. It starts with the usual tricks that you find all over the place, but I hope there will be some new tricks for you too.
{%youtube kQ-y5WRZ %}
:::
### Modern Network Protocols
#### IPv6
{%slideshare phdays/ipv6-76552155 %}
{%youtube J9zxUtshREs %}
#### DNSSEC
{%speakerdeck mattiasgeniar/dnssec-the-good-the-bad-and-the-secure %}
[DNSSEC: An Introduction](https://blog.cloudflare.com/dnssec-an-introduction/)
:::spoiler More DNSSEC & Dane
{%speakerdeck shuque/dnssec-tutorial %}
{%speakerdeck shuque/dane-and-application-uses-of-dnssec %}
:::
#### TLS 1.3
{%speakerdeck tiran/tls-certificates-and-tls-1-dot-3 %}
* [A Detailed Look at RFC 8446 (a.k.a. TLS 1.3)](https://blog.cloudflare.com/rfc-8446-aka-tls-1-3/)
* [An Overview of TLS 1.3 – Faster and More Secure](https://kinsta.com/blog/tls-1-3/)
* :thought_balloon: [Why TLS 1.3 isn't in browsers yet](https://blog.cloudflare.com/why-tls-1-3-isnt-in-browsers-yet/)
#### Encrypted SNI
* [Encrypt it or lose it: how encrypted SNI works](https://blog.cloudflare.com/encrypted-sni/)
* :thought_balloon: [Issues and Requirements for SNI Encryption in TLS](https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-tls-sni-encryption-04)
:::spoiler HTTP/2 & Beyond
#### HTTP/2 & Beyond
{%speakerdeck robcrowley/2-the-future-of-the-web-today-ndc-sydney-2017 %}
{%vimeo 239705543 %}
* [HTTP/2 Overview](https://developers.google.com/web/fundamentals/performance/http2/)
* [HTTP/2 FAQ](https://http2.github.io/faq/)
{%speakerdeck ipeychev/http-2-dot-0-and-quic-protocols-of-the-near-future %}
{%youtube qyexqwG6fGI %}
* [QUIC - Redefining Internet Transport](https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/15e1bLKYeN56GL1oTJSF9OZiUsI-rcxisLo9dEyDkWQs/edit#slide=id.g99041b54d_0_0)
* [The Road to QUIC](https://blog.cloudflare.com/the-road-to-quic/)
* :thought_balloon: [QUIC Specification](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1gY9-YNDNAB1eip-RTPbqphgySwSNSDHLq9D5Bty4FSU/edit)
* :thought_balloon: [UDP-FEC](https://github.com/wangyu-/UDPspeeder/blob/branch_libev/README.md)
> A Tunnel which Improves your Network Quality on a High-latency Lossy Link by using Forward Error Correction,for All Traffics(TCP/UDP/ICMP)
:::
#### Content Addressable Networks
* [Overview](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Content_addressable_network)
* [IPFS](https://blog.cloudflare.com/distributed-web-gateway/)
* :thought_balloon: [Whitepaper](https://github.com/ipfs/papers/raw/master/ipfs-cap2pfs/ipfs-p2p-file-system.pdf)
* Dat
#### Multipath & Link aggregation
* [Link aggregation primer - Linux with two ADSL uplinks for agregation and failover](https://mlvpn.readthedocs.io/en/latest/linux_example.html)
* :thought_balloon: [MPTCP whitepaper](http://multipath-tcp.org/data/MultipathTCP-netsys.pdf)
* :thought_balloon: [Implementation and assessment of Modern Host-based Multipath Solutions](https://inl.info.ucl.ac.be/publications/implementation-and-assessment-modern-host-based-multipath-solutions)
> The Internet is changing: while devices used to be connected to the Internet through a single access link, we now see smart phones equipped with a wireless and a 3G interface, data-centres with many links between each machine, or company networks connected to several providers. Today, however, the available multiple links are not efficiently used. Smartphones can use only one access link at a time. Data-centres cannot fully utilise the available capacity of their many, expensive links. Company networks cannot route individual data flows through two providers simultaneously, for example to improve the end-user experience. Many research proposals have appeared in the last few years to overcome the above problems, in the form of new protocols, but in most cases they have not been implemented and their impact in real-world applications is not widely understood.
>
> This thesis fills this gap by concentrating on two approaches, the Ipv6 host-based multihoming solution (Shim6) and Multipath TCP (MPTCP). We developed the first reference implementation of both protocols in the Linux kernel. Our efforts show that they can both be efficient and can co-exist elegantly with existing protocols and operating systems architectures.
>
> We have measured the performance of both implementations. Our measurements indicate that MPTCP can significantly improve the performance of various environments including large data-centres such as Amazon EC2.
