# 5. Binary Search (7) - Python
> 紀錄 NeetCode-150 與 LeetCode 的解題想法、刷題過程與錯誤,以 Python 或 C++ 兩種語言為主
>
> 其他 NeetCode-150 或 LeetCode 的主題請見 [Here](https://hackmd.io/-ovTFlzLRWaSgzDGhbSwsA)
<!-- 常用色碼紀錄
Easy: <font color="#00ad5f">**Easy**</font>
Medium: <font color="#ffbb00">**Medium**</font>
Hard: <font color="#ee2f56">**Hard**</font>
-->
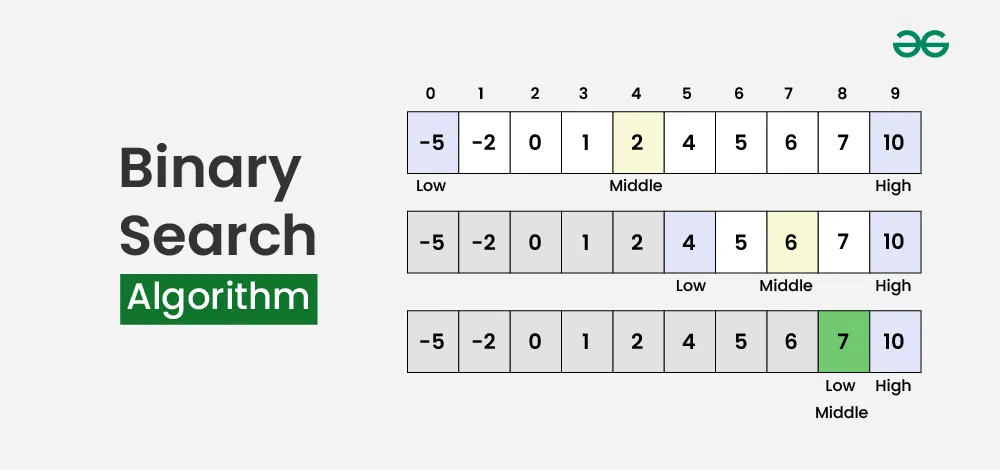
(圖片來源 [Here](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/binary-search/?ref=gcse_outind#what-is-binary-search))
##### Introduction
二分搜索(Binary search)是一種搜索演算法,目的是在排序好的陣列中尋找目標值的位置。藉由不斷分割搜索範圍直到找到目標或是範圍是空的。
Binary search 的使用條件有以下幾點:
* 必須是已經排序好的資料結構
* 每個元素的存取必須在常數時間內完成
##### Algorithm step
* 藉由尋找中間位置的元素(mid)來分割搜索空間
* 比較中間元素 mid 與目標元素 key
* 如果 mid == key 則搜索結束
* 如果 mid !- key 則選擇另一半的搜索空間繼續下一輪的搜索
* 如果 mid > key 則使用左半部分的搜索空間
* 如果 mid > key 則使用右半部分的搜索空間
* 持續上述過程直到目標值 key 被找到
##### Implement
Binary search 的實作上可以使用迭代(iteration)或遞迴(recursion)兩種方式 [1]。
不論是迭代或是遞迴的過程,都需要將陣列不斷做二分法,並依序搜索每層的陣列,所以時間複雜度皆為 $O(\log n)$,其中 n 為陣列的元素個數。
兩者的差異在於空間複雜度不同。在迭代過程中不需要有額外空間的使用,所以空間複雜度為 $O(1)$。但在遞迴過程中,每層的搜索都會呼叫一次函式,每呼叫一次函式就會調用並疊加一次的 stack,所以空間複雜度為 $O(\log n)$。
:::info
因為函式的特性符合 LIFO 的性質,越晚被呼叫的函式(越內層)必須越早有輸出結果,因此在記憶體中會是以 stack 的結構來做儲存。
:::
##### Reference
[[1] Binary Search Algorithm](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/binary-search/?ref=gcse_outind#what-is-binary-search)
[[2] 二分搜尋法(Binary Search)完整教學(一)](https://medium.com/appworks-school/binary-search-那些藏在細節裡的魔鬼-一-基礎介紹-dd2cd804aee1)
## 1. Binary Search
<font color="#00ad5f">**Easy**</font>
> You are given an array of distinct integers `nums`, sorted in ascending order, and an integer `target`.
>
> Implement a function to search for `target` within `nums`. If it exists, then return its index, otherwise, return `-1`.
>
> Your solution must run in $O(\log n)$ time.
### Example 1:
```java
Input: nums = [-1,0,2,4,6,8], target = 4
Output: 3
```
### Example 2:
```java
Input: nums = [-1,0,2,4,6,8], target = 3
Output: -1
```
### Constraints
* `1 <= nums.length <= 10000`.
* `-10000 < nums[i], target < 10000`.
### Solution
```python=
# iteration
class Solution:
def search(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
low, high = 0, len(nums) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = low + (high - low) // 2
if nums[mid] == target:
return mid
if nums[mid] > target: # target is in left half
high = mid - 1
if nums[mid] < target: # target is in right half
low = mid + 1
return -1
```
## 2. Search a 2D Matrix
<font color="#ffbb00">**Medium**</font>
> You are given an `m x n` 2-D integer array `matrix` and an integer `target`.
>
> * Each row in `matrix` is sorted in **non-decreasing** order.
> * The first integer of every row is greater than the last integer of the previous row.
>
> Return `true` if `target` exists within `matrix` or `false` otherwise.
### Example 1:

```java
Input: matrix = [[1,2,4,8],[10,11,12,13],[14,20,30,40]], target = 10
Output: true
```
### Example 2:

```java
Input: matrix = [[1,2,4,8],[10,11,12,13],[14,20,30,40]], target = 15
Output: false
```
### Constraints
* `m == matrix.length`
* `n == matrix[i].length`
* `1 <= m, n <= 100`
* `-10000 <= matrix[i][j], target <= 10000`
### Solution
對於一個 $m \times n$ 的矩陣,歷遍矩陣的每個 row,每選定一個 row 就對該列做 binary search,時間複雜度為 $O(m \cdot \log n)$
#### 1. Brute force
```python=
# brute force
class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
for col in range(len(matrix)):
row = matrix[col]
low, high = 0, len(row) - 1
if self.BinarySearch(row, low, high, target):
return True
return False
def BinarySearch(self, arr, low, high, target):
while low <= high:
mid = low + (high - low) // 2
if arr[mid] == target:
return True
if arr[mid] < target:
low = mid + 1
if arr[mid] > target:
high = mid - 1
return False
```
#### 2. Binary search

因為題目已經有說明此矩陣的每列都已經做 non-decreasing 的排序,也就是說第 i 列的末端元素必定會 <= 第 (i+1) 列的首項元素。因此可以先使用一次的 binary search 對列做搜尋,確定 target 會落在哪個列的範圍內,具體步驟如下:
* 以列為單位進行第一次的 binary search
* 選定的 row = mid = (top + bottom) / 2
* 如果 target 大於該列末項(`target > matrix[row][-1]`),則搜尋下半部的列
* 如果 target 小於該列的首項(`target < matrix[row][0]`),則搜尋上半部的列
* 選定 row 後再針對該列做第二次的 binary search
```python=
# Improvement (2)
class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
ROWS, COLS = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
top, bot = 0, ROWS - 1
# use binary search to select the row including target
while top <= bot:
row = top + (bot - top) // 2
if target > matrix[row][-1]:
top = row + 1
elif target < matrix[row][0]:
bot = row - 1
else:
break
# Did not find the row which including the target
if top > bot:
return False
# binary search to find the target in the particular row
row = top + (bot - top) // 2
low, high = 0, COLS - 1
while low <= high:
mid = low + (high - low) // 2
if target > matrix[row][mid]:
low = mid + 1
elif target < matrix[row][mid]:
high = mid - 1
else:
return True
return False
```
## 3. Koko Eating Bananas
<font color="#ffbb00">**Medium**</font>
> You are given an integer array `piles` where `piles[i]` is the number of bananas in the `ith` pile. You are also given an integer `h`, which represents the number of hours you have to eat all the bananas.
>
> You may decide your bananas-per-hour eating rate of `k`. Each hour, you may choose a pile of bananas and eats `k` bananas from that pile. If the pile has less than `k` bananas, you may finish eating the pile but you can not eat from another pile in the same hour.
>
> Return the minimum integer `k` such that you can eat all the bananas within `h` hours.
### Example 1:
```java
Input: piles = [1,4,3,2], h = 9
Output: 2
```
Explanation: With an eating rate of 2, you can eat the bananas in 6 hours. With an eating rate of 1, you would need 10 hours to eat all the bananas (which exceeds h=9), thus the minimum eating rate is 2.
### Example 2:
```java
Input: piles = [25,10,23,4], h = 4
Output: 25
```
### Constraints
* `1 <= piles.length <= 1,000`
* `piles.length <= h <= 1,000,000`
* `1 <= piles[i] <= 1,000,000,000`
### Solution
#### 1. Brute force
```python=
# brute force
class Solution:
def minEatingSpeed(self, piles: List[int], h: int) -> int:
maxSize = max(piles)
k = 1
while k <= maxSize:
needTime = 0
for pile in piles:
needTime += math.ceil(pile / k)
if needTime <= h:
return k
else:
k += 1
```
:::danger
Time Limit Exceeded. You may have an infinite loop or your code is too inefficient.
:::
#### 2. Binary search
題目要求在 $h$ 的時間內將所有香蕉吃完。再給定的速率 $k$ 下,吃完所有香蕉所需要的時間為
$$
\text{NeedTime} = \lceil \frac{x_1}{k} \rceil + \lceil \frac{x_2}{k} \rceil + ... + \lceil \frac{x_n}{k} \rceil \le h
$$
所需時間 $\text{NeedTime}$ 的最大值為(此時 $k = 1$)
$$
x_1 + x_2 + ... + x_n
$$
為了符合 $\text{NeedTime} \le h$,可以想見 $k$ 值必定會有一個上限。這個 $k$ 值的上限就是最大堆香蕉的數量 $x_n$,意即要在 $1 \le k \le x_n$ 的範圍內找到最小的 $k$ 值,並使用 $\text{NeedTime} \le h$ 來判斷找到的 k 是否合理。
```python=
# binary search
class Solution:
def minEatingSpeed(self, piles: List[int], h: int) -> int:
low, high = 1, max(piles)
res = high
while low <= high:
k = low + (high - low) // 2
needTime = 0
for pile in piles:
needTime += math.ceil(pile / k)
if needTime > h: # that means this k is too small
low = k + 1
else: # that means this k in valid
res = k
high = k - 1
return res
```
## 4. Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
<font color="#ffbb00">**Medium**</font>
> You are given an array of length `n` which was originally sorted in ascending order. It has now been **rotated** between `1` and `n` times. For example, the array `nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6]` might become:
>
> * `[3,4,5,6,1,2]` if it was rotated `4` times.
> * `[1,2,3,4,5,6]` if it was rotated `6` times.
>
> Notice that rotating the array `4` times moves the last four elements of the array to the beginning. Rotating the array `6` times produces the original array.
>
> Assuming all elements in the rotated sorted array `nums` are unique, return the minimum element of this array.
