# 2017q3 Homework2 (prefix-search)
contributed by <`ChiuYiTang`>
### Reviewed by `HTYISABUG`
* 正如老師所說, 效能分析用圖來顯示更簡單明瞭
* 雖然比較無關緊要, `lscpu` 的結果用 code block 包起來吧, 用列表的方式讓人看不清楚也不想看啊
[GitHub](https://github.com/ChiuYiTang/prefix-search)
## 開發環境
```
Ubuntu 16.04.5
Linux 4.4.0-96-generic
gcc version 5.4.0 20160609
L1d cache: 32K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 256K
L3 cache: 8192K
```
`$ lscpu`
```
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 8
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-7
Thread(s) per core: 2
Core(s) per socket: 4
Socket(s): 1
NUMA node(s): 1
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 94
Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6700 CPU @ 3.40GHz
Stepping: 3
CPU MHz: 1261.187
CPU max MHz: 4000.0000
CPU min MHz: 800.0000
BogoMIPS: 6816.00
Virtualization: VT-x
L1d cache: 32K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 256K
L3 cache: 8192K
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-7
```
> 列出處理器的型號
> [name="jserv"][color=red]
> 已修正
> [name="ChiuYiTang"][color=blue]
## TST 資料架構
* TST 為一種 Trie 資料結構,一般用來保存相關連的矩陣,常見於搜尋提示。
* 不同於 BST 僅有兩個子樹,TST 具備三個子樹架構,又稱為 prefix tree。
* 可藉此儲存大量字串,每個節點由一個字符構成,並包含分別指向三子樹的指標。分別為 equal kid, lower kid and higher kid,以及一個實現物件。
* 常用於 package routing 以及 Prefix matching (e.g. Google search)。
### 操作步驟 - 插入儲存
先加入cat 再加入apple 再加入cow
(a比c小,所以接左邊) (c相等,往下o大於a,所以接右邊)
c c c
| => / | => / |
a a a a a
| | | | | \
t p t p t o
| | |
p p w
| |
l l
| |
e e
### 應用場景
#### Autocompletion
* 輸入一個不完整字串,透過 prefix search 可以給出自動完成剩餘字串建議。
```
# Complete strings: States and regions that begin with "A" and "Al"
completeWord(US.CanadaTree, "A")
#> [1] "Alaska" "Alabama" "Alberta" "Arkansas" "Arizona"
completeWord(US.CanadaTree, "Al")
#> [1] "Alaska" "Alabama" "Alberta"
```
#### Spell checking
* 透過窮舉搜索方式,搜尋 TST 裡最接近(minimize Edit distance)輸入字串的元素。
## 修改 Makefile
* 參考大神們 [ryanwang522](https://github.com/ryanwang522/phonebook/blob/master/Makefile) 以及 [st9007a](https://hackmd.io/s/SkeKQEq3Z) ,修改 makefile,加入`$ make bench` :
```clike=
BIN = \
test_cpy \
test_ref
...
bench: $(BIN)
@for test in $(BIN); do\
perf stat --repeat 100 \
-e cache-misses,cache-references,instructions,cycles \
./$$test --bench;\
done
```
- [ ] 加入 bench 測試檔
## 修正 test_ref.c
* 透過 macro 觀察到兩個版本 `REF` 以及 `CPY`。
* 針對 FIXME 幾個部份做修正:
```clik=
while ((rtn = fscanf(fp, "%s", word)) != EOF) {
char *p = word;
/* FIXME: insert reference to each string */
if (!tst_ins_del(&root, &p, INS, CPY)) {
fprintf(stderr, "error: memory exhausted, tst_insert.\n");
fclose(fp);
return 1;
}
idx++;
}
t2 = t;
```
* 將`tst_ins_del(&root, &p, INS, CPY)`修正為`tst_ins_del(&root, &p, INS, REF)`後執行。
* 執行後發現以下幾點錯誤:
### tst_free_all
* 執行 Quit 會出現錯誤:
* 用 gdb 觀察:
```
choice: q
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x00007ffff7a91532 in __GI___libc_free (mem=0x7ffff70d1eea) at malloc.c:2967
2967 malloc.c: No such file or directory.