* :thought_balloon: [Improving datacenter performance and robustness with multipath TCP](https://inl.info.ucl.ac.be/publications/improving-datacenter-performance-and-robustness-multipath-tcp)
> The latest large-scale data centers offer higher aggregate bandwidth and robustness by creating multiple paths in the core of the network. To utilize this bandwidth requires different flows take different paths, which poses a challenge. In short, a single-path transport seems ill-suited to such networks. We propose using Multipath TCP as a replacement for TCP in such data centers, as it can effectively and seamlessly use available bandwidth, giving improved throughput and better fairness on many topologies. We investigate the reasons behind these benefits, teasing apart the contribution of each of the mechanisms used by MPTCP.
>
> Using MPTCP allows us to rethink data center networks, with a different mindset as to the relationship between transport protocols, routing and topology. MPTCP enables better topologies that single path TCP just can't use. As a proof-of-concept, we present a dual-homed variant of the FatTree topology. Using MPTCP, this outperforms FatTree for a wide range of workloads, but costs the same.
>
> In existing data center networks, MPTCP is readily deployable as it can leverage widely deployed technologies such as ECMP. We have run MPTCP on Amazon EC2 and found that it commonly outperforms TCP by a factor of three. But the biggest benefits will come when data centers are designed around the use of multipath transports.
## Private & Anonymous Communication
[5 Ways to Bypass Internet Censorship and Filtering](https://www.howtogeek.com/167418/5-ways-to-bypass-internet-censorship-and-filtering/)
> More and more Internet connections are being filtered, from public Wi-Fi and workplace connection filtering to ISP and country-level censorship. However, there are still ways to get around this filtering and view blocked websites.
[Internet anonymity overview](https://search.edwardsnowden.com/docs/InternetAnonymity20112014-12-28_nsadocs_snowden_doc)
:thought_balloon: [How to Watch Netflix or Hulu Through a VPN Without Being Blocked](https://www.howtogeek.com/239616/how-to-watch-netflix-hulu-and-more-through-a-vpn-without-being-blocked/)
:::info
[Streisand (an example setup for anonymous communications)](https://github.com/StreisandEffect/streisand)
> Streisand sets up a new server running your choice of WireGuard, OpenConnect, OpenSSH, OpenVPN, Shadowsocks, sslh, Stunnel, or a Tor bridge. It also generates custom instructions for all of these services. At the end of the run you are given an HTML file with instructions that can be shared with friends, family members, and fellow activists.
:::
### Tunneling
[Overview](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tunneling_protocol)
#### SSH
* [SSH Tunnelling](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/OpenSSH/Cookbook/Tunnels)
* [SSH Tunnelling TCP & UDP](https://blog.heyzimo.com/ssh-tunnels-udp-tcp/)
* [Proxies and Jump hosts](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/OpenSSH/Cookbook/Proxies_and_Jump_Hosts)
* :thought_balloon: [What is the difference between ssh ProxyCommand, -w, nc, exec nc?](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/22635613/what-is-the-difference-between-ssh-proxycommand-w-nc-exec-nc)
:::
##### Reverse Tunnels

* ==TODO: Something explaining the basic use case==
* [Poor man's ngrok with tcp proxy and ssh reverse tunnel](https://dev.to/k4ml/poor-man-ngrok-with-tcp-proxy-and-ssh-reverse-tunnel-1fm)
* :thought_balloon: [ngrok](https://ngrok.com/product), the industry standard for a reverse tunnel as a service, exposes local servers behind NATs and firewalls to the public internet over secure tunnels.
* :thought_balloon: [Roll your own Ngrok with Nginx, Letsencrypt, and SSH reverse tunnelling](https://jerrington.me/posts/2019-01-29-self-hosted-ngrok.html)
* :thought_balloon: [Serveo](https://serveo.net/) is an excellent alternative to ngrok. Serveo was inspired by ngrok and attempts to serve many of the same purposes. The primary advantage of Serveo over ngrok is the use of your existing SSH client, so there's no client application to install.
#### Onion Routing
* [Onion Routing](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Onion_routing)
* [The Onion Router](https://www.torproject.org/about/overview.html.en)
* :thought_balloon: [TOR FAQ](https://www.torproject.org/docs/faq.html.en)
> Ch. General, Advanced, Onion services, Anonymity & Security, Alternate Designs
* :thought_balloon: [Tor Path Specification](https://gitweb.torproject.org/torspec.git/tree/path-spec.txt)
> This document tries to cover how Tor chooses to build circuits and assign streams to circuits. Other implementations MAY take other approaches, but implementors should be aware of the anonymity and load-balancing implications of their choices.