### Example 1:
```java
Input: nums = [3,4,5,6,1,2]
Output: 1
```
### Example 2:
```java
Input: nums = [4,5,0,1,2,3]
Output: 0
```
### Example 3:
```java
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7]
Output: 4
```
### Constraint
* `1 <= nums.length <= 1000`
* `-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000`
### Solution
#### 1. Brute force
```python=
# brute force
class Solution:
def findMin(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
m = nums[0]
for i in nums:
if i < m:
m = i
return m
```
使用 linear search 的時間複雜度為 $O(n)$,不過因為題目的 array 是有特殊排序的陣列,所以可以再往下探詢 $O(\log n)$ 的時間複雜度。
#### 2. Binary search
因為題目給定的陣列有做特殊的排序(rotated sorted),所以一個陣列可分為兩個不同且有排序的子陣列,除了轉折點外,兩個陣列都是以遞增方式做排列
$$
\text{Rotated sorted array}:[3,\ 4,\ 5,\ 6,\ 0,\ 1,\ 2]
$$
(轉折點在 index = 4 的位置)
這種 rotated sorted array 因為每次的反轉過程是將後端元素移到前端,所以 index = 0 的元素必定大於 index = n 的元素(`nums[0] > nums[n]`)
使用 binart search 最小值的過程中,中間元素的更新邏輯如下
* 每次迭代過程中,將找到的中間元素 `mid` 與當前的最小值 `res` 比較
* 若 `num[mid] >= nums[low]` 表示 `mid` 在左側陣列
* 下一步應該往右搜尋找轉折點
* 下限 `low` 提高
* 若 `num[mid] < nums[low]` 表示 `mid` 在右側陣列
* 下一步應該往左搜尋找轉折點
* 上限 `high` 提高
* 直到上限元素 > 下限元素(`nums[high] > nums[low]`)時,表示當前範圍是某個子陣列,從當前最小值與下限元素 `nums[low]` 挑一個最小的
```python=
class Solution:
def findMin(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
res = nums[0]
# binary search
low, high = 0, len(nums) - 1
while low <= high:
if nums[low] < nums[high]:
res = min(res, nums[low])
break
mid = low + (high - low) // 2
res = min(res, nums[mid])
if nums[mid] >= nums[low]: # search right half
low = mid + 1
else: # search left half
high = mid - 1
return res
```
## 5. Search in Rotated Sorted Array
<font color="#ffbb00">**Medium**</font>
> You are given an array of length `n` which was originally sorted in ascending order. It has now been **rotated** between `1` and `n` times. For example, the array `nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6]` might become:
>
> * `[3,4,5,6,1,2]` if it was rotated `4` times.
> * `[1,2,3,4,5,6]` if it was rotated `6` times.
>
> Given the rotated sorted array `nums` and an integer `target`, return the index of `target` within `nums`, or `-1` if it is not present.
>
> You may assume all elements in the sorted rotated array `nums` are **unique**.
### Example 1:
```java
Input: nums = [3,4,5,6,1,2], target = 1
Output: 4
```
### Example 2:
```java
Input: nums = [3,5,6,0,1,2], target = 4
Output: -1
```
### Constraints
* `1 <= nums.length <= 1000`
* `-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000`
* `-1000 <= target <= 1000`
### Solution
**概念與想法**
如同上一題,rotated sorted array 的轉換方式是每次將右側元素移到左側,因此會有以下性質
* 每個 rotated sorted array 中會有兩個相同排序的 sub-array
* left sub-array 的元素 > right sub-aaray 的元素
這兩個相同排序的 sub-array 會有一個轉折點(pivot),例如
$$
\text{Rotated sorted array} = [3,\ 5,\ 6,\ 0,\ 1,\ 2]
$$
轉折點 = 0。只要找到轉折點後就可以把兩個陣列分開,再分別對兩個陣列做 binary search 即可找到 target。
**如何找 pivot point ?**
Pivot point 也是在陣列裡面做搜尋,所以也可以利用 binary search 找。在 binary search 每一次迭代找 pivot 的過程中可以分為以下兩種狀況
* `low` 與 `mid` 都在同一個 (left)sub-array 中
* 此時代表 pivot 在 right sub-array
* 左端元素 `low` 要右移
* 可以用 `nums[low] <= nums[mid]` 判斷
* `high` 與 `mid` 都在同一個 (right)sub-array 中
* 此時代表 pivot 在 left sub-array
* 右端元素 `high` 要左移
* 可以用 `nums[low] > nums[mid]` (上述條件的補集)判斷
迭代完成後,左端元素 `low` 就是 pivot
```plaintext=
# Algorithm to find pivot point
while (low < right)
mid = low + (high - low) / 2
if (arr[low] <= arr[mid])
search right
else
search left
pivot = low
```
**找到 pivot 之後**
找到 pivot 之後,以 pivot 的位置切割兩個陣列,再分別對兩個陣列做 binary search 找 target 即可。
```python=
class Solution:
def search(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
l, r = 0, len(nums) - 1
while l < r:
m = (l + r) // 2
if nums[m] > nums[r]:
l = m + 1
else:
r = m
pivot = l
def binary_search(left: int, right: int) -> int:
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if nums[mid] == target:
return mid
elif nums[mid] < target:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid - 1
return -1
result = binary_search(0, pivot - 1)
if result != -1:
return result
return binary_search(pivot, len(nums) - 1)
```
## 6. Time Based Key Value Store
<font color="#ffbb00">**Medium**</font>
> Implement a time-based key-value data structure that supports:
>
> * Storing multiple values for the same key at specified time stamps
> * Retrieving the key's value at a specified timestamp
>
> Implement the `TimeMap` class:
>
> * `TimeMap()` Initializes the object.
> * `void set(String key, String value, int timestamp)` Stores the key `key` with the value `value` at the given `time timestamp`.
> * `String get(String key, int timestamp)` Returns the most recent value of `key` if `set` was previously called on it *and* the most recent timestamp for that key `prev_timestamp` is less than or equal to the given timestamp (`prev_timestamp <= timestamp`). If there are no values, it returns `""`.
>
> Note: For all calls to `set`, the timestamps are in strictly increasing order.
### Example 1:
```java
Input:
["TimeMap", "set", ["alice", "happy", 1], "get", ["alice", 1], "get", ["alice", 2], "set", ["alice", "sad", 3], "get", ["alice", 3]]
Output:
[null, null, "happy", "happy", null, "sad"]
Explanation:
TimeMap timeMap = new TimeMap();
timeMap.set("alice", "happy", 1); // store the key "alice" and value "happy" along with timestamp = 1.
timeMap.get("alice", 1); // return "happy"
timeMap.get("alice", 2); // return "happy", there is no value stored for timestamp 2, thus we return the value at timestamp 1.
timeMap.set("alice", "sad", 3); // store the key "alice" and value "sad" along with timestamp = 3.
timeMap.get("alice", 3); // return "sad"
```
### Constraint
* `1 <= key.length, value.length <= 100`
* `key` and `value` only include lowercase English letters and digits`
* `1 <= timestamp <= 1000`
### Solution
**`set()` 方法與建構函式 `__init__()`**
依照題目的意思,每筆資料都是一組 key-value pair,且 value 儲存的是某個時間點所對應的狀態,也就是每個 value 會有兩筆資料。例如 `{alice:[(happy, 1), (sad, 2)]}` 的形式。可想而知可以使用 hash map 搭配 array 的資料結構來儲存。
**`get()` 方法**
先利用輸入的 key 找到 hash map 中對應的 2-D array。因為 array 中儲存的是狀況(`value`)與對應時間(`timestamp`),所以可以使用整數型態的 `timestamp` 來進行 binary search 尋找給定 `timestamp` 的狀態
以下兩個情況或回傳空字元
* 儲存的 `timestamp` > 給定輸入的 `timesamp`
* 沒有該組 (key,value)
```python=
class TimeMap:
def __init__(self):
self.hashDS = defaultdict(list)
def set(self, key: str, value: str, timestamp: int) -> None:
self.hashDS[key].append((value, timestamp))
def get(self, key: str, timestamp: int) -> str:
arr = self.hashDS[key]
# there are two situation will return ""
# (1) no corresponding value for the input key
# (2) minimum timestamp in the particular key is greater than input timestamp
# where the minumum timestamp is always the first item in the value list
if (not arr) or (arr[0][1] > timestamp):
return ""
# binary search to find recent timestamp
minTimeIdx = 0
low, high = 0, len(arr) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = low + (high - low) // 2
if arr[mid][1] > timestamp:
high = mid - 1
if arr[mid][1] <= timestamp:
minTimeIdx = mid
low = mid + 1
return arr[minTimeIdx][0]
```
## 7. Median of Two Sorted Arrays
<font color="#ee2f56">**Hard**</font>
> You are given two integer arrays `nums1` and `nums2` of size `m` and `n` respectively, where each is sorted in ascending order. Return the **median** value among all elements of the two arrays.
>
> Your solution must run in $O(\log (m+n))$ time.
### Example 1:
```java
Input: nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3]
Output: 2.0
```
### Example 2:
```java
Input: nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2,4]
Output: 2.5
```
### Constraints
* `nums1.length == m`
* `nums2.length == n`
* `0 <= m <= 1000`
* `0 <= n <= 1000`
* `-10^6 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 10^6`
### Solution
#### 1. Brute force
```python=
# brute force
class Solution:
def findMedianSortedArrays(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> float:
entireArr = sorted(nums1 + nums2)
low, high = 0, len(entireArr) - 1
if (low + high) % 2 == 1:
midLeft = (low + high) // 2
midRight = midLeft + 1
return (entireArr[midLeft] + entireArr[midRight]) / 2
else:
return float(entireArr[(low + high) // 2])
```
#### 2. Binary search
將長度為 n 與 m 的兩個 array 合併以後可以很輕鬆的知道中位數是哪一個。因此試著在合併(merge)兩個陣列之前就找中位數的位置。
題目所給定的兩個 array 都是排序好的,假設 array A 的長度較小的,若從 A 中挑選 x 個元素,則應該從 B 再挑選 half - x 個元素。但要如何確定兩個陣列選的個數是正確的?可以用各自的最大值來看,假設
* Aleft: the rightmost element in the left subarray of A
* Aright: the leftmost element in the right subarray of A
* Bleft: the rightmost element in the left subarray of B
* Bright: the leftmost element in the right subarray of B
若 `Aleft <= Bright` and `Bleft <= Argiht` 則表示選定的中間值是正確的。若 `Aleft > Bright` 則表示陣列 A選定的 half 太大需要變小。若 `Bleft > Aright` 則表示陣列 A 選定的 half 太小需要變大。

上述選擇適合 half 位置的過程可以使用 binary search 進行。當找到滿足條件的 half 值後就表示已經找到完整 array 的中間值。此時再依據 array 長度決定中位數要如何計算
* Array 長度 n 為偶數:則計算 smaller sub-array 的最大值與 greater sub-array 的最小值的平均
* Array 長度 n 為奇數:則取 greater sub-array 的最小值
```python=
class Solution:
def findMedianSortedArrays(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> float:
total = len(nums1) + len(nums2)
half = total // 2
# let A be the small size array
if len(nums1) < len(nums2):
A, B = nums1, nums2
else:
A, B = nums2, nums1
# binary search
# Aleft: the rightmost element in the left subarray of A
# Aright: the leftmost element in the right subarray of A
# Bleft: the rightmost element in the left subarray of B
# Bright: the leftmost element in the right subarray of B
low, high = 0, len(A) - 1
while 1:
IdxA = low + (high - low) // 2
IdxB = half - IdxA - 2 # IdxB = half - (IdxA + 1) - 1 = half - IdxA - 2
Aleft = A[IdxA] if IdxA >= 0 else float("-inf")
Aright = A[IdxA + 1] if (IdxA + 1) < len(A) else float("inf")
Bleft = B[IdxB] if IdxB >= 0 else float("-inf")
Bright = B[IdxB + 1] if (IdxB + 1) < len(B) else float("inf")
if (Aleft <= Bright) and (Bleft <= Aright):
if total % 2 == 0:
return (max(Aleft, Bleft) + min(Aright, Bright)) / 2
else:
return min(Aright, Bright)
elif Bleft > Aright: # middle value IdxA is too small
low = IdxA + 1
else: # middle value IdxA is too big
high = IdxA - 1
```