---
tags: linux2023
---
# 2022q1 Homework1 (lab0)
contributed by < `CLKaoB05` >
### Reviewed by `jim12312321`
- 在 `q_remove_head` 和 `q_remove_tail` 中 `len` 的求法可改用 bitwise 操作,減少分支使用以提升效率。
- 欲移除節點時,可用 `list_del_init` ,會更加安全,尤其之後還有可能用到該節點時。
- `q_delete_mid` 中應檢查 head 是否為 NULL 或 empty 的情況。
- `q_swap` 中利用 for 走訪 linked list 的做法由於會涉及到移除節點,應用類似 `list_for_each_entry_safe` 的寫法或是直接用該 API 取代。
---
## 實驗環境
```shell
$ gcc --version
gcc (Ubuntu 9.3.0-17ubuntu1~20.04) 9.3.0
$ lscpu
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
Address sizes: 39 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
CPU(s): 8
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-7
Thread(s) per core: 2
Core(s) per socket: 4
Socket(s): 1
NUMA node(s): 1
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 94
Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6700 CPU @ 3.40GHz
Stepping: 3
CPU MHz: 3400.000
CPU max MHz: 4000.0000
CPU min MHz: 800.0000
BogoMIPS: 6799.81
L1d cache: 128 KiB
L1i cache: 128 KiB
L2 cache: 1 MiB
L3 cache: 8 MiB
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-7
```
## [作業要求](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/linux2022-lab0)
* 依據上述指示著手修改 `queue.[ch]` 和連帶的檔案,測試後用 Git 管理各項修改,要能滿足 `$ make test` 自動評分系統的所有項目。
[queue.c](https://github.com/sysprog21/lab0-c/blob/master/queue.c) 僅提供介面 ([interface](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interface-based_programming)) 但尚未有完整程式實作,需要由學員補完並逐步精進,包含以下:
* `q_new`: 建立新的「空」佇列;
* `q_free`: 釋放佇列所佔用的記憶體;
* `q_insert_head`: 在佇列開頭 (head) 插入 (insert) 給定的新節點 (以 LIFO 準則);
* `q_insert_tail`: 在佇列尾端 (tail) 插入 (insert) 給定的新節點 (以 FIFO 準則);
* `q_remove_head`: 在佇列開頭 (head) 移去 (remove) 給定的節點;
* `q_release_element`: 釋放特定節點的記憶體空間;
* `q_size`: 計算目前佇列的節點總量;
* `q_delete_mid`: 移走佇列中間的節點,詳見 [LeetCode 2095. Delete the Middle Node of a Linked List](https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-the-middle-node-of-a-linked-list/)
* `q_delete_dup`: 在已經排序的狀況,移走佇列中具備重複內容的節點,詳見 [LeetCode 82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II](https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/)
* `q_swap`: 交換佇列中鄰近的節點,詳見 [LeetCode 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs](https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/)
* `q_reverse`: 以反向順序重新排列鏈結串列,該函式不該配置或釋放任何鏈結串列節點,換言之,它只能重排已經存在的節點;
* `q_sort`: 以==遞增順序==來排序鏈結串列的節點,可參閱 [Linked List Sort](https://npes87184.github.io/2015-09-12-linkedListSort/) 得知實作手法;
## 開發過程
### q_new
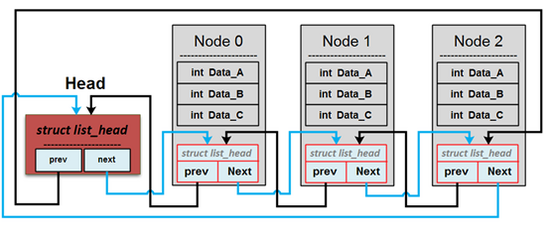
`q_new`: 建立新的「空」佇列,參閱 [你所不知道的 C 語言: linked list 和非連續記憶體](https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/c-linked-list) 可知第一個`head`是做為第一個entry,不做為存資料的節點。
```cpp
struct list_head *q_new()
{
struct list_head *hd = malloc(sizeof(struct list_head));
if (!hd)
return NULL;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(hd);
return hd;
}
```
### q_free
利用 `list_for_each_entry_safe` 可以刪除節點的特性,將所有節點進行刪除。
```cpp
void q_free(struct list_head *l)
{
element_t *tmp, *n;
list_for_each_entry_safe (tmp, n, l, list) {
free(tmp->value);
list_del(&tmp->list);
free(tmp);
}
free(l);
}
```
### q_insert_head
確認完所存取的指標都沒有 NULL pointer 後,利用 `list_add` 加入心節點。
```cpp
bool q_insert_head(struct list_head *head, char *s)
{
if (!head)
return false;
element_t *ihead = malloc(sizeof(element_t));
if (!ihead)
return false;
ihead->value = malloc(strlen(s) + 1);
if (!ihead->value) {
free(ihead);
return false;
}
strncpy(ihead->value, s, strlen(s) + 1);
list_add(&ihead->list, head);
return true;
}
```
### q_insert_tail
跟 q_insert_head 相似
```cpp
bool q_insert_tail(struct list_head *head, char *s)
{
element_t *itail = malloc(sizeof(element_t));
if (!itail)
return false;
itail->value = malloc(sizeof(s) + 1);
if (!itail->value) {
free(itail);
return false;
}
strncpy(itail->value, s, strlen(s) + 1);
list_add_tail(&itail->list, head);
return true;
}
```
