## ## 異常處理
- python 可以讓我們去捕捉異常跟撰寫異常處理程序
```python
# 除數為0
def division(x, y):
return x / y
print(division(10, 2))
print(division(6, 3))
```
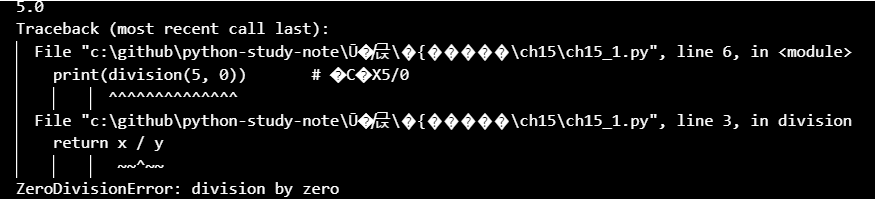
- 我們可以使用`try except來捕捉異常`
```python
def division(x, y):
try: # try - except指令
return x / y
except ZeroDivisionError: # 除數為0時執行
print("除數不可為0")
print(division(10, 2)) # 5.0
print(division(5, 0)) # 除數不可為0
print(division(6, 3)) # 2.0
```
- 可以再增加else
- try -> 預想可能會發生錯誤的指令
- except -> 抓錯
- else -> 沒事,繼續跑
```python
def division(x, y):
try: # try - except指令
ans = x / y
except ZeroDivisionError: # 除數為0時執行
print("除數不可為0")
else:
return ans # 傳回正確的執行結果
print(division(10, 2))
print(division(5, 0))
print(division(6, 3))
```
## 找不到檔案 file not found error
```python
fn = 'data.txt'
try:
with open(fn) as file_Obj:
data = file_Obj.read()
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"找不到 {fn} 檔案")
else:
print(data)
```
## 設計多組異常處理程序
### 常見異常處裡
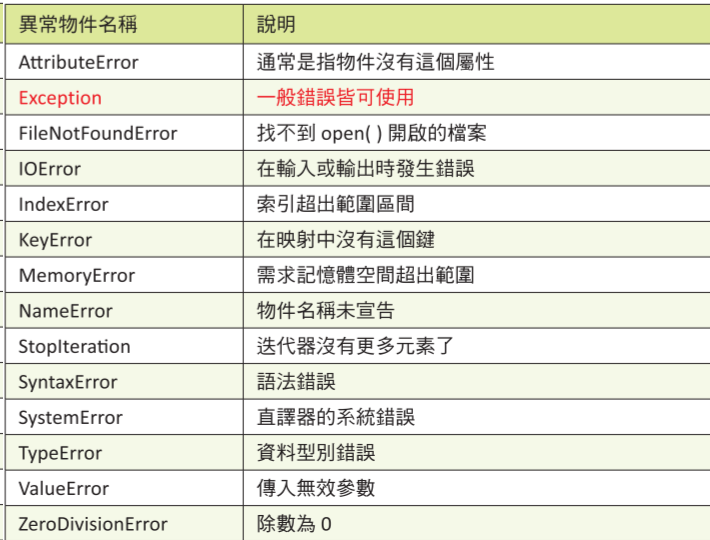
```python
# 通用錯誤
def division(x, y):
try:
return x / y
except Exception as e:
print("有錯誤")
print(division(10, 2))
print(division(5, 0)) #
print(division('a', 'b'))
print(division(6, 3))
```
```python
def division(x, y):
try:
return x / y
except (ZeroDivisionError, TypeError) as e: # 2個異常
print(e)
print(division(10, 2))
print(division(5, 0)) # division by zero
print(division('a', 'b')) # unsupported operand type(s) for /: 'str' and 'str'
print(division(6, 3))
```
```python
# 通用錯誤
def division(x, y):
try:
return x / y
except :
print("有錯誤")
print(division(10, 2))
print(division(5, 0)) #
print(division('a', 'b'))
print(division(6, 3))
```
## 丟出異常raise
- 前面的部分,著重於python發現異常後,丟出異常,如果不處理就中止執行
- 如果要改為,發現異常後會丟出異常,並且跳到設計好的except去處理
```python
def passWord(pwd):
"""檢查密碼長度必須是5到8個字元"""
pwdlen = len(pwd) # 密碼長度
if pwdlen < 5: # 密碼長度不足
raise Exception('password too short')
if pwdlen > 8: # 密碼長度太長
raise Exception('password too long')
print('correct')
for pwd in ('aaabbbccc', 'aaa', 'aaabbb'): # 測試系列密碼值
try:
passWord(pwd)
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
# password too long
# password too short
# correct
```
## 紀錄 Traceback 字串
- 將報錯放到記事本中
```python
import traceback
def passWord(pwd):
"""檢查密碼長度必須是5到8個字元"""
pwdlen = len(pwd) # 密碼長度
if pwdlen < 5: # 密碼長度不足
raise Exception('password too short')
if pwdlen > 8: # 密碼長度太長
raise Exception('password too long')
print('correct')
