# iExec
## Blockchain
* Smart contract: A protocol that can digitally facilated and verified.
* Blocks in bitcoin store only transactions.
* In ethereum network, they are stored as bytecode on chain
* Written in Solidary and needs to be compiled
* On ethereum network, there is a runtime running on top of each node. The network formed by these middlewares as a whole is known as EVM.
* token
* Buy certain tokens of that DAPP in exchange of your ether.
* Why tokens?
* By using tokens to execute certain functions in the smart contract of the DAPPS you make the process much more simple and seamless.
* Like a ticket to the theater
* [Mining](https://blockgeeks.com/guides/ethereum-mining-proof-stake/)
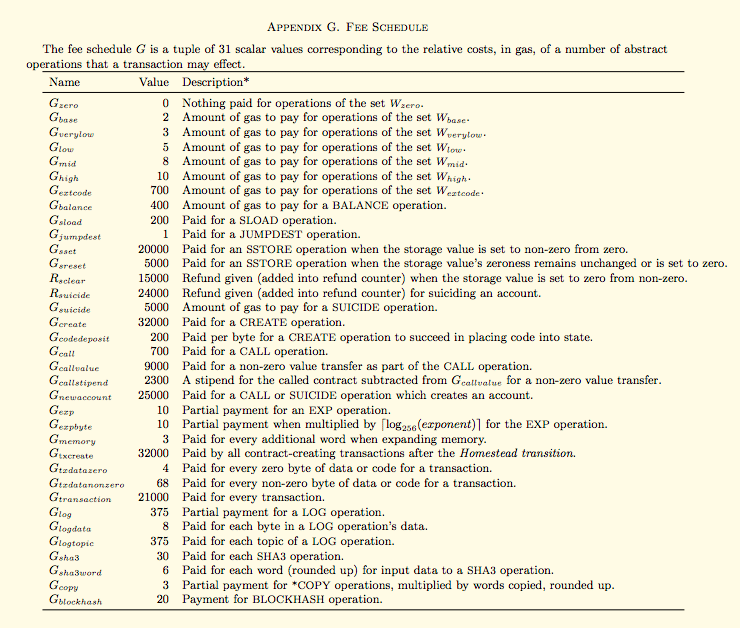
* Gas
* For each instruction in Solidity, there is a price for execution, paid by the requestor to the worker
## Overview
A decentralized computing power manager for DApps. Based on Etherum smart contract.
* DApps: Applications based on blockchain technology, usually have the following features
* Decentralized: All records for application's operations must be stored on public blockchain
* Protocol: All parties must agree on a cryptographic algorithm to show proof of value
* Incentived: Validators of the blockchain should be incentivized by rewarding them accordingly with cryptographic tokens.
* Mostly Open Source
* Ethereum
* Ethereum allowed developers from all over the world to run their Dapps on top of their platform.
* Now PoW(proof-of-work)
### Off-chain
* Why off-chian?
* High gas cost for compuataionally heavy tasks
* Execution time is bounded by the time it takes for the network to achieve consensus.
* Bad for video transcoding, 3D rendering, etc.
* Smart contracts may require volatile information from off-chain logic, such as a stock price
* Verifable computation
* Clients can not only retrieve the result and proof of correctness for an outsourced operation, but also verify the proof of correctness with less computational power than is required by the actual operation.
#### Oracles
Third parties that push external data onto the blockchain. Smart contracts can invoke oracles that answer questions in a deterministic fashion without knowing the full context of the transaction.

* Types
* Data carrier oracle
* Transfer the query result from the data source you trust to the smartt contract
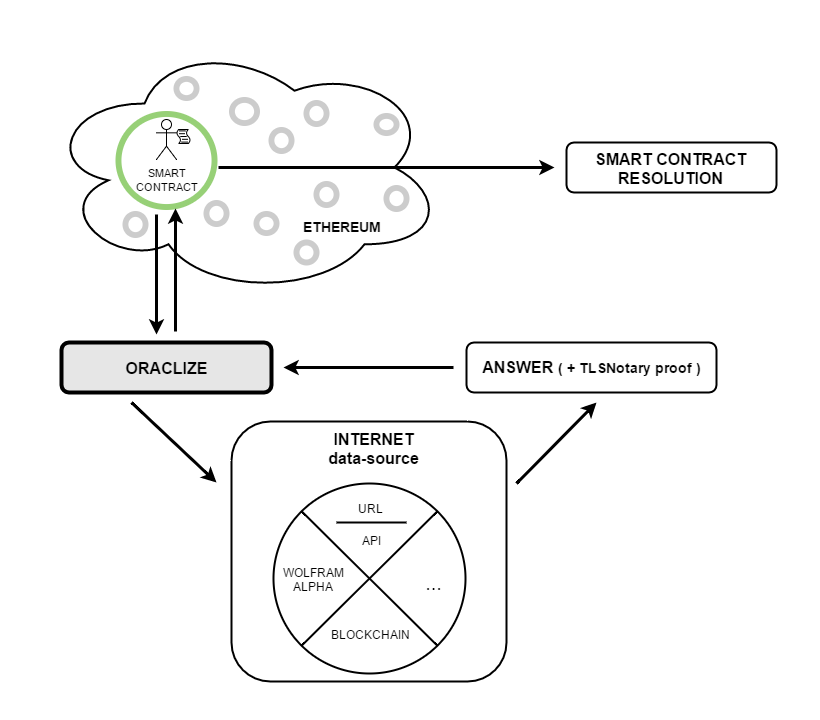
* A modification of TLS, called TLSNotary, is used by our oracle service to provide cryptographic proofs showing that the data we provided to you was really the one a given server gave back to us at a specific time.
* Computation oracle
* Perform computation and relay query result

* Truebit
* Introducing a system of solvers and verifier
* Solvers are compensated for performing computation
* Verifiers are compensated for detecting errors in solutions submitted by solvers
* [iExec dOracle](https://docs.iex.ec/doracle.html#the-doracle-generic-contract)
* A framework to build an oracle
## [iExec proof of Consensus](https://medium.com/iex-ec/about-trust-and-agents-incentives-4651c138974c)
Schedulers manage pools of worker and act as middlemen between the blockchain (listening to the iExec smart-contract) and the workers
### Sarmenta voting
* Based on the majority voting
* The scheduler dynamically “decides” how many contributions are necessary to achieve consensus
* Each worker has its reputation, which incentize them.
* Workers are required to commit a security deposit
### Steps
1. Workers register themselves to a scheduler.
2. Users submit tasks to scheduler managing the work pool they chose.
3. Worker waits for the scheuler for task assignment
### [Trusted execution](https://medium.com/iex-ec/poco-series-4-sgx-enclaves-and-trusted-executions-6f2ebed8d4fa)
* Enclave and PoCo
* PoCo is a protocol in charge of providing a trusted computing environment on top of untrusted resources, with an incentive system making the workers on the platform behave correctly. It includes a layer of certification that relies on the reputation of the workers
* Enclaves ensure that a worker is not able to interfere with the execution, thus removing the need for result certification.
* The downside of enclaves (For Intel)
* No GPU has support for enclave
* Performance overhead
* Not yet available on all processors
#### Current development
The application result calculated on Intel® SGX worker can be signed by enclave private key or a private key protected by enclave, the signature can then be transferred to on-chain network for verification via the corresponding public key that is registered on Blockchain.

1. A pair of private key and public key is generated inside an enclave
2. The worker sends the public key to the scheduler via a secure channel signed by Intel SGX
3. Remote Attestation for public key using IAS(Intel Attestation Server), proving the key is actually generated inside an enclave
4. The scheduler sends a message, which includes the public key, to the blockchain authorizing the worker to contribute to a specific work order.
5. The worker runs the dapp inside or outside the enclave and signs the result with the enclave’s private key inside the enclave.
6. The worker sends the contribution report, which includes a signature and can be verified on-chain, to the blockchain
## Considertion
Current data centers greatly consume energy while many enterprise couldn't afford
* DApp providers can perform off-chain computations on demand
* Server providers can monetize underused computing resources and increase the return on investment on their existing infrastructure
* Data provider can publish their data onto iexec marketplace
* Application providers can radically lower the computing costs of their DApp by using a safe, robust and reliable infrastructure.
### Advancement
* Proof of Contribution Protocol
## Technical Details
* RLC Token
* Application providers, dataset owners, owner of computing resources (workers) and users can value their assets using the RLC token
* Matchmaking Algorithm
* To pair a resource request with a resource offer according to their description. Answer "Can I run this task on this machine?"
* Some contracts will describe the requirements for running a task or deploying a VM instance (Disk space, etc.)
* ClassAds that powers the CondorHTC distributed system
* multi-criteria scheduler
* Domain Specific Sidechain
* Prevent [DAO attack](https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10196348) on smart contract