### q_remove_head
利用`list_del` 將節點移除,不過要考慮到 `bufsize` 的大小,若超出,則須限制回傳的 `sp` 長度,並確定最後一個字元為 `\0`。
```cpp
element_t *q_remove_head(struct list_head *head, char *sp, size_t bufsize)
{
if (!head)
return NULL;
if (!list_empty(head)) {
element_t *ele = list_first_entry(head, element_t, list);
if (sp) {
size_t len = strlen(ele->value) + 1 < bufsize
? strlen(ele->value) + 1
: bufsize;
strncpy(sp, ele->value, len);
sp[len - 1] = '\0';
}
element_t *removed = ele;
list_del(&removed->list);
return ele;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
```
### q_remove_tail
和 q_remove_head 類似
```cpp
element_t *q_remove_tail(struct list_head *head, char *sp, size_t bufsize)
{
if (!head)
return NULL;
if (!list_empty(head)) {
element_t *ele = list_last_entry(head, element_t, list);
if (sp) {
size_t len = strlen(ele->value) + 1 < bufsize
? strlen(ele->value) + 1
: bufsize;
strncpy(sp, ele->value, strlen(ele->value) + 1);
sp[len - 1] = '\0';
}
element_t *removed = ele;
list_del(&removed->list);
return ele;
} else {
return NULL;
}
return NULL;
}
```
### q_size
走訪除了head的節點,計算出大小
```cpp
int q_size(struct list_head *head)
{
if (!head)
return 0;
int size = 0;
struct list_head *node;
list_for_each (node, head) {
size++;
}
return size;
}
```
### q_delete_mid
參考:[案例探討: LeetCode 21. Merge Two Sorted Lists](https://hackmd.io/YA7RMqd6RE2UL8OmmjU9PQ?view#%E6%A1%88%E4%BE%8B%E6%8E%A2%E8%A8%8E-LeetCode-21-Merge-Two-Sorted-Lists)
```cpp
bool q_delete_mid(struct list_head *head)
{
if (list_is_singular(head))
return false;
if (head->next->next && head->next) {
struct list_head *slow = head->next;
struct list_head *fast = head->next->next;
while (fast != head && fast != head->prev) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
element_t *tmp = list_entry(slow, element_t, list);
free(tmp->value);
list_del(&tmp->list);
free(tmp);
return true;
} else {
return true;
}
}
```
### q_delete_dup
利用`list_for_each_entry_safe` 可以安全的移除節點的特性,進行重複節點的刪除。
```cpp
ool q_delete_dup(struct list_head *head)
{
if (!head) {
return false;
}
if (list_is_singular(head))
return true;
element_t *tmp, *n;
char dup[15];
list_for_each_entry_safe (tmp, n, head, list) {
// element_t *next = list_entry((&tmp->list)->next, element_t, list);
if (strcmp(tmp->value, dup) == 0) {
if (tmp->value)
free(tmp->value);
list_del(&tmp->list);
free(tmp);
} else if (strcmp(tmp->value, n->value) == 0) {
strncpy(dup, tmp->value, strlen(tmp->value) + 1);
if (tmp->value)
free(tmp->value);
list_del(&tmp->list);
free(tmp);
}
}
return true;
}
```
#### 利用 valgrind 進行 debug
剛開始的程式碼如下:
```cpp
bool q_delete_dup(struct list_head *head)
{
if (!head) {
return false;
}
if (list_is_singular(head))
return true;
element_t *tmp, *n;
char dup[128];
list_for_each_entry_safe (tmp, n, head, list) {
if (strcmp(tmp->value, dup) == 0) {
if (tmp->value)
free(tmp->value);
list_del(&tmp->list);
free(tmp);
} else if (&n->list != head && strcmp(tmp->value, n->value) == 0) {
if (tmp->value)
strncpy(dup, tmp->value, strlen(tmp->value) + 1);
else
break;
if (tmp->value)
free(tmp->value);
list_del(&tmp->list);
free(tmp);
}
}
return true;
}
```
會有如下的 segmentation fault
```shell
cmd> new
l = []
cmd> it a
l = [a]
cmd> it a
l = [a a]
cmd> dedup
Segmentation fault occurred. You dereferenced a NULL or invalid pointer
Aborted (core dumped)
```
利用 valgrind 進行測試
```shell
$ valgrind ./qtest
cmd> new
l = []
cmd> it a
l = [a]
cmd> it a
l = [a a]
cmd> dedup
==33466== Invalid read of size 1
==33466== at 0x483FED7: strcmp (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/valgrind/vgpreload_memcheck-amd64-linux.so)
==33466== by 0x10EA75: q_delete_dup (queue.c:241)
==33466== by 0x10B10A: do_dedup (qtest.c:499)
==33466== by 0x10D1CB: interpret_cmda (console.c:185)
==33466== by 0x10D717: interpret_cmd (console.c:208)
==33466== by 0x10E1C7: run_console (console.c:649)
==33466== by 0x10C6E0: main (qtest.c:962)
==33466== Address 0x4ba5040 is 32 bytes inside a block of size 49 free'd
==33466== at 0x483CA3F: free (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/valgrind/vgpreload_memcheck-amd64-linux.so)
==33466== by 0x10E454: test_free (harness.c:209)
==33466== by 0x10EA35: q_delete_dup (queue.c:250)
==33466== by 0x10B10A: do_dedup (qtest.c:499)
==33466== by 0x10D1CB: interpret_cmda (console.c:185)
==33466== by 0x10D717: interpret_cmd (console.c:208)
==33466== by 0x10E1C7: run_console (console.c:649)
==33466== by 0x10C6E0: main (qtest.c:962)
==33466== Block was alloc'd at
==33466== at 0x483B7F3: malloc (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/valgrind/vgpreload_memcheck-amd64-linux.so)
==33466== by 0x10E29C: test_malloc (harness.c:138)
==33466== by 0x10E7DE: q_insert_tail (queue.c:82)
==33466== by 0x10BD12: do_it (qtest.c:290)
==33466== by 0x10D1CB: interpret_cmda (console.c:185)
==33466== by 0x10D717: interpret_cmd (console.c:208)
==33466== by 0x10E1C7: run_console (console.c:649)
==33466== by 0x10C6E0: main (qtest.c:962)
==33466==
```
可以看到在`queue.c` 241行有`Invalid read of size 1` 241 行程式碼如下:
```c
if (strcmp(tmp->value, dup) == 0) {
```
`dup` 為指向 char 的指標,可以發現在做 dup沒有使用 `strncpy` 而是直接使用等號連接指標,造成在做 `strcmpy` 會 dereference NULL。
```c
char *dup = "";
dup = tmp->value;
```
### q_swap
將節點
```c
void q_swap(struct list_head *head)
{
if (!head)
return;
if (list_is_singular(head))
return;
struct list_head *tmp;
for (tmp = head->next; (tmp->next) != head && (tmp != head);
tmp = tmp->next) {
struct list_head *next = tmp->next;
list_del(tmp);
list_add(tmp, next);
}
}
```
### q_reverse
將所有節點的 `next` 以及 `prev` 指向反向的節點,並對起始節點做相似的操作。
```c
void q_reverse(struct list_head *head)
{
if (!head || list_is_singular(head))
return;
struct list_head *tmp, *n;
list_for_each_safe (tmp, n, head) {
struct list_head *x = tmp->next;
tmp->next = tmp->prev;
tmp->prev = x;
}
struct list_head *y = head->next;
head->next = head->prev;
head->prev = y;
}
```
### q_sort
參考 [案例探討: LeetCode 21. Merge Two Sorted Lists](https://hackmd.io/YA7RMqd6RE2UL8OmmjU9PQ?view#%E6%A1%88%E4%BE%8B%E6%8E%A2%E8%A8%8E-LeetCode-21-Merge-Two-Sorted-Lists) 以及 [Merge Sort 的實作](https://hackmd.io/YA7RMqd6RE2UL8OmmjU9PQ?view#Merge-Sort-%E7%9A%84%E5%AF%A6%E4%BD%9C) ,並考量因為在 `linux list` 的第一個節點並沒有值,在做 merge sort 的時候若依然考慮第一個節點的話,會造成額外節點的產生,所以這邊將 head 移除後,在做處理。
```c
struct list_head *merge_two_lists(struct list_head *L1, struct list_head *L2)
{
struct list_head *head = NULL, **ptr = &head, **node;
for (node = NULL; L1 && L2; *node = (*node)->next) {
char *L1_val = list_entry(L1, element_t, list)->value;
char *L2_val = list_entry(L2, element_t, list)->value;
node = (strcmp(L1_val, L2_val) < 0) ? &L1 : &L2;
*ptr = *node;
ptr = &(*ptr)->next;
}
*ptr = (struct list_head *) ((uintptr_t) L1 | (uintptr_t) L2);
return head;
}
/*
* Sort elements of queue in ascending order
* No effect if q is NULL or empty. In addition, if q has only one
* element, do nothing.
*/
struct list_head *merge_sort(struct list_head *head)
{
if (!head || !head->next)
return head;
struct list_head *slow = head;
struct list_head *fast = head->next;
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
struct list_head *mid = slow->next;
slow->next = NULL;
struct list_head *left = merge_sort(head), *right = merge_sort(mid);
return merge_two_lists(left, right);
}
void q_sort(struct list_head *head)
{
if (!head)
return;
if (!list_is_singular(head)) {
head->prev->next = NULL;
head->next = merge_sort(head->next);
struct list_head *prev = head, *cur = head->next;
for (; cur != NULL; prev = cur, cur = cur->next) {
cur->prev = prev;
}
prev->next = head;
head->prev = prev;
} else
return;
}
```
### 測試
透過 github 的 Action 測試 workflow 成功得到皮卡秋:

## Valgrind
## Dude, is my code constant time?
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet
 Sign in with Wallet
Sign in with Wallet