# SUNBURST / Solorigate Writeups & Major Points
[TOC]
###### Bit's and bytes yet left to document here
- [ ] Volexity post on SAML golden ticket
- [ ] Microsoft's view on the matter
## Timeline
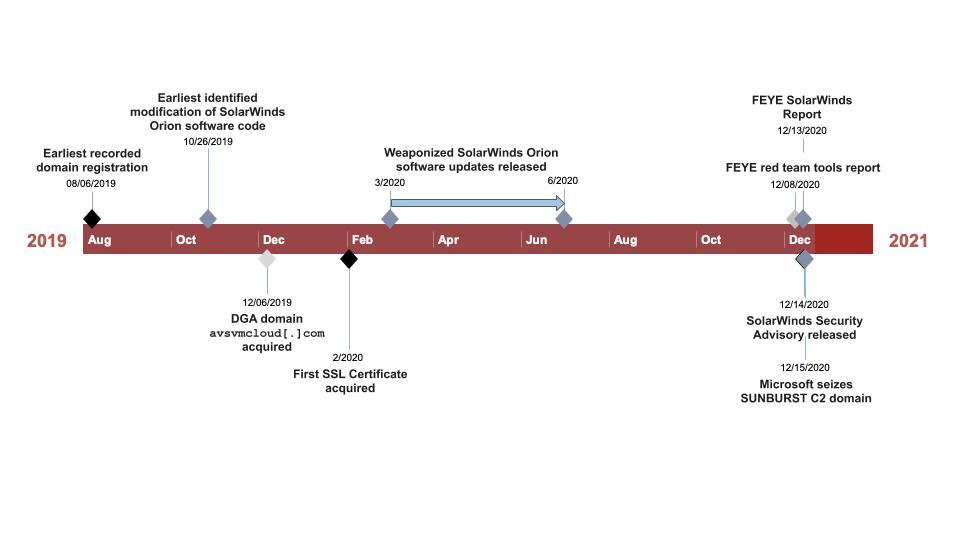
(Source: [A Timeline Perspective of the SolarStorm Supply-Chain Attack](https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/solarstorm-supply-chain-attack-timeline/))
## TTP Overview
## Detection
## References & Publications
### 08/12/2020
[FireEye Shares Details of Recent Cyber Attack, Actions to Protect Community](https://www.fireeye.com/blog/products-and-services/2020/12/fireeye-shares-details-of-recent-cyber-attack-actions-to-protect-community.html)
> Recently, Fireeye was attacked by a highly sophisticated threat actor, one whose discipline, operational security, and techniques lead Fireeye to believe it was a state-sponsored attack. Fireeye's number one priority is working to strengthen the security of Fireeye customers and the broader community. Fireeye hopes that by sharing the details of our investigation, the entire community will be better equipped to fight and defeat cyber attacks. During this attack Fireeye's red team tools were stolen.
>
> To empower the community to detect these tools, Fireeye are publishes countermeasures to help organizations identify these tools if they appear in the wild. In response to the theft of Fireeye's Red Team tools, Fireeye have released hundreds of countermeasures for publicly available technologies like OpenIOC, Yara, Snort, and ClamAV.
>
> [FireEye Red Team Tool Countermeasures](https://github.com/fireeye/red_team_tool_countermeasures)
### 09/12/2020
[Spies with Russia’s foreign intelligence service believed to have hacked a top American cybersecurity firm and stolen its sensitive tools](https://www.washingtonpost.com/national-security/leading-cybersecurity-firm-fireeye-hacked/2020/12/08/a3369aaa-3988-11eb-98c4-25dc9f4987e8_story.html)
> “Consistent with a nation-state cyber-espionage effort, the attacker primarily sought information related to certain government customers” << this is the critical sentence. “Primarily sought information related to certain government customers”. Not “primarily sought hacking tools
>
> —[thaddeus e. grugq (@thegrugq)](https://twitter.com/thegrugq/status/1336487831263346689)
### 13/12/2020
[Highly Evasive Attacker Leverages SolarWinds Supply Chain to Compromise Multiple Global Victims With SUNBURST Backdoor](https://www.fireeye.com/blog/threat-research/2020/12/evasive-attacker-leverages-solarwinds-supply-chain-compromises-with-sunburst-backdoor.html)
###### tags: `detection` `ttp`
==Worth reading atleast for the solid detection advice - which can be generally applicable.==
#### Main Takeaways
* FireEye discovered a supply chain attack trojanizing SolarWinds Orion business software updates in order to distribute malware.