* :thought_balloon: [Tor Rendezvous Specification](https://web.archive.org/web/20170828063408/https://gitweb.torproject.org/torspec.git/tree/rend-spec.txt)
> :::info
> One might think of TOR rendezvous as the TOR equivalent to SSH reverse tunnels
> :::
> Rendezvous points provide location-hidden services (server anonymity) for the onion routing network. With rendezvous points, Bob can offer a TCP service (say, a webserver) via the onion routing network, without revealing the IP of that service.
* :thought_balloon: [TOR pluggable transports](https://trac.torproject.org/projects/tor/wiki/doc/PluggableTransports)
* [meek](https://trac.torproject.org/projects/tor/wiki/doc/meek)
> meek is a pluggable transport, an obfuscation layer for Tor designed to evade Internet censorship. Traffic is relayed through a third-party server that is hard to block, for example a CDN. It uses a trick called domain fronting to talk to a Tor relay while appearing to talk to another domain.
#### VPN
* [Overview](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_private_network)
* [Protocol (IPSec, PPTP, OpenVPN, WireGuard) Comparison](https://www.ivpn.net/pptp-vs-ipsec-ikev2-vs-openvpn-vs-wireguard)
:::spoiler VPN Protocols
##### IPSec
* [VPNs and VPN Technologies](http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=24833&seqNum=3)
* [Understanding VPN IPSec Tunnel Mode and IPSec Transport Mode - What's the Difference?](http://www.firewall.cx/networking-topics/protocols/870-ipsec-modes.html)
##### OpenVPN
* [Understanding the User-Space VPN: History, Conceptual Foundations, and Practical Usage](https://web.archive.org/web/20161231020126/https://openvpn.net/papers/BLUG-talk/)
* :thought_balloon: [OpenVPN Protocol](https://openvpn.net/index.php/open-source/documentation/security-overview.html)
##### WireGuard
{%youtube BSI38qPRgXo %}
* :thought_balloon: [Whitepaper](https://www.wireguard.com/papers/wireguard.pdf)
* :thought_balloon: [BoringTun, a userspace WireGuard implementation in Rust](https://blog.cloudflare.com/boringtun-userspace-wireguard-rust/)
* [BoringTun](https://github.com/cloudflare/boringtun)
> BoringTun is an implementation of the WireGuard® protocol designed for portability and speed.
>
>The project consists of two parts:
>
> * The executable boringtun, a userspace WireGuard implementation for Linux and macOS.
> * The library boringtun that can be used to implement fast and efficient WireGuard client apps on various platforms, including iOS and Android. It implements the underlying WireGuard protocol, without the network or tunnel stacks, those can be implemented in a platform idiomatic way.
:::
### DNS Privacy
{%slideshare MenandMice/how-to-send-dns-over-anything-encrypted %}
:::spoiler Talk video
{%youtube HX4QwYofU98 %}
:::
* [The Problem](https://dnsprivacy.org/wiki/display/DP/DNS+Privacy+-+The+Problem)
* [The Solutions](https://dnsprivacy.org/wiki/display/DP/DNS+Privacy+-+The+Solutions)
* :::spoiler
* [DNS over TLS / DNS over HTTPS - Is it the privacy magic bullet?](https://blog.sean-wright.com/dns-over-tls-dns-over-https-is-it-the-privacy-magic-bullet-2/)
* [A cartoon intro to DNS over HTTPS](https://hacks.mozilla.org/2018/05/a-cartoon-intro-to-dns-over-https/)
* [DNScrypt](https://www.opendns.com/about/innovations/dnscrypt/)
* [DNS over TLS vs DNSCrypt](https://tenta.com/blog/post/2017/12/dns-over-tls-vs-dnscrypt)
* [A good comparison of different encrypted DNS solution](https://dnscrypt.info/faq/)
* [Anonymized DNS](https://github.com/DNSCrypt/dnscrypt-proxy/wiki/Anonymized-DNS)
* [Beating DNS-over-HTTPS & DNS-over-TLS](https://blog.sean-wright.com/beating-dns-over-https-dns-over-tls/)
:::
## Server Maintenace
### Management, Monitoring & Automation
* [Deploying at Scale](https://blog.appdynamics.com/engineering/deploying-at-scale-chef-puppet-ansible-fabric-and-saltstack/ )
{%slideshare MajorHayden/securing-openstack-and-beyond-with-ansible %}
{%youtube E67zaS_UZks %}
{%speakerdeck makash/system-hardening-using-ansible %}
* [Automated Infrastructure Security Monitoring & Defence](https://github.com/appsecco/nullblr-bachaav-aismd/blob/master/Docs/workshop.md)
* :thought_balloon: [Netdata - performance and health monitoring for systems and application](https://github.com/firehol/netdata/wiki)
{%slideshare AlexMaestretti/security-monitoring-with-ebpf %}
:::spoiler Performance analysis with eBPF
{%slideshare brendangregg/usenix-atc-2017-performance-superpowers-with-enhanced-bpf %}
{%youtube oc9000dM9-k %}
:::
{%slideshare Splunk/splunklive-zurich-2018-getting-started-hands-on %}
:::info