for pwd in ('aaabbbccc', 'aaa', 'aaabbb'): # 測試系列密碼值
try:
passWord(pwd)
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
errlog = open('err.txt', 'a') # 開啟錯誤檔案
errlog.write(traceback.format_exc()) # 寫入錯誤檔案
errlog.close() # 關閉錯誤檔案
# password too long
# password too short
# correct
```
## finally
- 他是【是否有錯】,都一定會執行
```python
def division(x, y):
try:
print(x / y)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
finally: # 離開函數前先執行此程式碼
print("complete")
division(10, 2)
division(5, 0)
division('a', 'b')
division(6, 3)
# 5.0
# complete
# division by zero
# complete
# unsupported operand type(s) for /: 'str' and 'str'
# complete
# 2.0
# complete
```
## 程式斷言 assert
- 主要用於開發階段做檢查
```python
class Banks():
# 定義銀行類別
title = 'Tainan Bank'
def __init__(self, uname, money):
self.name = uname
self.balance = money
def save_money(self, money): # 設計存款方法
self.balance += money
print("save money", money)
def withdraw_money(self, money): # 設計提款方法
self.balance -= money # 執行提款
print("Withdrawal money", money)
def get_balance(self): # 獲得存款餘額
print("Current balance ", self.balance)
hungbank = Banks('TA', 100)
hungbank.get_balance() # 獲得存款餘額
hungbank.save_money(-300) # 存款-300元
hungbank.get_balance() # 獲得存款餘額
hungbank.withdraw_money(700) # 提款700元
hungbank.get_balance() # 獲得存款餘額
# Current balance 100
# save money -300
# Current balance -200
# Withdrawal money 700
# Current balance -900
```
- 之所以會錯誤是因為,我們在提款前,應該要先檢查帳戶餘額
```python
class Banks():
# 定義銀行類別
title = 'Tainan Bank'
def __init__(self, uname, money):
self.name = uname
self.balance = money
def save_money(self, money): # 設計存款方法
self.balance += money
print("save money", money)
def withdraw_money(self, money): # 設計提款方法
assert money > 0, 'withdraw must > 0'
assert money <= self.balance, 'money not enough'
self.balance -= money # 執行提款
print("Withdrawal money", money)
def get_balance(self): # 獲得存款餘額
print("Current balance ", self.balance)
hungbank = Banks('TA', 100)
hungbank.get_balance() # 獲得存款餘額
hungbank.save_money(-300) # 存款-300元
hungbank.get_balance() # 獲得存款餘額
hungbank.withdraw_money(700) # 提款700元
hungbank.get_balance() # 獲得存款餘額
# Current balance 100
# save money -300
# Current balance -200
# Withdrawal money 700
# Current balance -900
```

## 程式日誌模組 logging
### logging level(低到高)
- DEBUG :
- 用於顯示程式的小細節,是最低層級的內容。
- 通常在調試程式問題時使用,可追蹤關鍵變數的變化過程。
- INFO :
- 用於記錄程式一般發生的事件。
- WARNING :
- 用於顯示可能影響程式執行但尚未造成問題的事件,未來可能導致問題的發生。
