## 3 Marks Questions:
### i) Explain `useEffect` with example?
- `useEffect` is a React Hook that lets you synchronize a component with an external system.
- `useEffect` Hook added in React on 2018
- Example:
```jsx
import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
useEffect(() => {
document.title = `You clicked ${count} times`;
}, [count]);
return <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Click me</button>;
}
```
### ii) Explain `useState` with example?
- `useState` is a React Hook that lets you add a state variable to your component.
- It returns an array with two values: the current state and a function to update the state.
- Example:
```jsx
import { useState } from "react";
function Example() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>You clicked {count} times</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Click me</button>
</div>
);
}
```
### iii) Explain MVC Components?
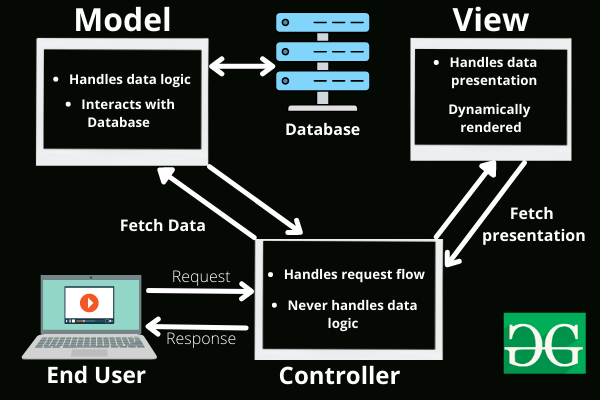
MVC (Model-View-Controller) is an architectural pattern that separates an application into three main components: the model, the view, and the controller.
Each of these components is built to handle specific development aspects of an application.
**Components of MVC:**
- **Model:** The model component represents the data and the business logic of the application.
- **View:** The view component represents the user interface of the application.
- **Controller:** The controller component acts as an interface between the model and the view components.
### iv) Explain different libraries in NodeJS?
Node.js libraries are pre-written JavaScript code that can be used to perform common tasks or add functionality to Node.js applications.
NodeJS libraries can be installed with npm, by using `npm install <librarie-name>` command.
You can use libraries by adding keyword `import` or `require`.
There are thousands of Node.js libraries available, covering a wide range of topics, including web development, database access, data manipulation, and more.
Node.js libraries include:
- Express: A web application framework that makes it easy to create and manage web applications and APIs.
- Async: A JavaScript library that provides helper functions for working with asynchronous code.
- Request: A JavaScript library for making HTTP requests.
- Lodash: A JavaScript utility library that provides a wide range of functions for working with data and objects.
- Puppeteer: A Node.js library for controlling a headless Chromium browser.
- Jest: A JavaScript testing framework.
### v) Explain Event Loop with example?
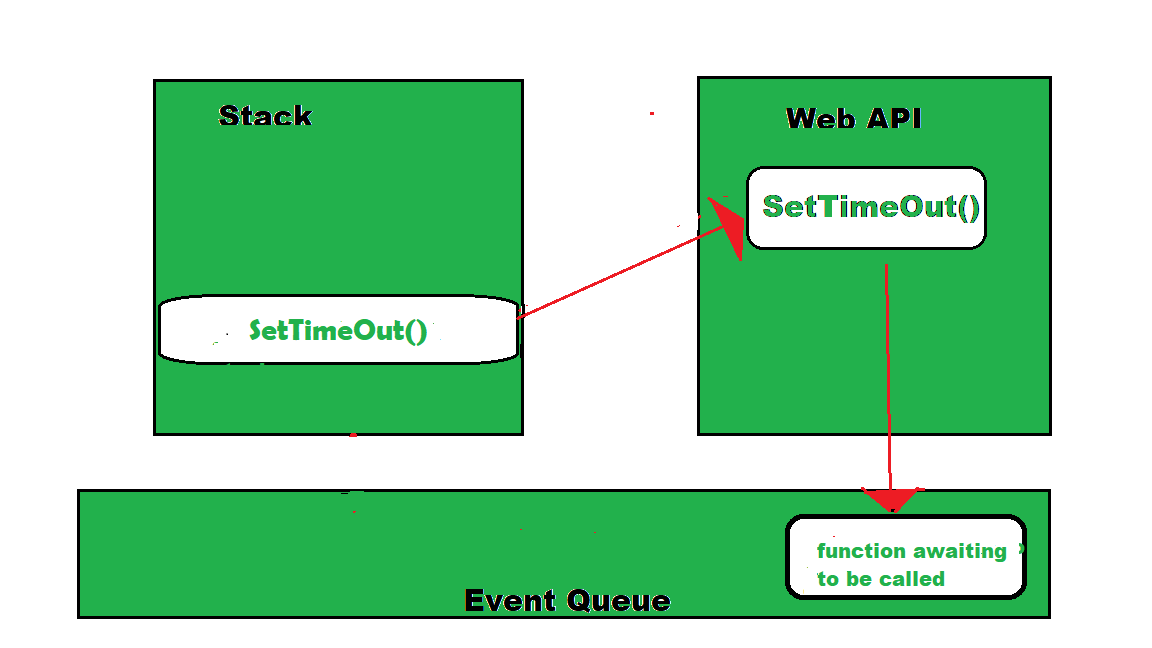
The event loop is a fundamental part of Node.js that enables asynchronous programming by ensuring the main thread is not blocked.