```
* 發現為 malloc 到不存在的地方,造成 [double free](https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Double_Free) 現象。
:::danger
這現象叫做 [double free](https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Double_Free),請調整共筆和 Git commit messages 用語
:notes: jserv
:::
* 前往 test_ref.c **151:Quit** 部份,並結合 tst.c 裡 tst_free_all 以及 tst_free Reference,兩者分別為` data storage internal`以及` data storage external`。
* 猜測分別為`test_cpy.c`以及`test_ref.c`所使用。
* 更正後:
```clik=
case 'q':
tst_free(root);
return 0;
break;
```
* 再次執行,Quit 錯誤消失。
### Error Search
* 執行 prefix search 發現
```
suggest[1013] : T
suggest[1014] : T
suggest[1015] : T
suggest[1016] : T
suggest[1017] : T
suggest[1018] : T
suggest[1019] : T
suggest[1020] : T
suggest[1021] : T
suggest[1022] : T
suggest[1023] : T
```
* Search prefix 可發現所有節點都變成輸入值。
* `test_cpy.c`以及`test_ref.c`兩者差異或許為使用到 Macro `REF` & `CPY`的部份。
```clike= if (*p++ == 0) {
void *tst_ins_del(tst_node **root, char *const *s, const int del, const int cpy)
{
...
for (;;) {
...
if (*p++ == 0) {
if (cpy) { /* allocate storage for 's' */
const char *eqdata = strdup(*s);
if (!eqdata)
return NULL;
curr->eqkid = (tst_node *) eqdata;
return (void *) eqdata;
} else { /* save pointer to 's' (allocated elsewhere) */
curr->eqkid = (tst_node *) *s;
return (void *) *s;
}
}
pcurr = &(curr->eqkid);
}
}
```
* 觀察發現`s`為指向`p`的指標,`p`為指向`word`的指標,`*s`為指向`word`的指標。
* 使用`cpy`時,將`*s`指向的 string 直接 malloc 一個空間,copy 到`eqdata`,因此每次皆可順利插入資料進 TST。
* 然使用`ref`時,直接將指向`word`的指標`*s`存入 TST。
* 再任何後續輸入都會修改`word`的值,進而使得整個 TST 的節點都指向以`word`為起點的連續記憶體位址。
* 因此需要透過每次動態配置新的記憶體位址,避免`*s`存取到`word`位址。
* 最簡單的方式即在`char *p = word;`前後,分配新的記憶體空間,或直接透過`strdup()`將`word`複製給`p`。
```
choice: s
find words matching prefix (at least 1 char): Taiwa
Taiwa - searched prefix in 0.000002 sec
suggest[0] : Taiwala,
suggest[1] : Taiwan
```
* 然而頻繁地動態分配,容易造成記憶體破碎,亦增加 Cache miss 的機會。
* 因此透過 phonebook 作業所使用之 memory pool 的方法,事先分配足夠記憶體位置來解決。
#### Memory pool
* 事前給定一塊巨大記憶體,並透過指標操作分配記憶體空間。
* 透過此種方式能避免記憶體破碎,並避免配置與釋放記憶體所需時間。
```clike=
/* Memory pool size */
#define MemoryPoolSize 10000000
...
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
...
char *pptr = (char *) malloc(MemoryPoolSize * sizeof(char)); /* Memory pool */
char *pTop = pptr; /* assign a pointer to top of memory pool */
...
/* Use memory pool top pointer to insert reference to each string */
while ((rtn = fscanf(fp, "%s", pTop)) != EOF) {
char *p = pTop;
if (!tst_ins_del(&root, &p, INS, REF)) {
fprintf(stderr, "error: memory exhausted, tst_insert.\n");
fclose(fp);
return 1;
}
idx++;
/* If memory exhausted, pTop++ for next memory */
pTop += (strlen(pTop) + 1);
}
...
for (;;) {
...
switch (*word) {
char *p = NULL;
case 'a':
printf("enter word to add: ");
if (!fgets(pTop, sizeof word, stdin)) {
fprintf(stderr, "error: insufficient input.\n");
break;
}
rmcrlf(pTop);
p = pTop;
t1 = tvgetf();
/* FIXME: insert reference to each string */
res = tst_ins_del(&root, &p, INS, REF);
t2 = tvgetf();
if (res) {
idx++;
pTop += (strlen(pTop) + 1);
printf(" %s - inserted in %.6f sec. (%d words in tree)\n",
(char *) res, t2 - t1, idx);
} else
printf(" %s - already exists in list.\n", (char *) res);
break;
...
