---
tags: Specialised Notes
---
[](https://hackmd.io/@Chieh) [](https://github.com/chiehpower)
# DVC
[DVC](https://dvc.org/) is meaning of **Data Version Control**.
- [GitHub](https://github.com/iterative/dvc)
# Introduction
We usually used Git to control code versions, but we knew that it was not good for controling large files or non-code documents.
Also, suppose if we add one large file by git and push to registry such as Github, there are some potential issues inside actually. As we know, usually deep learning or mahcine learning developers / researhers request to do a lot of trainings based on many verious experiments, so we need to find a proper way to maintain and manage those models.
First of all, it will highly increase `.git` folder size ; for example, if your whole files size are 1GB, it will have another 1GB in the `.git` folder. Hence, it will account for 2GB.
Second, it will take too much time on git clone repository.
Of course, DVC not only can do this kinds of things, but also implement the DL/ML pipeline things.
It provides a lot of functionality inside if you are interested in it, you can take a look its website.
In this article, I only showcased how to easily use DVC to control the models (DL/ML); in other word, control large files or put large files in the git folder.
Here is a simple and main workflow for DVC below:
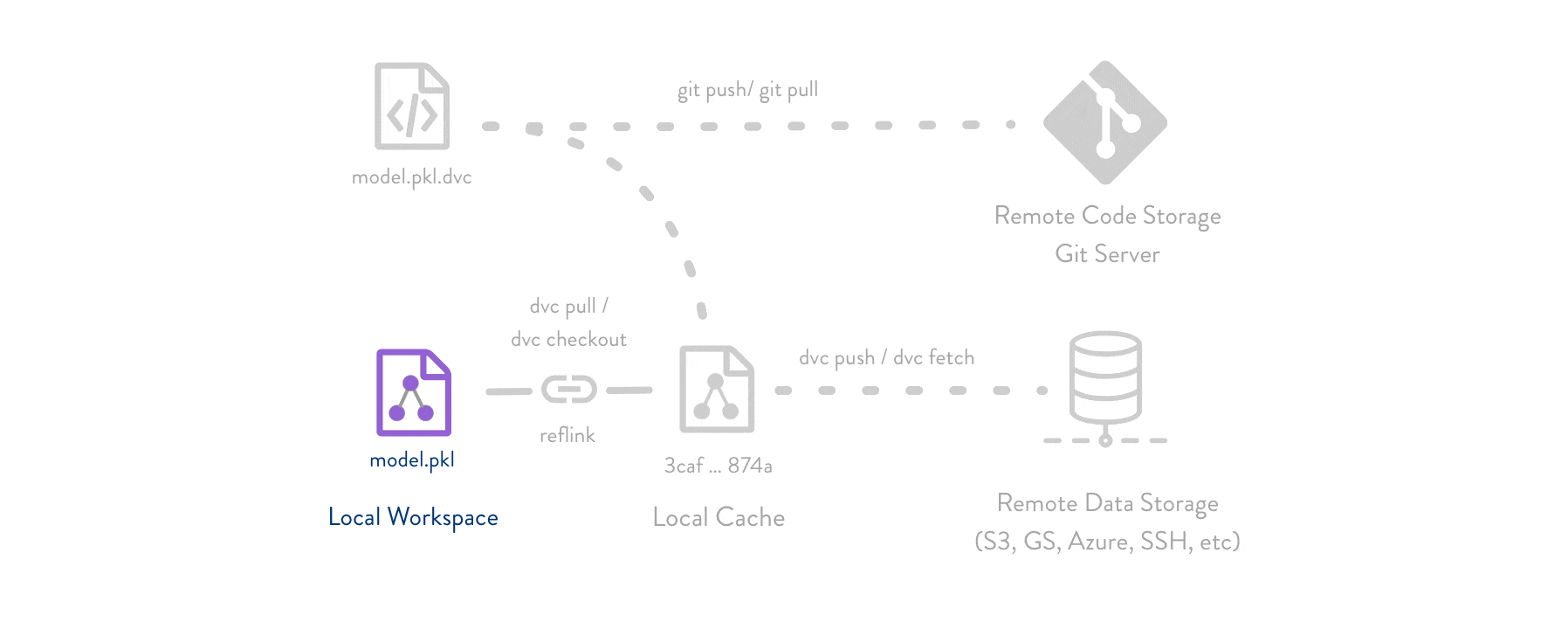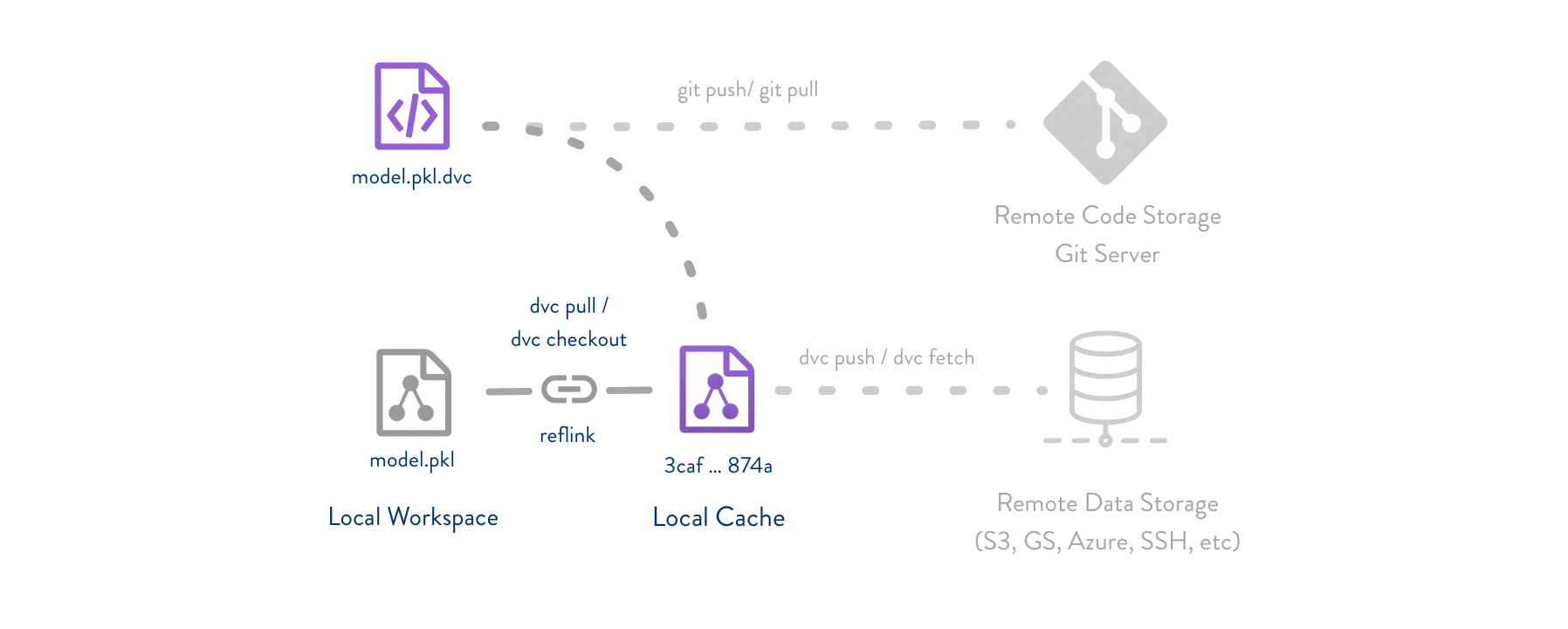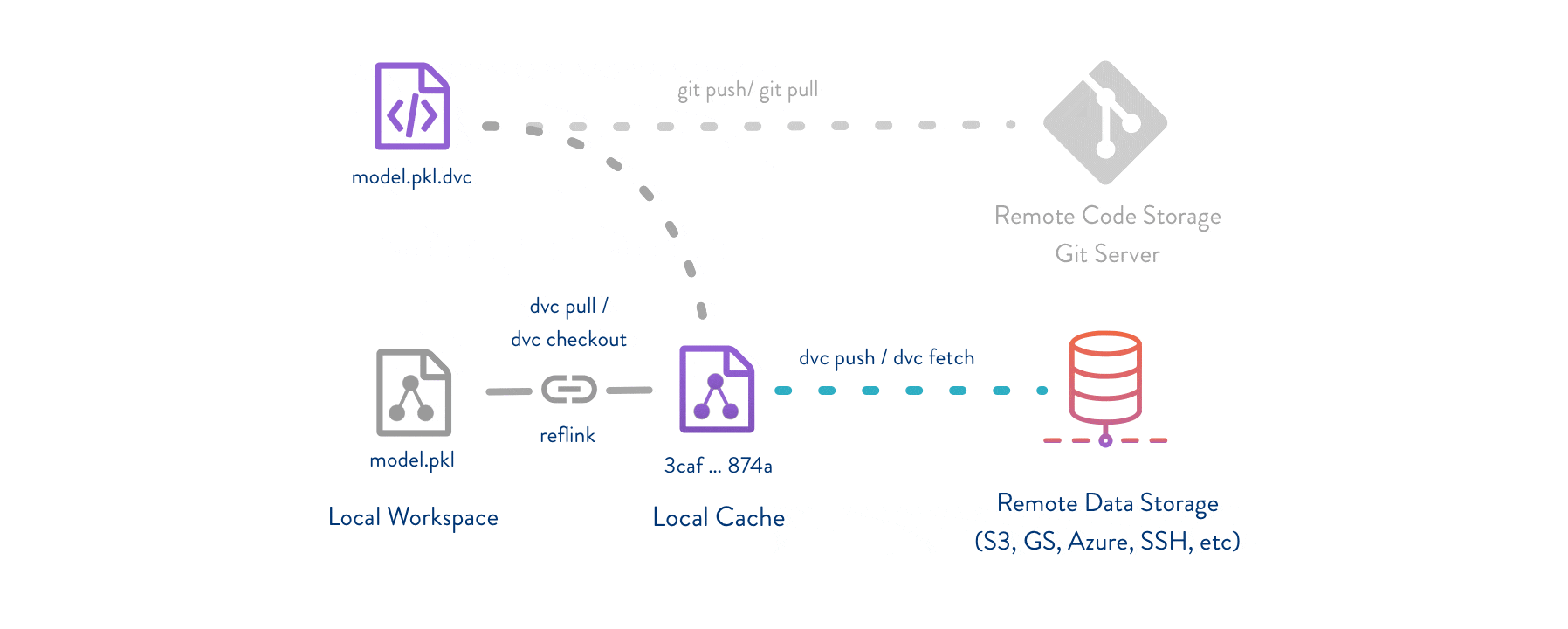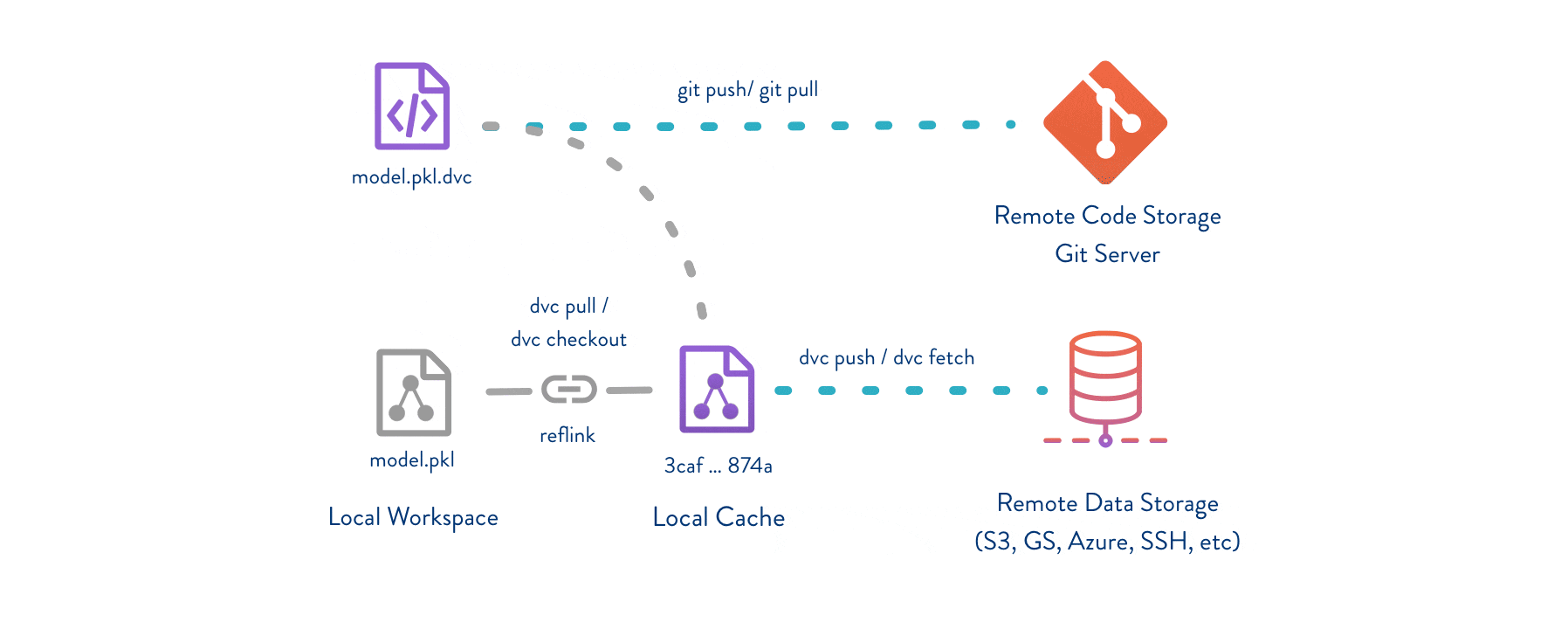
The simplest critical concept for DVC workflow is that we use our "files" to exchange one "document" or you can say a "receipt", and then DVC will put (store) your files to remote place, where can be in the local (in your PC somewhere) or remote servers or cloud drive, etc. Hence, we use **git** control this "receipt" to achieve data version controlled.
I can separate the parts for using DVC. If you can nail it these points, there is no problem to use it smoothly.
1. Set up the `config` file in the `.dvc` folder.
2. Find a remote place such as local place (same device), remote server, or cloud drive (e.g., S3, AWS, etc.)
3. Remember the steps for usage.
To be honest, the second point is the most difficult part if you do not have a cloud drive to store your files.
In my case, I was stored the data in our server via **ssh** in the end. Hence, if you have an account such as S3, then you can use that way.
---
# Usage
## Step:
*Do it in the directory which includes `.git` folder.*
First, if this folder hasn't been controlled by dvc before, you need to do once in the beginning.
```
dvc init
```
Second, let's add the files that we wanna store in the remote place.
When we `dvc add` one file, it will automatically generate one `.dvc` file give you. In addition, it will also automatically add your original file into `.gitignore` file to avoid being controlled by **git**.
```
## Add file
dvc add test
git add test.dvc
git commit -m "Add raw data"
```
Let's set up the config file in the first time.
Basically we need to add the remote side such as your personal server. We have to make sure dvc which can connect to there!! So you can test it by yourself first. For instance, we can use ssh to access your server to see whether there is a denied issue or not.
Official website provided a lot of ways that you guys can find the commands on there.
```
### Add the remote source
# For now, we only use local folder.
dvc remote add -d myremote /tmp/dvcstore
### If you use webhdfs
dvc remote add -d myremote webhdfs://10.1.2.84:9870/tmp/webhdfs
# check the information
cat .dvc/config
```
After we finish the setup config file, let's push the file to remote side. Next, let's git add this `.dvc` file and git commit & git push as usual.
```
# Push the test folder to dvc
dvc push
### Add "test" folder into .gitignore
git add .dvc/configsolomon
git commit -m "Configure remote storage"
git push
```
If you wanna pull the models or files or updates, use it:
```
dvc pull
```
---
# Setup WebHDFS Part [Failure]
Sorry I am not really familiar wiht using HDFS that I still failed in this way. I will update it if I have succeeded to use it.
Reference:
1. [hub.docker-hadoop-docker](https://hub.docker.com/r/sequenceiq/hadoop-docker/)
2. [Hadoop REST API – WebHDFS使用详解](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45083975/article/details/106137674)
3. [DOCKER的HADOOP一鍵啟動之旅](http://paulfun.net/wordpress/?p=307)
Use Docker to start HDFS:
```
sudo docker run -d --name=hadoop-dev-server \
-p 8020:8020 \
-p 8030:8030 \
-p 8040:8040 \
-p 8042:8042 \
-p 8088:8088 \
-p 19888:19888 \
-p 49707:49707 \
-p 50010:50010 \
-p 50020:50020 \
-p 50070:50070 \
-p 50075:50075 \
-p 50090:50090 \
-p 9000:9000 \
762e8eefc162 /etc/bootstrap.sh -d
```
4. [big-data-europe / docker-hadoop](https://github.com/big-data-europe/docker-hadoop)
```
docker-compose up
```
## Commands
- Check the status:
```
curl -i http://localhost:50070/webhdfs/v1/tmp\?user.name\=istvan\&op\=GETFILESTATUS
```
- Create a folder at the `/tmp/webhdfs`
```
curl -i -X PUT http://localhost:50070/webhdfs/v1/tmp/webhdfs\?user.name\=istvan\&op\=MKDIRS
```
---
# Via SSH Part [Success]
Reference:
1. [How do I use DVC with SSH remote](https://discuss.dvc.org/t/how-do-i-use-dvc-with-ssh-remote/279/2)
SUPPOSE :
>hostname/ip: 10.1.2.30
user: Chieh
password: 123456789
port: 22
Let's add SSH remote.
I wanna put it in my remote server at `/home/user/tmp/`
```
dvc remote add --default ssh-storage ssh://10.1.2.30/home/user/tmp/
dvc remote modify ssh-storage user Chieh
dvc remote modify ssh-storage port 22
dvc remote modify --local ssh-storage password 123456789
```
If you dont wanna record any information into `.dvc/config`, then you can use `--local` option.
Otherwise, it will be added into the git control.
---
# How to add new files?
When we change something new files in the tracked dvc folder, how can we add this new files into dvc?
For example, suppose I have a tmp folder, there is one `index` file inside.
**Before**:
└── tmp
└── index
After we `dvc add tmp`, it will generate a file as `tmp.dvc`.
And I add one document, `confusion.json`, into the tmp folder like below:
**After**:
└── tmp
├── index
└── confusion.json
We can use `dvc add tmp` again, then it will update the tmp.dvc again.
Dont forget to `git commit` this `tmp.dvc` file and `dvc push`.
We use `tmp.dvc` to control the files; hence, if you wanna get one files from specific commit, you can `git checkout (specific commit)` back to that one commit, and remove the original tmp folder and dvc pull the files from server.
Step:
```
dvc unprotect tmp
dvc add tmp
# Let's push to server
dvc push
# It will also update the .dvc file, so we need to git add it to do git control again.
git add tmp.dvc
# Regularly git commit and push it to git server.
git commit -m "Update tmp.dvc file"
git push
```
---
# Docker
Here is a simple dockerfile to create a stored space that you can set up your remote side in here.
**Dockerfile:**
```
FROM ubuntu:latest
RUN sed -i -e 's/archive.ubuntu.com/free.nchc.org.tw/' /etc/apt/sources.list
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y ssh openssh-server vim ca-certificates wget sudo
# RUN mkdir /var/run/sshd
RUN echo 'root:Root' | chpasswd
RUN sed -i 's/#PermitRootLogin/PermitRootLogin/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
RUN sed -i 's/#PasswordAuthentication/PasswordAuthentication/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
EXPOSE 22
ARG USER_ID=1000
RUN useradd -m --no-log-init --system --uid ${USER_ID} user -g sudo
RUN echo 'user:user' | sudo /usr/sbin/chpasswd
RUN echo '%sudo ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL' >> /etc/sudoers
# ENTRYPOINT sudo service ssh restart
WORKDIR /home/user
USER $USER_NAME
RUN chmod 700 /home/user
CMD [ "bash" ]
```
**Build image:**
```
docker build -t dvc:0.1 .
docker run --rm -ti -p 8787:22 dvc:0.1 bash
```
---
# Requirements
```
pip3 install dvc
```
If you use WebHDFS, you need to install this requirement.
```
pip3 install 'dvc[webhdfs]'
or
pip3 install 'dvc[ssh]'
```
Or you can use `dvc[all]` to install all packages.
# Reference:
- [DVC 介紹](https://www.dazhuanlan.com/wdgann/topics/1008692)