Example:
```js
console.log('start');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('timeout');
}, 0);
console.log('end');
```
Output:
```
start
end
timeout
```
#### Phases of the Event loop:

1. Timers: This phase processes timers that have been set using setTimeout() and setInterval().
2. Pending Callbacks: This phase processes any callbacks that have been added to the message queue by asynchronous functions.
3. Idle, Prepare: The “idle” phase is a period of time during which the event loop has nothing to do and can be used to perform background tasks, such as running garbage collection or checking for low-priority events.
4. Poll: This phase is used to check for new I/O events and process any that have been detected.
5. Check This phase processes any setImmediate() callbacks that have been added to the message queue.
6. Close Callbacks: This phase processes any callbacks that have been added to the message queue by the close event of a socket.
## 2 Marks Questions:
### i) Write short notes on ExpressJS Authentication?

Authentication is a process in which the credentials provided are compared to those on file in a database of authorized users' information on a local operating system or within an authentication server.
ExpressJS is a popular web framework for Node.js that provides a flexible and easy-to-use API for building web applications.
Here are someways to apply authentication in ExpressJS:
- JSON Web Tokens (JWT): Uses JSON to authenticat user.
- Session-based authentication: Session-based authentication is a traditional authentication mechanism that uses cookies to store session information on the client-side.
- Middleware: Middleware is a powerful feature of ExpressJS that can be used to implement authentication.
Example:
```js
const express = require('express');
const passpost = require('passport');
const LocalStrategy = require('passport-local').Strategy;
passport.use(new LocalStrategy((username, password, done) => {
if (username === "admin" && password === "password") {
return done(null, { username: "admin" });
} else {
return done(null, false, { message: "Not found" });
}
)
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send("Home")
}
app.get("/login", (req, res) => {
res.send("Login page');
})
app.post('/login', passport.authenticate('local', { successRedirect: '/', failureRedirect: '/login' }));
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server started on port 3000');
});