* Actor tracked as UNC2452/DarkHalo.
* Employed malware is tracked as SUNBURN/Solorigate.
* This campaign may have begun as early as Spring 2020 (==starting at least from March 2020==).
* IOCs are available at [SunBurst Countermeasures](https://github.com/fireeye/sunburst_countermeasures) and developments (including additional IOCs) can be tracked at [OTX](https://otx.alienvault.com/pulse/5fdce61ef056eff2ce0a90de)
* > [name=Fireeye SUNBURST Report]
> ==After an initial dormant period of up to two weeks, it retrieves and executes commands, called “Jobs”, that include the ability to transfer files, execute files, profile the system, reboot the machine, and disable system services. The malware masquerades its network traffic as the Orion Improvement Program (OIP) protocol and stores reconnaissance results within legitimate plugin configuration files allowing it to blend in with legitimate SolarWinds activity. The backdoor uses multiple obfuscated blocklists to identify forensic and anti-virus tools running as processes, services, and drivers.==
>
* 12-14 Days dwell time (checked on execution - by comparing current time to the filesystem write time).
* Command and control traffic masquerades as the legitimate Orion Improvement Program
* Code hides in plain site by using fake variable names and tying into legitimate components
* Tries to resolve api.solarwinds.com to test the network for connectivity.
* Co-occurs with COSMICGALE and SUPERNOVA malwares, but yet to be proven conected to them.
* The attackers deployed a previously unseen memory-only dropper Fireeye dubbed TEARDROP to deploy Cobalt Strike BEACON.
* The actor sets the hostnames on their command and control infrastructure to match a legitimate hostname found within the victim’s environment.
> [name=Fireeye SUNBURST Report]
> ==The attacker infrastructure leaks its configured hostname in RDP SSL certificates, which is identifiable in internet-wide scan data. This presents a detection opportunity for defenders -- querying internet-wide scan data sources for an organization’s hostnames can uncover malicious IP addresses that may be masquerading as the organization. (Note: IP Scan history often shows IPs switching between default (WIN-\*) hostnames and victim’s hostnames) Cross-referencing the list of IPs identified in internet scan data with remote access logs may identify evidence of this actor in an environment. There is likely to be a single account per IP address.==
>
* DGA encoded machine domain name, used to selectively target victims
* A userID is generated by computing the MD5 of a network interface MAC address that is up and not a loopback device, the domain name, and the registry value HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Cryptography\MachineGuid.
* Subdomains are generated by concatenating a victim userId with a reversible encoding of the victims local machine domain name.
> [name=Fireeye SUNBURST Report]
> Records within the following ranges will terminate the malware and update the configuration key ReportWatcherRetry to a value that prevents further execution:
> * 10.0.0.0/8
> * 172.16.0.0/12
> * 192.168.0.0/16
> * 224.0.0.0/3
> * fc00:: - fe00::
> * fec0:: - ffc0::
> * ff00:: - ff00::
> * 20.140.0.0/15
> * 96.31.172.0/24
> * 131.228.12.0/22
> * 144.86.226.0/24
* The attacker primarily used only IP addresses originating from the same country as the victim, leveraging Virtual Private Servers.
* The attacker gained access to the network with compromised credentials, they moved laterally using multiple different credentials.
> [name=Fireeye SUNBURST Report]
> ==The credentials used for lateral movement were always different from those used for remote access.==
>
* > [name=Fireeye SUNBURST Report]
> ==The attacker used a temporary file replacement technique to remotely execute utilities: they replaced a legitimate utility with theirs, executed their payload, and then restored the legitimate original file. They similarly manipulated scheduled tasks by updating an existing legitimate task to execute their tools and then returning the scheduled task to its original configuration. They routinely removed their tools, including removing backdoors once legitimate remote access was achieved.==

> [name=Fireeye SUNBURST Report]
> ==This campaign’s post compromise activity was conducted with a high regard for operational security, in many cases leveraging dedicated infrastructure per intrusion. This is some of the best operational security that FireEye has observed in a cyber attack, focusing on evasion and leveraging inherent trust.==
### 14/12/2020
###### tags: `detection`
:information_source: A really nice overview from Nick Carr, including some solid, and less talked about, detection advice.