case 'd':
printf("enter word to del: ");
if (!fgets(pTop, sizeof word, stdin)) {
fprintf(stderr, "error: insufficient input.\n");
break;
}
rmcrlf(pTop);
p = pTop;
printf(" deleting %s\n", pTop);
t1 = tvgetf();
/* FIXME: remove reference to each string */
res = tst_ins_del(&root, &p, DEL, REF);
t2 = tvgetf();
if (res)
printf(" delete failed.\n");
else {
printf(" deleted %s in %.6f sec\n", word, t2 - t1);
idx--;
pTop -= (strlen(pTop) + 1);
}
break;
...
case 'q':
tst_free(root);
free(pptr);
...
...
}
}
return 0;
}
```
* 再次執行後,可以順利 Search。
```
...
suggest[962] : Tayuman,
suggest[963] : Taywanak
suggest[964] : Tayzhina,
suggest[965] : Taza,
suggest[966] : Tazacorte,
suggest[967] : Tazewell,
suggest[968] : Tazlău,
suggest[969] : Tazoult-Lambese,
suggest[970] : Tazovskiy,
```
### Search word 'A'
* Search Prefix : A,出現 Segmentation fault。
* 用 gdb 確認錯誤訊息
```
choice: s
find words matching prefix (at least 1 char): A
Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
0x0000000000401e3a in tst_suggest (p=0x18985e0, c=65 'A', nchr=1, a=0x7fffffffba80, n=0x7fffffffba30, max=1024) at tst.c:331
331 a[(*n)++] = (char *) p->eqkid;
```
* 觀察程式碼
```clike=
void tst_suggest(const tst_node *p,
const char c,
const size_t nchr,
char **a,
int *n,
const int max)
{
if (!p || *n < max)
return;
tst_suggest(p->lokid, c, nchr, a, n, max);
if (p->key)
tst_suggest(p->eqkid, c, nchr, a, n, max);
else if (*(((char *) p->eqkid) + nchr - 1) == c)
a[(*n)++] = (char *) p->eqkid;
tst_suggest(p->hikid, c, nchr, a, n, max);
}
```
* 將`p->eqkid`儲存到`a[]`中時,因未正確檢驗輸入 index,造成讀取到危險區域 ,經修正後如下:
```clike=
void tst_suggest(const tst_node *p,
const char c,
const size_t nchr,
char **a,
int *n,
const int max)
{
if (*n >= max || !p)
return;
tst_suggest(p->lokid, c, nchr, a, n, max);
if (p->key)
tst_suggest(p->eqkid, c, nchr, a, n, max);
else if (*(((char *) p->eqkid) + nchr - 1) == c)
a[(*n)++] = (char *) p->eqkid;
tst_suggest(p->hikid, c, nchr, a, n, max);
}
```
* 確保`*n`不越界到不可存取之範圍。
## 效能分析
- [ ] 待補
```
Performance counter stats for './test_ref --bench':
4,509,511 cache-misses # 47.705 % of all cache refs
9,452,930 cache-references
505,184,022 instructions # 1.11 insns per cycle
454,265,288 cycles
2.513052543 seconds time elapsed
```
```
Performance counter stats for './test_cpy --bench':
5,229,904 cache-misses # 51.312 % of all cache refs
10,192,322 cache-references
533,208,563 instructions # 1.03 insns per cycle
518,309,114 cycles
2.138658243 seconds time elapsed
```
## 針對現代處理器架構之改善方式
* Linux Kernel 的 Slab Allocator 機制為一種 memory pool 的實現。
`sudo slabtop`
```
OBJS ACTIVE USE OBJ SIZE SLABS OBJ/SLAB CACHE SIZE NAME
140931 140918 99% 0.19K 6711 21 26844K dentry
96174 96174 100% 0.10K 2466 39 9864K buffer_head
52032 50612 97% 0.06K 813 64 3252K kmalloc-64
49860 49860 100% 1.05K 1662 30 53184K ext4_inode_cache
48360 47006 97% 0.20K 2418 20 9672K vm_area_struct
34986 34986 100% 0.12K 1029 34 4116K kernfs_node_cache
22338 22338 100% 0.04K 219 102 876K ext4_extent_status
20808 20076 96% 0.08K 408 51 1632K anon_vma
19328 18511 95% 0.03K 151 128 604K kmalloc-32
15988 15832 99% 0.57K 571 28 9136K radix_tree_node
15484 15484 100% 0.55K 553 28 8848K inode_cache
13504 12667 93% 0.25K 422 32 3376K kmalloc-256
10024 10024 100% 0.07K 179 56 716K Acpi-Operand
9472 9472 100% 0.02K 37 256 148K kmalloc-16
8192 8192 100% 0.01K 16 512 64K kmalloc-8
7310 7310 100% 0.05K 86 85 344K ftrace_event_field
7176 7009 97% 0.61K 276 26 4416K proc_inode_cache
5814 5814 100% 0.04K 57 102 228K Acpi-Namespace
5586 4738 84% 0.19K 266 21 1064K kmalloc-192
4074 4074 100% 0.09K 97 42 388K kmalloc-96
4448 4033 90% 0.12K 139 32 556K kmalloc-128
4176 3833 91% 0.64K 174 24 2784K shmem_inode_cache
2816 2650 94% 0.50K 88 32 1408K kmalloc-512
2720 2582 94% 1.00K 85 32 2720K kmalloc-1024
2380 2287 96% 0.56K 85 28 1360K ecryptfs_key_record_cache
1840 1840 100% 0.09K 40 46 160K trace_event_file
1428 1331 93% 0.12K 42 34 168K jbd2_journal_head
1325 1325 100% 0.62K 53 25 848K sock_inode_cache
1376 1275 92% 2.00K 86 16 2752K kmalloc-2048
1152 1152 100% 0.06K 18 64 72K ext4_free_data
1120 1120 100% 0.14K 40 28 160K btrfs_path
1008 961 95% 3.75K 126 8 4032K task_struct
896 896 100% 0.03K 7 128 28K jbd2_revoke_record_s
768 768 100% 0.02K 3 256 12K jbd2_revoke_table_s
680 680 100% 0.05K 8 85 32K jbd2_journal_handle
657 657 100% 0.05K 9 73 36K Acpi-Parse
```
* 透過 [slab allocation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Slab_allocation) 為記憶體動態智慧管理的 memory allocator。
* 若將 linux kernel 之 slab 技術運用至程式中,可進一步智慧地動態分配記憶體。
> 或許是殺雞焉用牛刀?
> [name="ChiuYiTang"][color=blue]
## tst_traverse_f 與 callback function 運作模式
* 觀察程式碼
```clike=
void tst_traverse_fn(const tst_node *p,
void(*fn)(const void *, void *),
void *data)
{
if (!p)
return;
tst_traverse_fn(p->lokid, fn, data);
if (p->key)
tst_traverse_fn(p->eqkid, fn, data);
else
fn(p, data);
tst_traverse_fn(p->hikid, fn, data);
}
```
* 此為 Inorder traversal of ternary search tree。
* 遍歷順序為:lower kid > middle kid > root > higher kid
* 以下圖為例,遍歷順序為:e > l > p > p > a > t > a > w > o > c
```
c
/ |
a a
| | \
p t o
| |
p w
|
l
|
e
```
* 每遍歷一個節點,透過 Call back function 回傳函式指標呼叫`void(*fn)(const void *, void *)`。
#### Call back function
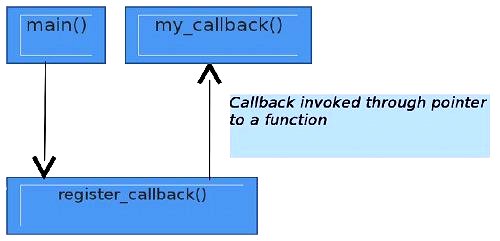
* 當我們希望某個事件發生時,會有通知,以方便進行一些相對應的處理工作。
* 方法即透過呼叫某函式`tst_traverse_fn`時,於過程中傳入一個函式指標`fn`給他。待條件觸發(上例為『中序遍歷到該節點』),會呼叫函式指標。此時會回到主程式並傳入函式 `fn`,結束後再回到函式`tst_traverse_fn`繼續執行未完事項。
[[source](http://www.opensourceforu.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/function-callback-1.jpg)]
## 問題探討
### 詳細觀察 tst.h 和 tst.c 為何要 forward declaration 呢?分離介面和實作有何好處呢?這樣的思維又該如何運用於 phonebook 呢?
* 透過 forward declaration 除了與 function pointer 結合,可以使用 C 語言實現資料封裝、繼承與多型等等物件導向思維之程式碼,亦可實作介面快速抽換程式碼。例如:
> 用一致的 coding style 編排以下程式碼列表:
> [name="jserv"][color=red]
```clike=
//Person.h
typedef struct _Person Person;
//declaration of pointers to functions
typedef void(*fptrDisplayInfo)(Person*);
typedef void(*fptrWriteToFile)( Person*, const char*);
typedef void(*fptrDelete)( Person *) ;
//Note: In C all the members are by default public. We can achieve
//the data hiding (private members), but that method is tricky.
//For simplification of this article
// we are considering the data members //public only.
typedef struct _Person
{
char* pFName;
char* pLName;
//interface for function
fptrDisplayInfo Display;
fptrWriteToFile WriteToFile;
fptrDelete Delete;
}Person;
person* new_Person(const char* const pFirstName,
const char* const pLastName); //constructor
void delete_Person(Person* const pPersonObj); //destructor
void Person_DisplayInfo(Person* const pPersonObj);
void Person_WriteToFile(Person* const pPersonObj, const char* pFileName);
```
* 此外,透過 forward declaration 亦可於編譯時取代原先`#include <head file.h>`,於大型專案下可大幅減少重新編譯之時間。
```clike=
#include <A.h>
class B
{
private:
A* PtrA ;
public:
...
};
```
變為:
```clike=
class A;
class B
{
private:
A* PtrA ;
public:
...
};
```
#### 應用於 phonebook
- [ ] 待補
### 針對各國城市的 prefix search 有無缺陷呢?比方說無法區分城市和國家,並提出具體程式碼的修正
* 觀察測資:
```
Taipei, Taiwan
Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Lima, Peru
Cairo, Egypt
London, United Kingdom
Beijing, China
Tehrān, Iran
Nanchong, China
Bogotá, Colombia
Hong Kong, China
Lahore, Pakistan
```
* 測資格式為:**城市, 國家**。
* 城市與國家之差異在
* 城市以『,』結尾,以此線索修改:
```clike=
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
for(;;) {
...
case 's':
printf("find words matching prefix (at least 1 char): ");
if (!fgets(word, sizeof word, stdin)) {
fprintf(stderr, "error: insufficient input.\n");
break;
}
rmcrlf(word);
t1 = tvgetf();
res = tst_search_prefix(root, word, sgl, &sidx, LMAX);
t2 = tvgetf();
if (res) {
printf(" %s - searched prefix in %.6f sec\n\n", word, t2 - t1);
for (int i = 0; i < sidx; i++){
char *flag = sgl[i] + strlen(sgl[i]) - 1;
if(*flag == ',')
printf("suggest[%d] for CITY : %s\n", i, sgl[i]);
else printf("suggest[%d] for COUNTRY: %s\n", i, sgl[i]);
}
} else
printf(" %s - not found\n", word);
break;
}
}
```
* 結果:
```clike=
...
suggest[23] for COUNTRY: Tairan
suggest[24] for CITY : Tairua,
suggest[25] for CITY : Taisen-ri,
suggest[26] for CITY : Taissy,
suggest[27] for COUNTRY: Taitung
suggest[28] for CITY : Taivalkoski,
suggest[29] for CITY : Taivassalo,
suggest[30] for CITY : Taiwala,
suggest[31] for COUNTRY: Taiwan
suggest[32] for CITY : Taixing,
suggest[33] for CITY : Taiynsha,
suggest[34] for CITY : Taiyuan,
suggest[35] for CITY : Taizhou,
```
## 參考資料
[嵌入式的復健筆記](http://fiend1120.pixnet.net/blog/post/196941375-callback-function)
[你所不知道的 C 語言:物件導向程式設計篇](https://hackmd.io/s/HJLyQaQMl)
[你所不知道的C語言:技巧篇](https://hackmd.io/s/HyIdoLnjl)
[Inheritance and Polymorphism in C](https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/108830/Inheritance-and-Polymorphism-in-C)
[Slab allocation
](http://neokentblog.blogspot.tw/2010/10/slab-allocation.html)
[Ternary search trees for autocompletion and spell checking](https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/TSTr/vignettes/TSTr.html)
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet