# 3. Sliding Window (6)
> 紀錄 NeetCode-150 與 LeetCode 的解題想法、刷題過程與錯誤,以 Python 或 C++ 兩種語言為主
>
> 其他 NeetCode-150 或 LeetCode 的主題請見 [Here](https://hackmd.io/-ovTFlzLRWaSgzDGhbSwsA)
<!-- 常用色碼紀錄
Easy: <font color="#00ad5f">**Easy**</font>
Medium: <font color="#ffbb00">**Medium**</font>
Hard: <font color="#ee2f56">**Hard**</font>
-->
Sliding window 可以廣義的視為 two pointer 中的左右指標方法,通常用在 string 或 array 的問題,可以將 $O(n^3)$ 或 $O(n^2)$ 的暴力解降到 $O(n)$ 的線性時間。這類問題通常會面臨到以下情境(包含但不限於)
* 連續的片段資料會重複進行相同操作
* 找出 array/string 中的 sub-array/sub-string
Sliding window 大致可以分為可變(varied-size)視窗或固定(fixed-size)視窗大小,變動視窗大小的實作通常是先固定 left pointer 在 index = 0 的位置,接著 right pointer 不斷往右擴大視窗大小。當符合/不符合某些限制條件時,透過將 left pointer 往右移動來縮減(shrink)視窗大小
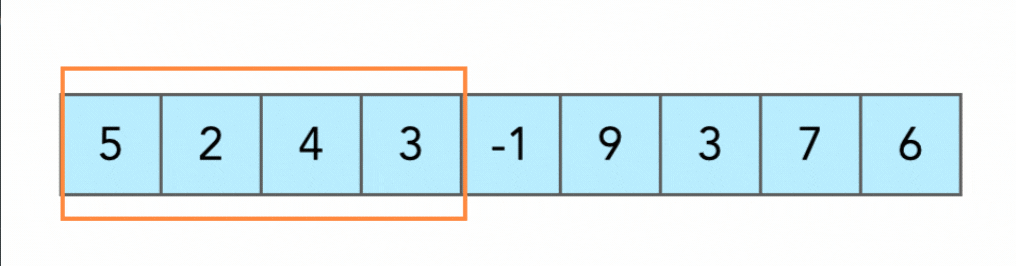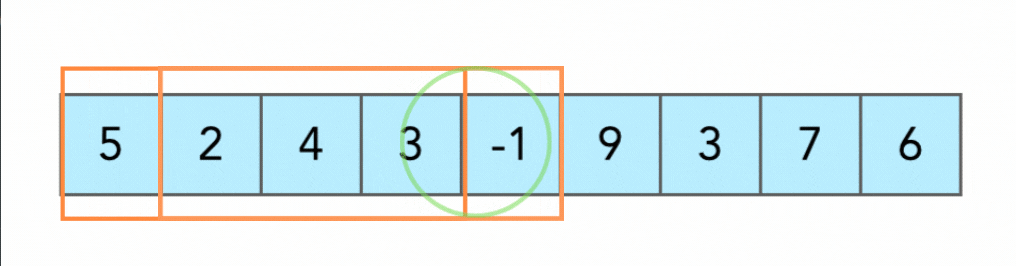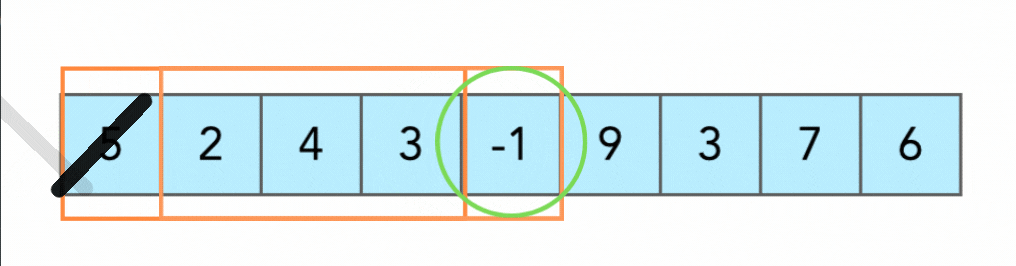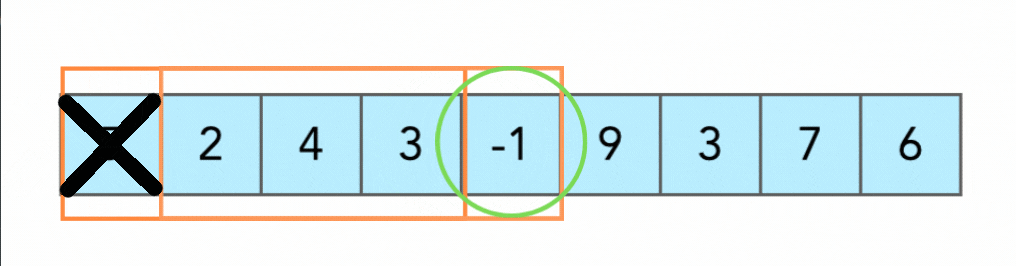
如上圖所示,要找到 array 中連續 4 個數字使得 4 個數字的和最小。就可以用一個 sub-array 去做移動,每次移動過程中
* 新增右側元素
* 刪除左側元素
如此一來就不用搜索整個 array
**Reference**
* [Sliding Window Algorithm](https://tealfeed.com/sliding-window-algorithm-r93tk)
* [滑動視窗(Sliding Window)](https://hackmd.io/@SupportCoding/Sliding_Window)
* [演算法筆記系列 — Two Pointer 與Sliding Window](https://medium.com/%E6%8A%80%E8%A1%93%E7%AD%86%E8%A8%98/%E6%BC%94%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95%E7%AD%86%E8%A8%98%E7%B3%BB%E5%88%97-two-pointer-%E8%88%87sliding-window-8742f45f3f55)
* [Leetcode刷題學習筆記 – Sliding Window](https://hackmd.io/@meyr543/Sk99l4OjY)
## 1. Best Time to Buy And Sell Stock
<font color="#00ad5f">**Easy**</font>
> You are given an integer array `prices` where `prices[i]` is the price of NeetCoin on the `ith` day.
>
> You may choose a **single day** to buy one NeetCoin and choose a **different day in the future** to sell it.
>
> Return the maximum profit you can achieve. You may choose to **not make any transactions**, in which case the profit would be `0`.
### Example 1:
```java
Input: prices = [10, 1, 5, 6, 7, 1]
Output: 6
```
Explanation: Buy `prices[1]` and sell `prices[4]`, `profit = 7 - 1 = 6`.
### Example 2:
```java
Input: prices = [10, 8, 7, 5, 2]
Output: 0
```
Explanation: No profitable transactions can be made, thus the max profit is 0.
### Constraints
* `1 <= prices.length <= 100`
* `0 <= prices[i] <= 100`
### Solution
#### 1. Brute-force
```python=
# brute force
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
buyPointer, sellPointer = 0, 0
res = 0
for buyPointer in range(len(prices)-1):
for sellPointer in range(buyPointer+1, len(prices)):
profit = prices[sellPointer] - prices[buyPointer]
if profit > res:
res = profit
return res
```
最直觀的解法,時間複雜度為 $O(n^2)$
#### 2. Two pointer
核心思想就是買低賣高,使用兩個指標 `buyPtr` 與 `sellPtr` 分別代表買進與賣出的點,賣出指標 `sellPtr` 會歷遍整個 array,尋找比買入指標 `buyPtr` 更高的價格。
但因為核心思考是買低賣高,所以當賣出指標 `sellPtr` 碰到比當前買進指標 `buyPtr` 更低的價格時,就可以作為新的買入點。這樣操作後在未來如果有更高的賣點時,就可以獲得更高的報酬。
```python=
# two pointer
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
# initialize
buyPtr, sellPtr = 0, 1
res = 0
while (sellPtr < len(prices)):
if prices[sellPtr] > prices[buyPtr]:
profit = prices[sellPtr] - prices[buyPtr]
res = max(res, profit)
else:
buyPtr = sellPtr
sellPtr += 1
return res
```
## . Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
<font color="#ffbb00">**Medium**</font>
> Given a string `s`, find the *length of the longest substring* without duplicate characters.
>
> A **substring** is a contiguous sequence of characters within a string.
### Exmple 1:
```java
Input: s = "zxyzxyz"
Output: 3
```
Explanation: The string "xyz" is the longest without duplicate characters.
### Example 2:
```java
Input: s = "xxxx"
Output: 1
```
### Constraint
* `0 <= s.length <= 1000`
* `s` may consist of printable AXCII characters.
### Solution
#### 1. Inspiration
How to implement a slidng window with variable size :question:
We can use two pointers to represent the bound of window. In order to vary its size, we assign the first element to left pointer and then use right pointer to iterate the whole string from first element.
When the right pointer point some character such that the window have duplicate then we plus 1 to left pointer to shrink the window size until no more duplicate
However, how to we check the sliding window having no duplicate ? In Python, we can use a Set() to check repeat element or not.
#### 2. Correct: sliding window
```python=
# correct - sliding window
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
LP = 0
res = 0
charSet = set() # sliding window
for RP in range(len(s)):
while s[RP] in charSet:
charSet.remove(s[LP]) # shrink the window until no duplicate
LP += 1 # left pointer increase 1
charSet.add(s[RP])
res = max(res, RP - LP + 1)
return res
```
## 3. Longest Repeating Character Replacement
<font color="#ffbb00">**Medium**</font>
> You are given a string `s` consisting of only uppercase english characters and an integer `k`. You can choose up to `k` characters of the string and replace them with any other uppercase English character.
>
> After performing at most `k` replacements, return the length of the longest substring which contains only one distinct character.
### Example 1:
```java
Input: s = "XYYX"M L = 2
Output: 4
```
Explanation: Either replace the 'X's with 'Y's, or replace the 'Y's with 'X's.
### Example 2"
```java
Input: s = "AAABABB", k = 1
Output: 5
```
### Constraints
* `1 <= s.length <= 1000`
* `0 <= k <= s.length`
### Solution
#### 1. Inspiration
This problem involve substring or subarray which have to satisfy some condition, so we can use sliding window to solve it. Since we have to return a length of longest substring which contains only distinct elements, we must decide how to find this subarray first.
Given a varied-size subarray and we make it have same elements, so we have to determine how many elements we can replace. We can use the length of window to minus the mximum counts of some element (`window_len - max_count`) to compute it.
If this answer is less than k, then we can replace it nd find a length = `l - r + 1`. If this answer is greather than k, that means the subarray is too long an invalid, so we must shrink it and check above condition again.
#### 2. Sliding window
```python=
# correct: sliding window
class Solution:
def characterReplacement(self, s: str, k: int) -> int:
charSet = set(s)
res = 0
for ch in charSet:
count = 0
LP = 0
for RP in range(len(s)):
if s[RP] == ch:
count += 1
while (RP - LP + 1) - count > k:
if s[LP] == ch:
count -= 1
LP += 1 # shrink window size
res = max(res, RP - LP + 1)
return res
```
* `for ch in charSet` 表示對給定陣列 s 內的所有元素都分別計算一次各自的可能數量
* 縮減 window size 時要檢查刪去的元素,如果是目前正在檢查的元素,則次數 `count` 需減 1
## 4. Permutaion In String
<font color="#ffbb00">**Medium**</font>
> You are given two strings `s1` and `s2`.
>
> Return `True` if `s2` contains a permutation os `s1`, or `False` otherwise. That means if a permutation of `s1` exists as a substring of `s2`, then return `True`.
>
> Both strings only contain lowercase letters.
### Example 1:
```java
Input: s1 = "abc", s2 = "lecabee"
Output: True
```
Explanation: The substring `"cab"` is a permutation of `"abc"` and is present in `"lecabee"`.