```
### ii) Write short notes on ExpressJS Session.
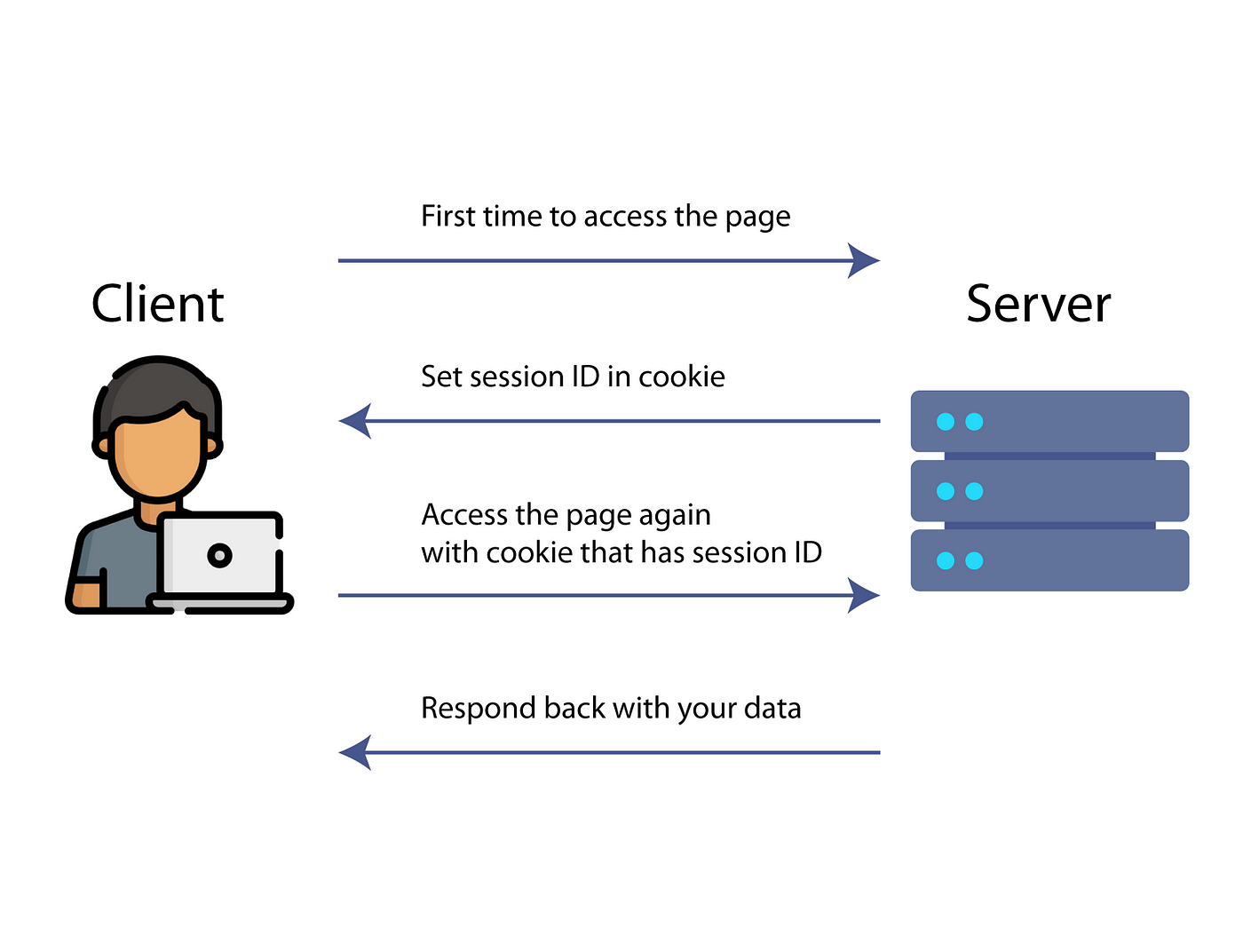
ExpressJS session is a middleware that allows you to store user data between HTTP requests.
HTTP is stateless, which means that there is no way to associate a request with any other request.
Cookies and URL parameters are both suitable ways to transport data between the client and the server, but they are both readable and on the client-side.
Sessions solve this problem by assigning the client an ID and making all further requests using that ID.
```js
const express = require("express");
const session = require("express-session");
const app = express();
app.use(session({}));
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
if (req.session.views) {
req.session.views++;
} else {
req.session.views = 1;
}
res.send("You visited: " + req.session.views + " times.")
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server started on port 3000')
}
```
### iii) Write short notes on Refs?
When you want a component to “remember” some information, but you don’t want that information to trigger new renders, you can use a ref.
```jsx
import { useRef } from 'react';
export default function App() {
let ref = useRef(0);
function click() {
ref.current = ref.current + 1;
alert("Clicked: " + ref);
}
return <button onClic={handleClick}>Click me!</button>;
}
```
### iv) What is callback explain?
A callback is a function that is passed as an argument to another function, and is called after the main function has finished its execution.
(Basically it is a function inside a fucntion)
The main function is called with a callback function as its argument, and when the main function is finished, it calls the callback function to provide a result.