> So you want to talk about the massive software supply chain intrusion & the most carefully-planned, complex espionage I’ve ever helped uncover?
>
> Start here: https://fireeye.com/blog/threat-research/2020/12/evasive-attacker-leverages-solarwinds-supply-chain-compromises-with-sunburst-backdoor.html :star-struck:
>
> But then what?? Let’s talk about some post-compromise techniques...
>
> —[Nick Carr (@ItsReallyNick)](https://twitter.com/ItsReallyNick/status/1338382939835478016)
---
###### tags: `pdns` `intel`
:information_source: A twitter post by Brian Krebs, alleging, based on PDNS data that the SUNBURST backdoor was first deployed on 22/03/2020 at the earliset.
> Researchers at @oscontext say the first traffic they saw to the malware controllers in the SolarWinds infrastructure was on 4/4/2020. Fireeye said the malware was config'd to sleep for 2 weeks post-install. Suggests first targets were hit sometime in March
>
> —[Brain Krebs (@briankrebs)](https://twitter.com/briankrebs/status/1338544262435237892)
---
### 15/12/2020
[Microsoft and industry partners seize key domain used in SolarWinds hack](https://www.zdnet.com/article/microsoft-and-industry-partners-seize-key-domain-used-in-solarwinds-hack/)
###### tags: `mitigation`
> [name=Catalin Cimpanu]
> An overview of a protective action taken by Microsoft & FireEye to sieze the domain used by SUNBURN to create a killswitch & a sinkhole.
>

### 16/12/2020
###### tags: `pdns` `intel`
:information_source: QiAnXin Technology published a way to decode the SUNBURST DGA sub-domains, thus creating a probable victim list (or at least a partial list of domains SUNBURST was deployed to).
> By decoding the #DGA domain names, we discovered nearly a hundred domains suspected to be attacked by #UNC2452 #SolarWinds, including universities, governments and high tech companies such as @Intel and @Cisco. Visit our github project to get the script.
>
> https://github.com/RedDrip7/SunBurst_DGA_Decode
> —[RedDrip Team (@RedDrip7)](https://twitter.com/RedDrip7/status/1339168187619790848)
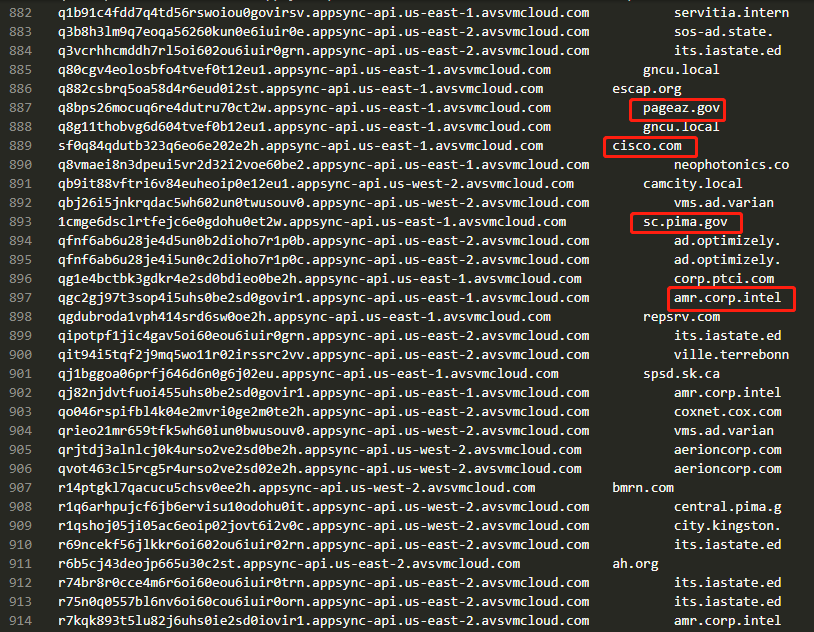
:::spoiler Full decoded list
https://intelx.io/?did=68ef7949-8ebd-4cfb-98ad-7eda25f26cc5
(Based on [DGA sub-domains gathered by bambenek](https://github.com/bambenek/research/blob/main/sunburst/uniq-hostnames.txt), based on Open-Source Context & Farsight. And some [important notes](https://github.com/bambenek/research/blob/main/sunburst/Important-Notes.md) on how this list was generated \[and the limits of PDNS\])
:::
---
###### tags: `ttp`
:information_source: A Twitter thread by Checkpoint's Itay Cohen - highlighting some more OPSEC aspects of SUNBURN, this time describing their approach to avoid the SolarWinds network itself.