[Do the Splunk tutorial](https://www.splunk.com/goto/book)
:::
### Linux Server Hardening
* [How to secure a Linux system](https://linux-audit.com/how-to-secure-linux-systems-auditing-hardening-and-security/)
* [OpenSSH security and hardening](https://linux-audit.com/audit-and-harden-your-ssh-configuration/)
* :thought_balloon: [TCP/IP stack hardening](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Sysctl#TCP/IP_stack_hardening)
* :thought_balloon: [Kernel hardening](https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Security#Kernel_hardening)
* :thought_balloon: [Automated security hardening for Linux hosts with Ansible](https://docs.openstack.org/ansible-hardening/latest/)
* :thought_balloon: [Server Hardening Automation](https://dev-sec.io/)
* [Lynis (auditing tool) - Introduction & How it works?](https://cisofy.com/lynis/#introduction)
* :thought_balloon: Run Lynis on a server and dig into the tests
* [Port Knocking](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Port_knocking)
* [Critique](https://www.linux.com/news/critique-port-knocking)
* :thought_balloon: [In-depth overview](http://portknocking.org/view/)
* :thought_balloon: Tutorials
* [How To Use Port Knocking to Hide your SSH Daemon from Attackers](https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-use-port-knocking-to-hide-your-ssh-daemon-from-attackers-on-ubuntu)
* [How To Use fwknop to Enable Single Packet Authentication](https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-use-fwknop-to-enable-single-packet-authentication-on-ubuntu-12-04)
* [How To Configure Port Knocking Using Only Iptables](https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-configure-port-knocking-using-only-iptables-on-an-ubuntu-vps)
* :thought_balloon: [Webknocking](https://stefan.lebelt.info/old/?item=webknocking_en)
:::info
[fwknop](https://github.com/mrash/fwknop)
> fwknop implements an authorization scheme known as Single Packet Authorization (SPA) for strong service concealment. SPA requires only a single packet which is encrypted, non-replayable, and authenticated via an HMAC in order to communicate desired access to a service that is hidden behind a firewall in a default-drop filtering stance. The main application of SPA is to use a firewall to drop all attempts to connect to services such as SSH in order to make the exploitation of vulnerabilities (both 0-day and unpatched code) more difficult. Because there are no open ports, any service that is concealed by SPA naturally cannot be scanned for with Nmap.
:::
:::info
[fail2ban](https://github.com/fail2ban/fail2ban)
> Daemon to ban hosts that cause multiple authentication errors
:::
* [How Fail2Ban Works to Protect Services on a Linux Server](https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-fail2ban-works-to-protect-services-on-a-linux-server)
* [How To Protect an Nginx Server with Fail2Ban](https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-protect-an-nginx-server-with-fail2ban-on-ubuntu-14-04)
* :thought_balloon: [ENRW Linux Hardening Guide](https://github.com/ernw/hardening/blob/master/operating_system/linux/ERNW_Hardening_Linux.md)
:::spoiler A Guide to Securing Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
* [Chapter 1.3. Vulnerability Assessment](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html-single/security_guide/#sec-Vulnerability_Assessment)
* [Chapter 1.4. Security Threats](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html-single/security_guide/#sec-Security_Threats)
* [Chapter 1.5. Common Exploits and Attacks](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html-single/security_guide/#sec-Common_Exploits_and_Attacks)
* [Chapter 4. Hardening Your System with Tools and Services](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html-single/security_guide/#chap-Hardening_Your_System_with_Tools_and_Services)
* [Chapter 5. Using Firewalls](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html-single/security_guide/#sec-Using_Firewalls)
* [Chapter 6. System Auditing](https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html-single/security_guide/#chap-system_auditing)
:::
* :thought_balloon: [psad: Intrusion Detection and Log Analysis with iptables](https://cipherdyne.org/psad/)
> psad is a collection of three lightweight system daemons (two main daemons and one helper daemon) that run on Linux machines and analyze iptables log messages to detect port scans and other suspicious traffic. A typical deployment is to run psad on the iptables firewall where it has the fastest access to log data.
* :thought_balloon: [LRKG](https://openwall.info/wiki/p_lkrg/Main)
> The Linux Kernel Runtime Guard protects system by comparing hashes which are calculated from the most important kernel region / sections / structures with the internal database hashes. Additionally, special efforts have been made to individually protect all extensions of the kernel (modules). To make the project fully functional, the module should be initially loaded on a clean system – e.g. directly after installation or after booting clean system. At this mom
:::info
#### Server forensic examination
* [Fishing for Hackers: analysis of a Linux Server Attack](https://sysdig.com/blog/fishing-for-hackers/)
* [Fishing for Hackers (Part 2): Quickly Identify Suspicious Activity With Sysdig](https://sysdig.com/blog/fishing-for-hackers-part-2/)
* [Catching a new CDorked.A variant](https://reverse.put.as/2014/02/05/linuxhackingteamrdorks-a-a-new-and-improved-version-of-linuxcdorked-a/)
:::
## Web Hosting
### Basics & Overview
* [Web Hosting & Domain 101: How Hosting a Website Works](https://www.webhostingsecretrevealed.net/web-hosting-beginner-guide/)
* [The Basics of Web Hosting](https://www.hostingadvice.com/the-basics/)
* :thought_balloon: Apples, Oranges and Hosting Providers: Heterogeneity and Security in the Hosting Market
{%pdf http://mkorczynski.com/Noms16Tajalizadehkhoob.pdf %}
#### Hosting products

[The Shared Responsibility Model](https://www.synopsys.com/blogs/software-security/shared-responsibility-model-cloud-security/)
:::spoiler Additional "Shared Responsibility Model" infographics
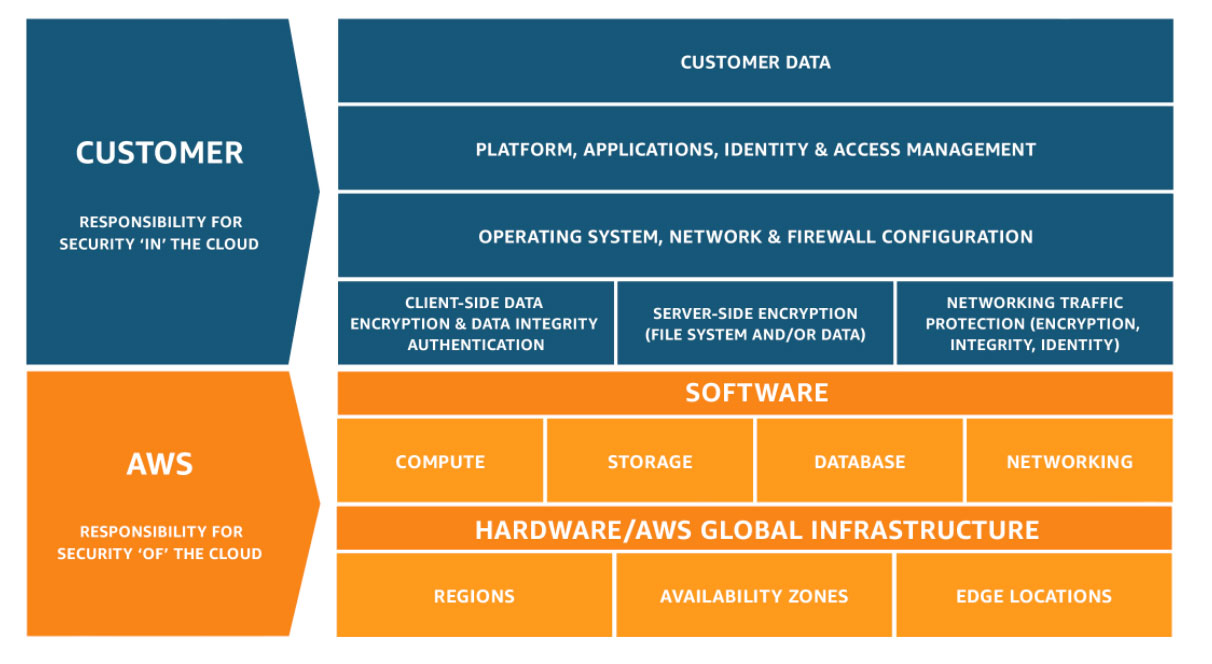
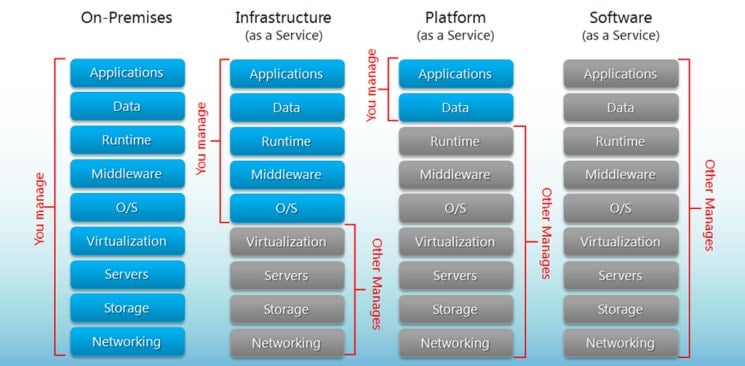
:::
[IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS Cloud Models](https://www.hostingadvice.com/how-to/iaas-vs-paas-vs-saas/)
> In the context of hosting services/products -
> * [Dedicated server hosting](https://hostadvice.com/hosting-guides/dedicated-server-hosting-guide/) is the equivalent of on-prem solution, where sometimes a service agreement with the provider is sometimes available.
> * [VPS Hosting](https://hostadvice.com/hosting-guides/vps-hosting-guide/) can be considered a very limited (up to legacy) version of PaaS offering.
> * A modern PaaS alternatives are often called [container hosting](https://hostadvice.com/hosting-guides/container-hosting/) or [elastic cloud hosting](https://hostadvice.com/hosting-guides/elastic-cloud-hosting/).
> True IaaS solutions are often marketed as [cloud hosting](https://hostadvice.com/hosting-guides/guide-to-cloud-hosting/) or [public cloud hosting](https://hostadvice.com/hosting-guides/public-cloud-hosting).
* [Ultimate Guide to Web Hosting Panels](https://hostadvice.com/hosting-guides/ultimate-guide-to-web-panels/)
* [What is WHMCS and Why Is It Crucial for Reseller Hosting?](https://www.liquidweb.com/blog/whmcs-crucial-reseller-hosting/)
* [WHMCS overview](https://www.whmcs.com/tour/)
* [Ultimate Guide to Billing Management Software for Web Hosts](https://www.hostingadvice.com/blog/whmcs-vs-blesta-vs-billmanager-vs-others/)
:::info
#### Malicious Infrastructure
* Under the Shadow of Sunshine: Understanding and Detecting Bulletproof Hosting on Legitimate Service Provider Networks
{%pdf https://www.computer.org/csdl/proceedings/sp/2017/5533/00/07958611.pdf %}
* The Role of Hosting Providers in Fighting Command and Control Infrastructure of Financial Malware
{%pdf https://pure.tudelft.nl/portal/files/24953899/asiaccs2017_zeus_hosting_3.pdf %}
:::
### DNS
* [Managing DNS for web hosting](https://hostadvice.com/hosting-guides/managing-dns-for-web-hosting/)
* [The Privacy Conundrum in Domain Registration](http://actnowdomains.com/the-privacy-conundrum-in-domain-registration.htm)
* :thought_balloon: Alt-DNS
* [OpenNIC](https://wiki.opennic.org/start)
* [EmerDNS](https://emercoin.com/en/documentation/blockchain-services/emerdns/emerdns-introduction)
* [Namecoin (dot-bit)](https://bit.namecoin.org/)
* [DNS sinkhole](http://www.sans.org/reading-room/whitepapers/dns/dns-sinkhole-33523)
* [No, DNSSEC Would NOT Help Prevent Microsoft's Seizure Of Domains](https://www.internetsociety.org/blog/2014/07/no-dnssec-would-not-help-prevent-microsofts-seizure-of-domains/)
### SSL/TLS & PKI
* [SSL/TLS and PKI History](https://www.feistyduck.com/ssl-tls-and-pki-history/)
* [The Ultimate Guide to SSL and TLS](https://www.dreamhost.com/blog/ultimate-guide-ssl-tls/)
* [What is a CSR (Certificate Signing Request)?](https://www.sslshopper.com/what-is-a-csr-certificate-signing-request.html)
* [SSL Issuer Popularity](https://web.archive.org/web/20180627085132/https://nettrack.info/ssl_certificate_issuers.html)
* [Let's Encrypt](https://letsencrypt.org/how-it-works/)
* [Free Certs Come With a Cost](https://threatpost.com/free-certs-come-with-a-cost/126861/)
* :thought_balloon: [Let's Encrypt are enabling the bad guys, and why they should](https://scotthelme.co.uk/lets-encrypt-are-enabling-the-bad-guys-and-why-they-should/)
* :thought_balloon: [What Are The Different Types of SSL Certificates?](https://www.globalsign.com/en/ssl-information-center/types-of-ssl-certificate/)
* :thought_balloon: [Are EV certificates worth the paper they're written on?](https://scotthelme.co.uk/are-ev-certificates-worth-the-paper-theyre-written-on/)
* :thought_balloon: [SSL and TLS Deployment Best Practices](https://github.com/ssllabs/research/wiki/SSL-and-TLS-Deployment-Best-Practices)
* :thought_balloon: [Certificate Transparency Logs Overview](https://www.certificate-transparency.org/what-is-ct)
* [How Certificate Transparency Works](https://www.certificate-transparency.org/how-ct-works)
* [How Log Proofs Work](https://www.certificate-transparency.org/log-proofs-work)
:::info
[Nginx Quick Reference](https://github.com/trimstray/nginx-quick-reference)
> These notes describe how to improve Nginx performance, security and other important things
:::
## Privacy & Anonymous Payments
### Anonymous payment methods
* [The difference between a prepaid card, a credit card, and a debit card](https://www.consumerfinance.gov/ask-cfpb/what-is-the-difference-between-a-prepaid-card-a-credit-card-and-a-debit-card-en-433/)
* [What is Cryptocurrency: Everything You Must Need To Know!](https://blockgeeks.com/guides/what-is-cryptocurrency/)
* :thought_balloon: [Through introduction to cryptocurrency](https://cryptocurrencyfacts.com/)
* [What are Virtual Credit Cards and how and where do you get them?](https://www.thewindowsclub.com/virtual-credit-cards)
* :thought_balloon: [Best Virtual and Prepaid Cards for International Shoppers](https://tech-vise.com/vise-review-best-virtual-debit-cards/)
* :thought_balloon: [A list of payment methods accepted by QHoster](https://www.qhoster.com/payment-methods.html)
### Fraud & money laundering
#### Legislation
* [4th EU AML Directive: What you should know](http://www.bobsguide.com/guide/news/2017/Sep/14/4th-eu-aml-directive-what-you-should-know/)
* [Entropay Classic Account](http://support.entropay.com/customer/en_gb/portal/articles/2829859-what-is-a-classic-account-?b_id=908)
> Showcasing the effect of anti-gambling regulation
#### Credit card verification
* [KYC, CDD, EDD](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Know_your_customer)
* [AVS](https://chargebacks911.com/knowledge-base/what-is-address-verification-service/)
* :thought_balloon: [Address Verification System](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Address_Verification_System)
##### Putting it all together
> An example (from Entorpay, a virtual debit card supplier) to limits imposed by regulation and KYC & verification process used to lift those limits
* [What are the Entropay account levels?](http://support.entropay.com/customer/en_gb/portal/articles/2829866-what-are-the-entropay-account-levels-?b_id=908)
* [How do I upgrade my Entropay account level?](http://support.entropay.com/customer/en_gb/portal/articles/2829867-how-do-i-upgrade-my-entropay-account-level-?b_id=908)
* :thought_balloon: [Card Security Code](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Card_security_code)
#### AntiFraud
* [Overview]() #TODO
* Maxmind minFraud
* [Overview](https://www.maxmind.com/en/solutions/minfraud-services)
* [Data Points](https://www.maxmind.com/en/solutions/minfraud-services/data-points)
* [Factors](https://www.maxmind.com/en/solutions/minfraud-services/minfraud-factors)
### Privacy Regulation
* [The GDPR Overview](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/General_Data_Protection_Regulation)
* [MarTech Today’s Guide to GDPR — The General Data Protection Regulation](https://martechtoday.com/guide/gdpr-the-general-data-protection-regulation)
* :thought_balloon: [The GDPR (annotated) full text](https://gdpr-info.eu/)
* [GPDR & WHOIS](https://www.recordedfuture.com/whois-gdpr-icann/)
## Red Team Infrastructure
* [Red Team Infrastructure Wiki](https://github.com/bluscreenofjeff/Red-Team-Infrastructure-Wiki)
> A wiki to collect Red Team infrastructure hardening resources
* [Being a Good Domain Shepherd](http://posts.specterops.io/being-a-good-domain-shepherd-57754edd955f)
> Consideration for choosing domains
:::info
#### Automation
* [Automated Red Team Infrastructure Deployment with Terraform - Part 1 ](https://rastamouse.me/2017/08/automated-red-team-infrastructure-deployment-with-terraform---part-1/)
* [Automated Red Team Infrastructure Deployment with Terraform - Part 2 ](https://rastamouse.me/2017/09/automated-red-team-infrastructure-deployment-with-terraform---part-2/)
* [Red Baron](https://github.com/byt3bl33d3r/Red-Baron)
> Automate creating resilient, disposable, secure and agile infrastructure for Red Teams
:::
:::info
#### Primer - CIA Hive
> WikiLeaks leaked CIA redirector infrastructure
* [Vault7 - Hive documentation leak](https://wikileaks.org/vault7/document/#hive)
* [Vault8 - Hive source code leak](https://wikileaks.org/vault8/)
* [Kaspersky Lab Responds To New Wikileaks Analysis Of Fake SSL Certificates Used By The CIA's Project Hive](https://steemit.com/wikileaks/@fortified/vault-8-or-kaspersky-lab-responds-to-new-wikileaks-analysis-of-fake-ssl-certificates-used-by-the-cia-s-project-hive)
* :thought_balloon: [Vault8 Hive](https://github.com/soufianetahiri/Vault-8-Hive)
> The leaked Hive source code
:::
### C&C Communication
Command and Control (C2) is at the center of successful malware development.
[Flying a False Flag: Advanced C2, Trust Conflicts, and Domain Takeover](http://i.blackhat.com/USA-19/Wednesday/us-19-Landers-Flying-A-False-Flag-Advanced-C2-Trust-Conflicts-And-Domain-Takeover.pdf)
{%pdf http://i.blackhat.com/USA-19/Wednesday/us-19-Landers-Flying-A-False-Flag-Advanced-C2-Trust-Conflicts-And-Domain-Takeover.pdf %}
> This talk discusses the methodology, selection process, and challenges of modern C2. It covers the details of recent HTTP/S advancements and tooling for new cloud service primitives such as SQS, AppSpot, S3, and CloudFront.
#### Abusing 3rd-Party Services ([T1102](https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1102/))
* [An Overview of Public Platform C2's](https://kindredsec.com/2019/08/12/an-overview-of-public-platform-c2s/) - A very good article describing the dis/advantages and various considerations for using public platforms (services) for C2 comms, including real life examples.
> Firstly, in order for a platform to be utilized in a coherent P2C2 the platform must have a somewhat mature and accessible API. Programmatically interacting with any sort of service requires an API that developers can easily utilize;
> ...
> The next requirement is disposable and easy-to-obtain accounts and API keys.
> ...
> The final requirement is the ability to control access to your communications within the platform.
* C&C-as-a-Service: abusing third-party web services as C&C channels
{%pdf https://virusbulletin.com/uploads/pdf/conference_slides/2015/Lehtio-VB2015.pdf %}
:::info
{%youtube RNvJcdmd894 %}
:thought_balloon: Whitepaper
{%pdf https://www.virusbulletin.com/uploads/pdf/conference/vb2015/Lehtio-VB2015.pdf %}
:::
{%slideshare sixdub/abusing-accepted-risk-with-3rd-party-c2-hackmiamicon5 %}
:::info
{%youtube 0DJfrfuSy44 %}
:::
:::info
[CloudFusion](https://github.com/joe42/CloudFusion)
> Linux file system (FUSE) to access Dropbox, Sugarsync, Amazon S3, Google Storage, Google Drive or WebDAV servers.
:::
* [Simplifying Domain Fronting](https://medium.com/@malcomvetter/simplifying-domain-fronting-8d23dcb694a0)
* :thought_balloon: [Domain fronting through Cloudflare](https://digi.ninja/blog/cloudflare_example.php)
* Blocking-resistant communication through domain fronting
{%pdf http://www.icir.org/vern/papers/meek-PETS-2015.pdf %}
* [Facing the Darkness: Domain Shadowing is Breaking the Internet](https://www.riskiq.com/blog/labs/facing-the-darkness-domain-shadowing-is-breaking-the-internet/)
* :thought_balloon: [Angler Lurking in the Domain Shadows](https://blogs.cisco.com/security/talos/angler-domain-shadowing)
## Misc
### Architecture
* N-Tier architecture - http://www.bmc.com/blogs/n-tier-architecture-tier-2-tier-3-and-multi-tier-explained/
* Distributed vs Decentralized - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7S1IqaSLrq8
* :thought_balloon: Distributed architecture - https://www.tutorialspoint.com/software_architecture_design/distributed_architecture.htm
#### Web Applications
* Proxy server - https://www.tutorialspoint.com/internet_technologies/proxy_servers.htm
* Web server - https://www.tutorialspoint.com/internet_technologies/web_servers.htm
* App server - https://www.javaworld.com/article/2077354/learn-java/app-server-web-server-what-s-the-difference.html
* :thought_balloon: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/936197/what-is-the-difference-between-application-server-and-web-server/936257#936257
### Project Management
* Software Project Survival Guide/Steve McConnell (https://www.zuj.edu.jo/download/software-project-survival-guide-pdf/)
* Agile Coach - https://www.atlassian.com//agile