Example:
```js
function parent(a, b, sub) {
const add = a + b;
sub(add);
}
function child(num) {
console.log(num);
}
parent(2, 2, child)
```
Ouptut:
```
4
```
### v) Write short notes on MongoDB Connection.
MongoDB is a NoSQL database that stores data in JSON-like documents.
To connect to a MongoDB database, you can use the MongoDB shell or a MongoDB driver for your programming language.
The following is an example of how to connect to MongoDB using the Node.js driver:
```js
const MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
client.connect(() => {
console.log('Connected to MongoDB database!');
client.close();
}
```
## 5 Marks Questions:
### 1) What is NodeJS? Explain features of NodeJS. State different types of NodeJS modules?
#### What is NodeJS?
- Node.js is a open-source, cross-platform JavaScript runtime enviroment and library for running web appliction outside the client's browser.
- It is used extensively for server-side programming, making it possible for developers to use JavaScript for client-side and server-side code without needing to learn an additional language.
#### Explain features of NodeJS.
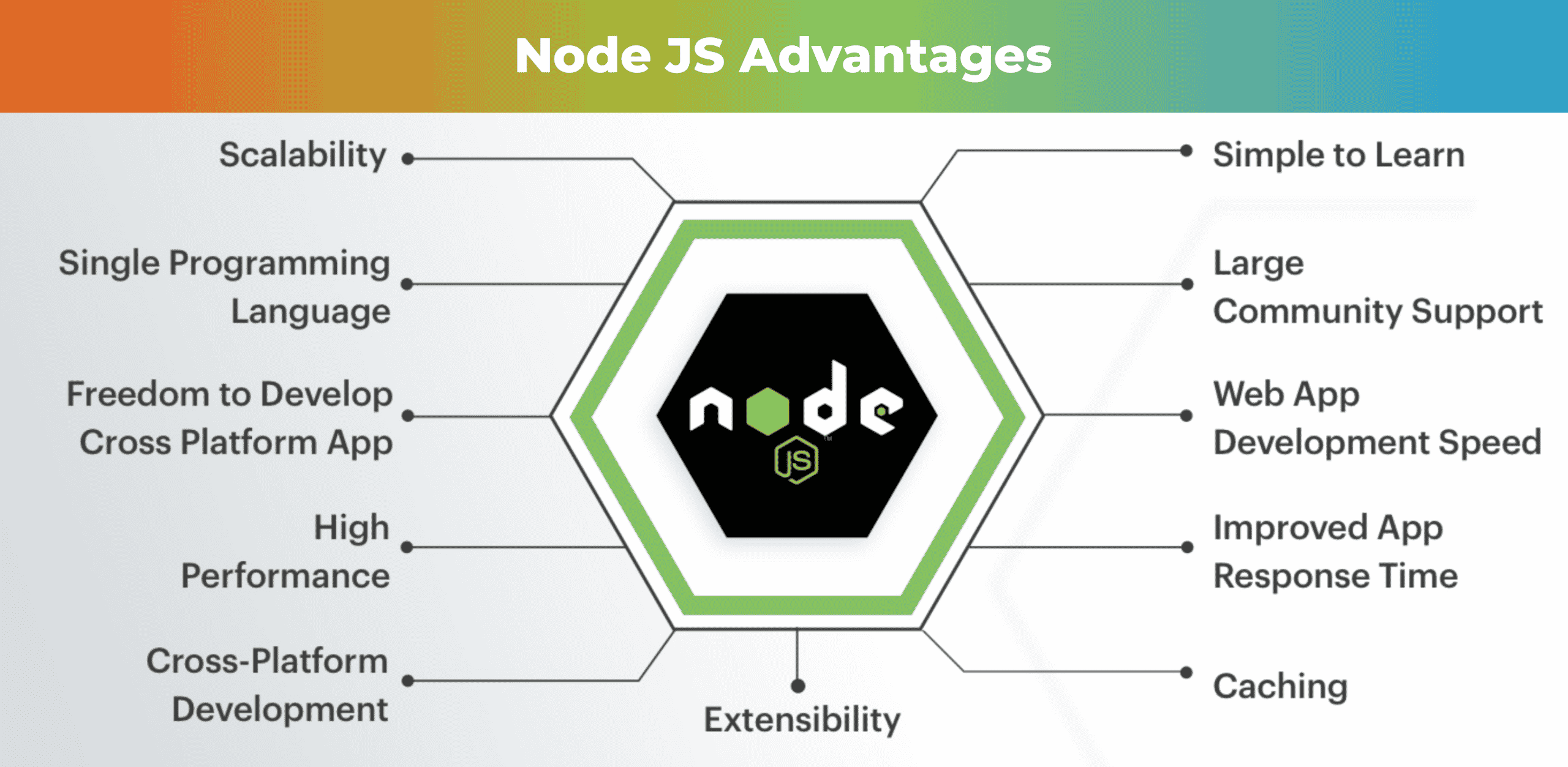
- **Asynchronous and Event-Driven**
- 
- It uses an eventpdriven nono-blocking I/O model that makes it lightweight and efficient.