### Example 2:
```java
Input: s1 = "abc", s2 = "lecaabee"
Output: False
```
### Constraints:
* `1 <= s1.length, s2.length <= 1000`
### Solution
#### 1. My
```python=
# my solution
class Solution:
def checkInclusion(self, s1: str, s2: str) -> bool:
charDict1 = dict()
for ch in s1:
charDict1[ch] = 1 + charDict1.get(ch, 0)
windowSize = len(s1)
LP = 0
RP = LP + windowSize
while (RP <= len(s2)):
subString = s2[LP:RP]
charDict2 = dict()
for ch in subString:
charDict2[ch] = 1 + charDict2.get(ch, 0)
if charDict1 == charDict2:
return True
LP += 1
RP += 1
return False
```
因為只要比較字串是否有排列,不用在意字串的順序,所以只要檢查字串的出現頻率即可。這個方法使用 hash map 的概念來計算目標字串與滑動視窗字串中各自的字母出現頻率。
但缺點是每次更新視窗時都需要完成下面兩件事
* 每次都重建一個 hash map
* 重建後每次都要比較兩個 hash map
所以時間複雜度為 $O(m \cdot n)$,其中 m 為字母個數。優化方式可以針對上面兩點做改善。
### Correct: sliding window
為了避免每次迭代更新窗口都要重新建構與比較 hash map,所以使用 matches 的概念比較兩者的字母出現頻率。matches 是計算兩個 hash map 的匹配度,當兩個 hash map 中的所有字母出現次數都相同,則 matches = 26。
此外,此題是要找在固定字串長度中是否有目標字串的排列,所以可以使用 fixed-size 的滑動視窗處理。滑動步驟如下
* 右邊擴增後更新條件與狀況
* 左邊縮減後更新條件與狀況
做完上述步驟即完成一次的滑動。整段解法的思考過程如下
* 初始化兩個長度為 26 的固定長度的 array,一個是目標字串,一個是滑動窗口。
* 計算兩者的 matches 值
* 每次更新窗口大小時,檢查兩者的 matches 值,當 `matches == 26` 時,表示該窗口中的字元頻率與目標字串的字元頻率相同
```python=
# correct
class Solution:
def checkInclusion(self, s1: str, s2: str) -> bool:
if len(s1) > len(s2):
return False
# 2 hash map that we have and we need
countTarget = [0] * 26 # for target string s1
countWindow = [0] * 26 # for sliding window s2
for i in range(len(s1)):
countWindow[ord(s2[i]) - ord("a")] += 1
countTarget[ord(s1[i]) - ord("a")] += 1
# first matches
matches = 0
for i in range(26):
if countWindow[i] == countTarget[i]:
matches += 1
# start sliding
LP = 0
for RP in range(len(s1), len(s2)):
if matches == 26:
return True
# expand the window
index = ord(s2[RP]) - ord('a')
countWindow[index] += 1
#------------------------------------------------#
if countTarget[index] == countWindow[index]:
matches += 1
elif countTarget[index] + 1 == countWindow[index]:
matches -= 1
#------------------------------------------------#
# shrink the window
index = ord(s2[LP]) - ord('a')
countWindow[index] -= 1
#------------------------------------------------#
if countTarget[index] == countWindow[index]:
matches += 1
elif countTarget[index] - 1 == countWindow[index]:
matches -= 1
#------------------------------------------------#
LP += 1
return matches == 26
```
:::danger
注意 matches 更新的邏輯。只有當兩個 hash map 從:(1) 匹配變不匹配或 (2) 不匹配變匹配時才需要更新 matches
* 不匹配 :arrow_right: 匹配: matches + 1
* 匹配 :arrow_right: 不匹配(兩種狀況):matches - 1
* 擴增時 `countWindow[index]` 多 1
* 縮減時 `countWindow[index]` 少 1
因次在擴增(縮減亦同)檢查匹配度時 `elif countTarget[index] + 1 == countWindow[index]` 不能改成 `elif countTarget[index] != countWindow[index]`,因為有可能會檢查到不匹配變不匹配的狀況,而這種狀況本來就不匹配,所以 matches 不用減 1。
:::
## 5. Minimum Window Substring
<font color="#ee2f56">**Hard**</font>
> Given two strings `s` and `t`, return the shortest substring of `s` such that every character in `t`, including duplicates, is present in the substring. If such a substring does not exist, return an empty string `""`.
>
> You may assume that the correct output is always unique.
### Example 1:
```java
Input: s = "OUZODYXAZV", t = "XYZ"
Output: "YXAZ"
```
**Explanation:**
`"YXAZ"` is the shortest substring that includes `"X"`, `"Y"`, and `"Z"` from string `t`.
### Example 2:
```java
Input: s = "xyz", t = "xyz"
Output: "xyz"
```
### Example 3:
```java
Input: s = "x", t = "xy"
Output: ""
```
### Constraints
* `1 <= s.length <= 1000`
* `1 <= t.length <= 1000
* `s` and `t` consist of uppercase and lowercase English letters
### Solution
如下圖所示,將兩個字串建立 hash map 後,在 sliding window 的過程中逐一比較兩個 hash map 中各元素數量。在比較的過程中, brute force solution 每滑動一次視窗大小就會需要比較一次 hash map,因此時間複雜度會是 $O(n^2)$

改善方法是增加兩個變數,`Need` 用來表示目標字串中的字元種類有幾種,`Have` 用來計算給定字串中滿足條件的字元有幾個。當 `Have == Need` 的時候表示滿足條件,此時的 window size 即為題目要求的一個解。
找到滿足條件的解以後就可以開始縮減 window size 來尋找最小長度。在縮小的過程中如果不滿足條件則在繼續擴大。
Algorithm:
1. 建立目標 hash map
2. 建立 have 與 need
3. 迭代整個給定字串
* 更新 hashWindow 與 have
4. 檢查 have == need
* 相等 -> 縮小 window size
* 更新 hashWindow 與 have
* 不等 -> 擴張 window size
```python=
# correct
class Solution:
def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:
if t == "":
return ""
# build taeget hash map
hashTarget, hashWindow = {}, {}
for ch in t:
hashTarget[ch] = 1 + hashTarget.get(ch, 0)
# compute "have value" and "need value"
have, need = 0, len(hashTarget)
res, resLen = [-1, -1], float("inf") # initialize result value
# sliding window
LP = 0
for RP in range(len(s)):
ch = s[RP]
hashWindow[ch] = 1 + hashWindow.get(ch, 0)
if (ch in hashTarget) and (hashWindow[ch] == hashTarget[ch]):
have += 1
while have == need:
if (RP - LP + 1) < resLen:
res = [LP, RP]
resLen = (RP - LP + 1)
hashWindow[s[LP]] -= 1
if (s[LP] in hashTarget) and (hashWindow[s[LP]] < hashTarget[s[LP]]):
have -= 1
LP += 1
LP, RP = res
return s[LP:RP + 1] if resLen != float("inf") else ""
```
## 6. Sliding Window Maximum
<font color="#ee2f56">**Hard**</font>
> Youare given an array of integers `nums` and an integer `k`. There is a sliding window of size `k` that starts at the left edge of the array. The window slides one position to the right until it reaches the right edge of the array.
>
> Return a list that contains the maximum element in the window at each step.
### Example 1:
```java
Input: nums = [1,2,1,0,4,2,6], k = 3
Output: [2,2,4,4,6]
Explanation:
Window position Max
--------------- -----
[1 2 1] 0 4 2 6 2
1 [2 1 0] 4 2 6 2
1 2 [1 0 4] 2 6 4
1 2 1 [0 4 2] 6 4
1 2 1 0 [4 2 6] 6
```
### Constraints:
* 1 <= nums.length <= 1000
* -1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000
* 1 <= k <= nums.length
### Solution
#### 1. My solution - sort
因為滑動視窗的長度大小固定為 k 且要找每個視窗中的最大值。因此視窗每滑動一次,就進行排序,排序後取最大值即為題目所求。
完整看過長度為 n 的陣列,時間複雜度為 $O(n)$,每一次的滑動中都需要對 k 個元素進行排序,複雜度為 $O(k \log k)$,因此整體時間複雜度為 $O(n \cdot k \log k)$(依照不同的排序方法有不同的複雜度)
```python=
# my solution - sorted
class Solution:
def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
res = []
for LP in range(len(nums)-k+1):
RP = LP + k
subArray = sorted(nums[LP:RP])
res.append(subArray[k-1])
return res
```
#### 2. Brute force
不用排序,直接透過 Python 內建函式 `max()` 找最大值,時間複雜度為 $O(n \cdot k)$
```python=
# brute force
class Solution:
def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
res = []
for i in range(len(nums) - k + 1):
MAX = nums[i]
for j in range(i, i+k):
MAX = max(MAX, nums[j])
res.append(MAX)
return res
```
#### 3. Correct - deque
使用雙向佇列(double queue, deque)進行。以一個 deque 來儲存給定串列中最大可能元素的索引值,並以遞減方式儲存。
當新元素比 dequq 後端元素小,直接添加。當新的元素比後端元素大,則把後端元移除並添加新的元素。

```python=
class Solution:
def maxSlidingWindow(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
output = []
q = deque() # index
l = r = 0
while r < len(nums):
while q and nums[q[-1]] < nums[r]:
q.pop()
q.append(r)
if l > q[0]:
q.popleft()
if (r + 1) >= k:
output.append(nums[q[0]])
l += 1
r += 1
return output
```