> The attackers behind the #SUNBURST malware put a lot of effort into trying to avoid detection by analysts and security vendors. Not only this, but they also tried to make sure to stay under the radar of #SolarWinds developers and employees. A thread >>
> —[Itay Cohen (@megabeets_)](https://twitter.com/megabeets_/status/1339308801112027138)
---
[SunBurst: the next level of stealth](https://blog.reversinglabs.com/blog/sunburst-the-next-level-of-stealth?utm_campaign=2020%20Research&utm_content=149279712&utm_medium=social&utm_source=twitter&hss_channel=tw-146486666)
###### tags: `ttp`
> [name=Tomislav Peričin]
> ReversingLabs' research into the anatomy of this supply chain attack unveiled conclusive details showing that Orion software build and code signing infrastructure was compromised. The source code of the affected library was directly modified to include malicious backdoor code, which was compiled, signed and delivered through the existing software patch release management system.
>
:information_source: Analysis of metadata (especially timestamps) & decompiled code for various versions of `SolarWinds.Orion.Core.BusinessLayer.dll` to forensically support the claim that Orion software build and code signing infrastructure was compromised, and source code was directly modified to include the malicious backdoor.
### 18/12/2020
[Hackers last year conducted a 'dry run' of SolarWinds breach](https://news.yahoo.com/hackers-last-year-conducted-a-dry-run-of-solar-winds-breach-215232815.html)
###### tags: `intel`
> [name=Kim Zetter]
> Some additional details about the SolarWinds breach time line and the way the FireEye breach was discovered.
#### Main Takeaways
* The SolarWinds compromise -
* Probaly started mid-2019 at the latest
* Test run of backdooring capability during October 2019
* The breach of FireEye's systems was discovered after the hackers enrolled a device into FireEye’s multifactor authentication system, which FireEye employees use to remotely sign into the company’s VPN.
---
[Analyzing Solorigate, the compromised DLL file that started a sophisticated cyberattack, and how Microsoft Defender helps protect customers]()
> [name=Microsoft 365 Defender Research Team]
> Microsot's investigation into the SUNBURST basckdoored DLL
#### Main Takeaways
- [ ] Read the article & extarct main takeaways

---
[Sunburst: connecting the dots in the DNS requests](https://securelist.com/sunburst-connecting-the-dots-in-the-dns-requests/99862/)
###### tags: `intel` `pdns`
> [name=Igor Kuznetsov, Costin Raiu - Kaspresky GReAT]
> Knowing that the DNS requests generated by Sunburst encode some of the target’s information, the obvious next step would be to extract that information to find out who the victims are!
>
#### Main Takeaways
* In depth discussion of the various way to decode SUNBURST DGA subdomain
> [A script do decode SUNBUSRT DGA domains](https://github.com/2igosha/sunburst_dga) released to GitHub by Igor Kuznetsov.
* A method to get probable 2^nd^-stage victims identities by using UID decoded from the 1^st^-stage DGA domains, with decoded 2^nd^-stage DGA domains.
* Rare public statement on the [lack of ] forensic evidence that allow attribution to APT29/Cozy Bear.
* Some statements in relation to why the detection of SUNBURST was so hard
> * ==The slow communication method== [...].
> * The other one is the lack of x86 shellcode;
> * [...] ==there was no significant change in the file size of the module when the malicious code was added=== [...].
### 23/12/2020
[A Timeline Perspective of the SolarStorm Supply-Chain Attack](https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/solarstorm-supply-chain-attack-timeline/)
###### tags:
> [name=]
>
#### Main Takeaways
- [ ] Read the article & extarct main takeaways