- This means that NodeJS can handle thousands of concurrent connections.
- **Fast and Scalable**
- It is built on the V8 JavaScript engine which compliles JavaScript internally, using just-in-time(JIT) processes to speed up execution.
- **Cross-platform**
- NodeJS can run on MacOS, Linux, Windows, or any other system.
- **Large Library of Modules**
- NodeJS comes with a large library of JavaScript modules.
- **Single-Threaded**
- NodeJS employs a single-threadedd architecture with event looping, making it very scalable.
#### State different types of NodeJS modules?
- **Core Modules**
- These are built-in modules that are part of the platform and come with NodeJS installation.
- They can be loaded into the program by using the required function or import expression.
- Ex: http, fs, path and many more.
- **Local Modules**
- These are modules that are created locally and can be used in the application.
- They can be a single file or a collection of multiple file/folders.
- **Third-party modules**
- These are modules that are created by third-party developers and can be used in the application.
- They can be installed using npm (Node Package Manager) command.
### 2) Explain routing in ExpressJS with example?

- Routing in ExpressJS refers to how an application responds to client requests to a perticular endpoint.
- It consists of a URI (a path such as `/` or `/books`) and an HTTP method such as GET, POST, PUT, DELETE and PATCH.
- Example:
```javascript
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello World')
})
```
Output: `Hello World`
- In the above example, the `app.get()` method is used to define a route for the GET method to root of the app.
### 3) Explain Flux architecture in details?
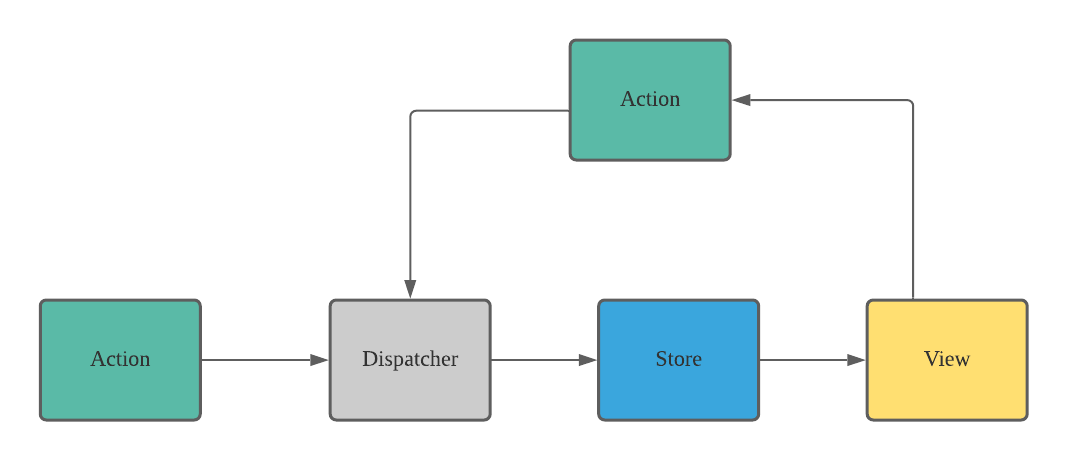
- Flux is an archituctural pattern proposed by Facebook for building single-page application (SPAs) using JavaScript.
- Flux is not a framework or a library, but rather a patten that can be implemented using any JavaScript libray or framework.
#### Components of Flux architecture
- **View:** The view is responsible for rendering the user interface and dispatching action to the dispatcher.
- **Action:** An action is a plain JavaScript object that describes a change in the appliction state.
- **Dispatcher:** The dispatcher is responsible for receiving actions from the view and for dispatching them to the appropriate store.
- **Store:** The store is responsible for managing the application state and for notifying the view of any cahnges to the state.
#### Features of the Flux architecture
- Unidirectional data flow: The data flows in a single direction, from the view to the store, which makes it easier to debug it.
- Centralized state management: The state of an application is managed by stores, which makes it easier to manage the state of an application and to avoid race conditions.
- Explicit updates: The updates to the state of an application are explicit, which makes it easier to trace changes during development and to fix bugs.
- Modularity: The Flux architecture is modular, which makes it easier to maintain and test an application.
#### Pros and Cons of the Flux architecture
- Pros:
- Provides a unidirectional flow where a central unit for the entire application is called the store.
- Actions can be persisted and then replayed.
- Cons:
- Requires more boilerplate code than other architectures.
- Can add unnecessary complexity to an application.
### 4) What is asynchronous programming? Explain in details.

- Asynchronous programming is a programming paradigm that allows a program to execute multiple tasks simultaneously, rather than executing them one after the other.
- In traditional (synchronous) programming, each task is executed in sequence, which can lead to blocking and slow performance.
- Asynchronous programming allows a program to continue working on other tasks while waiting for external events, such as network requests, to occur.
#### Key concepts of asynchronous programming in Node.js
- **Callbacks:**
- 
- A callback is a function that is executed when a task is completed. Callbacks are used to handle the results of asynchronous tasks.
- **Promises:**
- 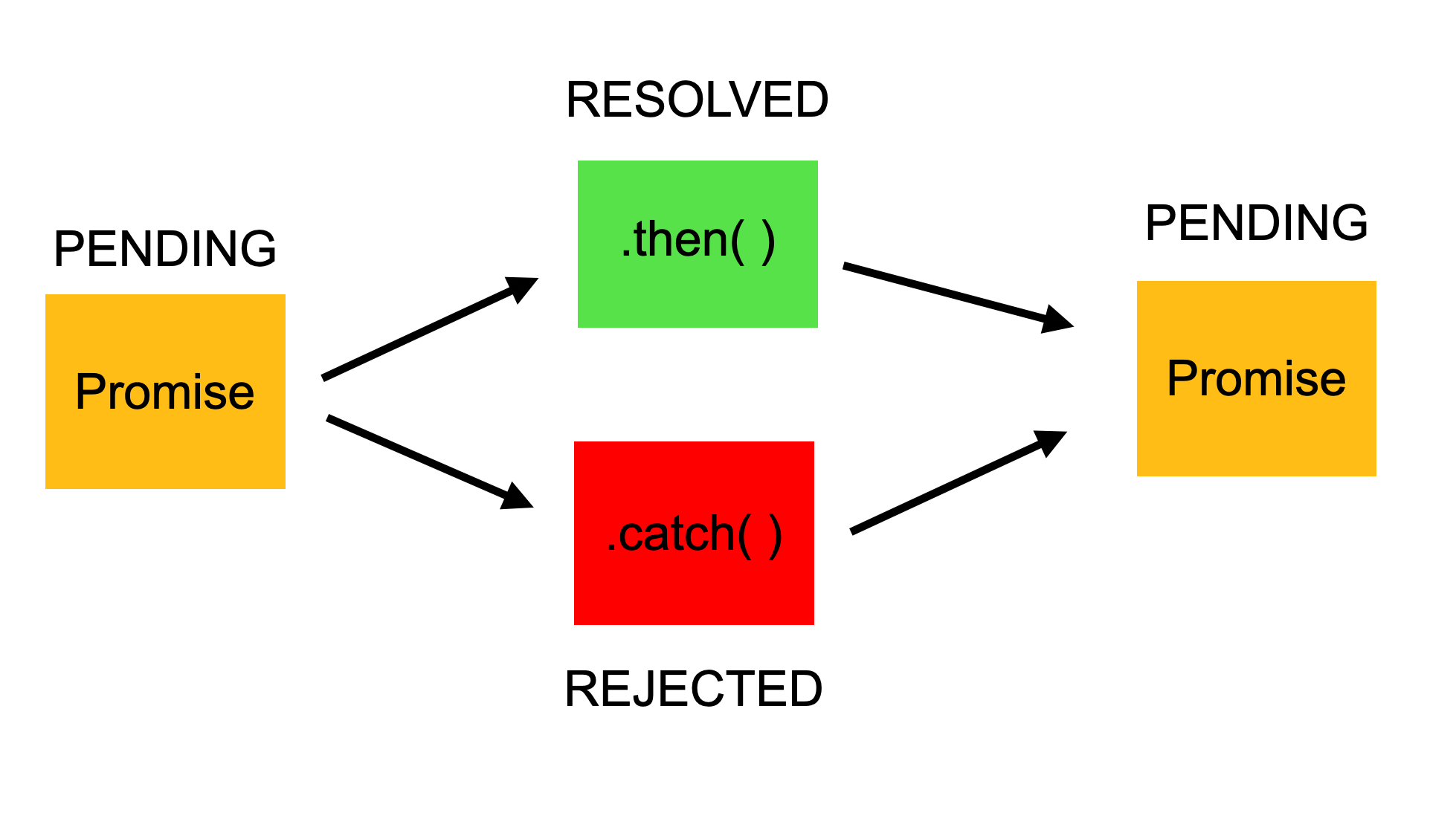
- A promise is an object that represents the eventual completion (or failure) of an asynchronous task. Promises provide a cleaner and more structured way to handle asynchronous tasks than callbacks.
- **Async/await:**
- Async/await is a syntax for writing asynchronous code that looks like synchronous code. Async/await makes it easier to write and read asynchronous code, and it is supported in Node.js.
### 5) Explain NodeJS web module? And what is HTTP connection explain?
#### NodeJS web module
- The Node.js HTTP module is a built-in module that allows Node.js to transfer data over the Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
- It provides a way to create an HTTP server that listens to server ports and gives a response back to the client.
- The HTTP module can be used to create an HTTP client of a server.
#### HTTP connection

- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) connection is a protocol used for transferring files, such as text, images, sound, video, and other multimedia files, over the web.
- An HTTP connection is a connection between a client and a server that uses the HTTP protocol to transfer data.
- When a client sends an HTTP request to a server, the server responds with an HTTP response.
- The HTTP connection is closed after the response is sent.
##### Types of HTTP connections:
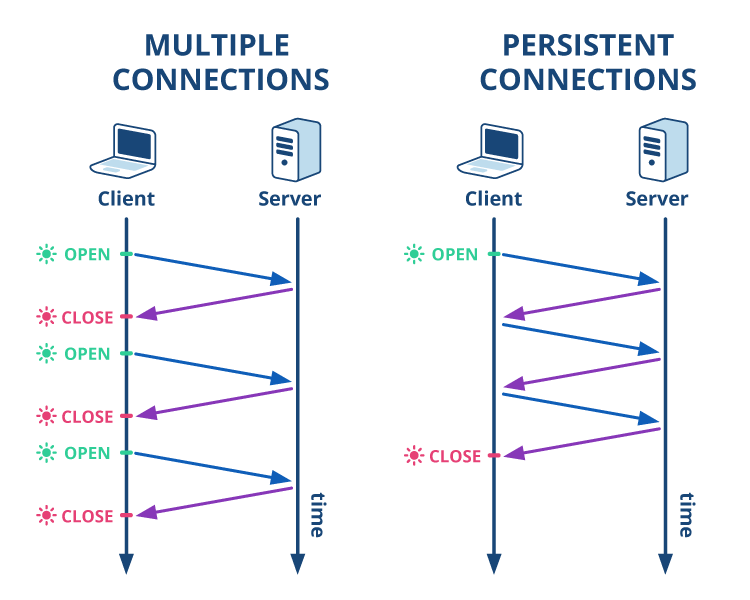
- **Non-Persistent Connection**
- Everytime new connection is formed.
- **Persistent Connection**
- Same connection is continue.
### 6) Explain REST API in details?
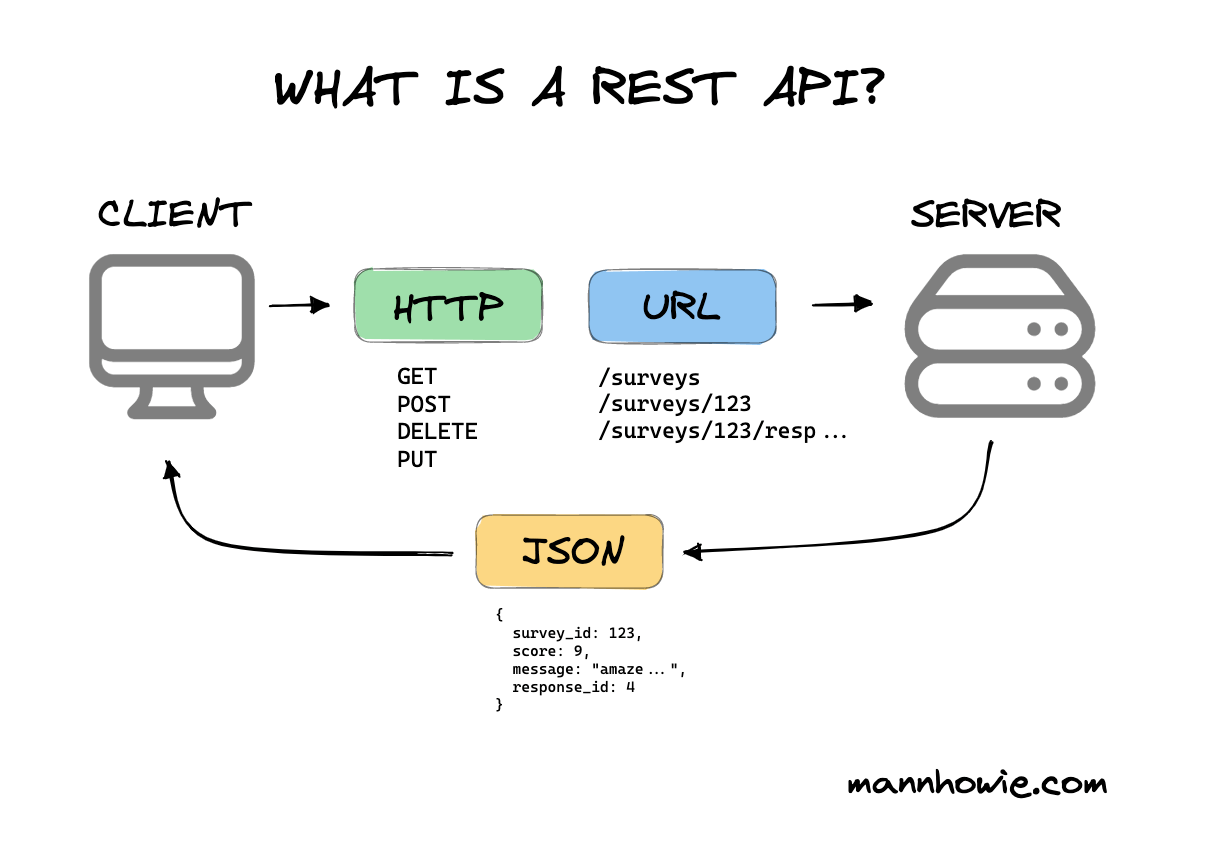
- REST (Representational State Transfer) API is an architectural style for building web services that allows for interaction with RESTful web services.
- It is a specific type of API that follows a set of guidelines that software can use to communicate over the internet in order to make integrations simple and scalable.
- HTTP methods are used to perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on resources.
- The most commonly used HTTP methods in RESTful API are GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE.
#### REST API methods
- **GET**
- It is used to retrieve data from server.
- It does not modify the data of the server.
- **POST**
- Create new data on the server.
- It does not modify the data of the server
- **PUT**
- Updates an existing data on the server.
- **PATCH**
- Updates an existing data on the server.
- **DELETE**
- Deletes data on the server.
#### **Working**
- A request is sent from client to server in the form of a web URL as HTTP GET or POST or PUT or DELETE request.
- A response comes back from the server in the form of a resource which can be anything like HTML, XML, Image, or JSON.