- ERROR :
- 顯示程式發生的錯誤,通常是在某些狀態下引發錯誤的原因。
- CRITICAL :
- 通常表示將導致系統崩潰或中斷的錯誤。
```python
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG, format="") # 等級是DEBUG
logging.debug('logging message, DEBUG')
logging.info('logging message, INFO')
logging.warning('logging message, WARNING')
logging.error('logging message, ERROR')
logging.critical('logging message, CRITICAL')
# logging message, DEBUG
# logging message, INFO
# logging message, WARNING
# logging message, ERROR
# logging message, CRITICAL
```
```python
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.WARNING, format="") # 等級是DEBUG
logging.debug('logging message, DEBUG')
logging.info('logging message, INFO')
logging.warning('logging message, WARNING')
logging.error('logging message, ERROR')
logging.critical('logging message, CRITICAL')
# logging message, WARNING
# logging message, ERROR
# logging message, CRITICAL
```
```python
# 列出時間、等級、地點
logging.basicConfig(filename="logging.txt" level=logging.WARNING, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s : %(message)s') # 等級是DEBUG
logging.debug('logging message, DEBUG')
logging.info('logging message, INFO')
logging.warning('logging message, WARNING')
logging.error('logging message, ERROR')
logging.critical('logging message, CRITICAL')
# logging message, WARNING
# logging message, ERROR
# logging message, CRITICAL
```
- 最後要停用logging
```python
logging.disable(logging.CRITICAL)
```
# module & package
- 以下是python常見的module
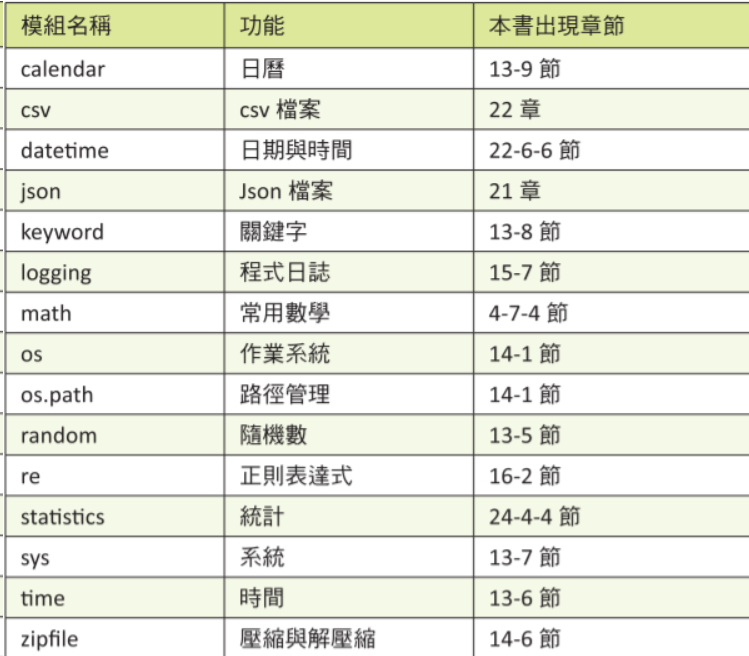
- 外部module會使用pip去安裝
## 自己建立模組
```python
def make_icecream(*toppings):
"""這邊寫關於函數的說明
Args:
toppings (string): 各種配料
Return:
none
"""
print("這個冰淇淋所加配料如下")
for topping in toppings:
print("--- ", topping)
def make_drink(size, drink):
"""這邊寫關於函數的說明
Args:
size (string):
drink (string): 各種飲料
Return:
none
"""
print("所點飲料如下")
print("--- ", size.title())
print("--- ", drink.title())
make_icecream('草莓醬')
make_icecream('草莓醬', '葡萄乾', '巧克力碎片')
make_drink('large', 'coke')
# 這個冰淇淋所加配料如下
# --- 草莓醬
# 這個冰淇淋所加配料如下
# --- 草莓醬
# --- 葡萄乾
# --- 巧克力碎片
# 所點飲料如下
# --- Large
# --- Coke
```
- 那我覺得我知還會再用到這個func,所以我把它放到module
## 應用自己寫的module
- 副檔名為py
```python
%%writefile make_food.py
def make_icecream(*toppings):
"""這邊寫關於函數的說明
Args:
toppings (string): 各種配料
Return:
none
"""
print("這個冰淇淋所加配料如下")
for topping in toppings:
print("--- ", topping)
def make_drink(size, drink):
"""這邊寫關於函數的說明
Args:
size (string):
drink (string): 各種飲料
Return:
none
"""
print("所點飲料如下")
print("--- ", size.title())
print("--- ", drink.title())
```
- 要使用的地方把它引入 `from module_name import func_name`
```python
from make_food import make_icecream
make_icecream('草莓醬', '葡萄乾', '巧克力碎片')
# 這個冰淇淋所加配料如下
# --- 草莓醬
# --- 葡萄乾
# --- 巧克力碎片
```
- 如果要導入多組函數 `from make_food import make_icecream, make_drink`
- 如果要導入所有函數 `from make_food import *`
### module 使用別稱as
- 可以分為:
- 幫module取名
- 幫module的func取名
```python
from make_food import make_icecream as m
m('草莓醬', '葡萄乾', '巧克力碎片')
```
```python
import make_food as m
m.make_icecream('草莓醬', '葡萄乾', '巧克力碎片')
```
## if name == "main"
## 將自己寫的class建立在module內
- 類別也可以用module的方式去處理
```python
class Banks():
def __init__(self, name):
self.__name = name
self.__balance = 0
self.__title = "Bank"
def save_money(self, money): # 設計存款方法
self.__balance += money
print("存款 ", money, " 完成")
def withdraw_money(self, money): # 設計提款方法
self.__balance -= money
print("提款 ", money, " 完成")
def get_balance(self): # 獲得存款餘額
print(self.__name.title(), " 目前餘額: ", self.__balance)
def bank_title(self): # 獲得銀行名稱
return self.__title
class Tainan_bank(Banks):
def __init__(self, name):
self.__title = "Tainan bank"
def bank_title(self): # 獲得銀行名稱
return self.__title
```
## 應用自己寫的class
```python
from make_band import Banks, Tainan_bank
TA = Banks('James')
print("TA's banks = ", TA.bank_title()) # 列印銀行名稱
TA.save_money(500) # 存錢
TA.get_balance() # 列出存款金額
hung = Tainan_bank('Hung') # 定義Shilin_Banks類別物件
print("hung's banks = ", hung.bank_title()) # 列印銀行名稱
```
## random module
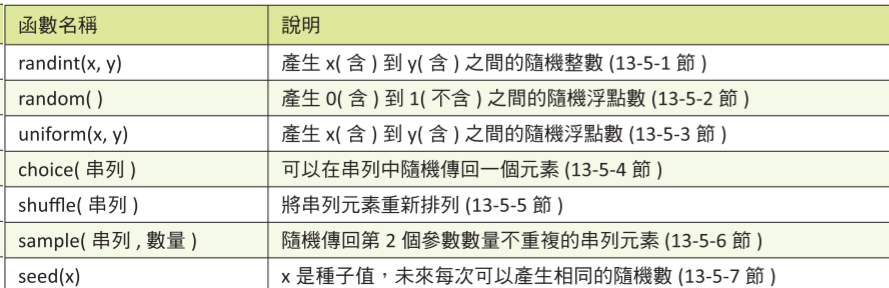
```python
import random
random.seed(24)
print(random.randint(1, 10)) # 隨機整數
print(random.random()) # 0-1 隨機浮點數
print(random.uniform(1,3)) # 範圍間隨機浮點數
print(random.choice(["a", "b", "c"])) # 範圍間隨機選
print(random.sample(["a", "b", "c"], 2)) # 範圍間隨機選要求數量
# 隨機排列
arr = ["a", "b", "c"]
random.shuffle(arr)
print(arr)
# 7
# 0.8397997363118733
# 1.365183773909035
# a
# ['a', 'c']
# ['b', 'a', 'c']
```
## time module
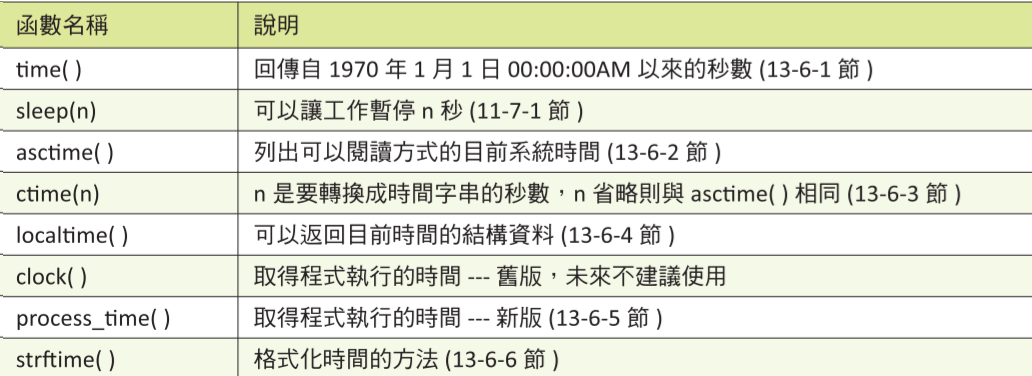
```python
import time
print(time.time()) # 1970.01.01到現在秒數
print(time.ctime()) # 目前系統時間
print(time.localtime()) # 返回tuple結構時間
print(time.localtime().tm_year)
print(time.localtime()[0])
# 1723896127.5555916
# Sat Aug 17 20:02:07 2024
# time.struct_time(tm_year=2024, tm_mon=8, tm_mday=17, tm_hour=20, tm_min=2, tm_sec=7, tm_wday=5, tm_yday=230, tm_isdst=0)
# 2024
# 2024
```
## keyword module
- 檢查關鍵字
```python
import keyword
print(keyword.kwlist) # 列出所有關鍵字
# 檢查關鍵字
arr = ['False', 'and', 'as']
for i in arr:
print(keyword.iskeyword(i))
# ['False', 'None', 'True', 'and', 'as', 'assert', 'async', 'await', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'nonlocal', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
# True
# True
# True
```
## sys module
- 可以了解python shell的訊息
```python
import sys
# 顯示python訊息
print(sys.version)
print(sys.version_info) # 比較結構化
```
```python
##### stdin #####
# standard input 的縮寫
import sys
# 要額外開+terminal
print("請輸入字串")
msg = sys.stdin.readline()
print(msg)
# 規定要取幾個字元
print("請輸入字串")
msg = sys.stdin.readline(3)
print(msg)
```
```python
##### stdout #####
# standard output 的縮寫
import sys
# 要額外開+terminal
sys.stdout.write("122323")
```
```python
# 列出module所在的路徑
import sys
for i in sys.path:
print(i)
# D:\anaconda3\python312.zip
# D:\anaconda3\DLLs
# D:\anaconda3\Lib
# D:\anaconda3
# D:\anaconda3\Lib\site-packages
# D:\anaconda3\Lib\site-packages\win32
# D:\anaconda3\Lib\site-packages\win32\lib
# D:\anaconda3\Lib\site-packages\Pythonwin
```
## module searching
- 針對模組放的路徑,可以有一下選擇:
- 放在該專案資料夾裡面的 sys.path
- 跟 main program 放在一起
- 放在任何地方,再去更改 sys.path
```python
import sys
# 電腦會根據以下每一個路徑去找module
print(*sys.path, sep="\n")
# c:\github\python-study-notes\python基本教學
# c:\Users\33313\anaconda3\python311.zip
# c:\Users\33313\anaconda3\DLLs
# c:\Users\33313\anaconda3\Lib
# c:\Users\33313\anaconda3
# ...
```
```python
# TODO:更改sys.path
sys.path.append("要增加的路徑")
```
## namespace
- 其實就是前面提到 LEGB 規則的延伸,程式在找變數(函數),會先從區域命名空間(local namespace)去找,接著是全域命名空間(global namespace),最後是 built-in(內建函式庫)
```python
# 輸出內建函式庫
print(__builtins__) # <module 'builtins' (built-in)>
# 輸出所有函數名稱
print(*dir(__builtins__), sep="\n")
# ArithmeticError
# AssertionError
# AttributeError
# BaseException
# ...
```
## package
- package 是一種包含很多 python 模組的字典
- PyPI:全名 Python Package Index,是指 Python 生態系統中的一個中央軟件存儲庫。
- Pip:安裝第三方庫的指令:
```terminal=
# TODO: pip相關指令
pip install <package_name>
pip install -upgrade <package_name>
# 安裝指定版本
pip install <package_name> == <指定版本>
# 確認目前安裝所有模組及版本
pip freeze
```
## Lab07作業題目
- 繳交方式 :請到https://140.116.179.59:8080完成作業題目,並將程式碼加上註解(你的理解),很重要,否則助教有權利扣你分數
- 禁止抄襲,否則助教會來查水表。
- 本次Lab
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet