---
tags: technical blog post
reference: typescript types
---
# Synchronizing TypeScript Types with SQL Schemas
## Introduction
> **Note**: In the rapidly evolving landscape of application development, TypeScript's robust type system and SQL's powerful data management capabilities stand as critical tools for developers.
- **TypeScript's Robust Type System**: Enhances code quality and developer productivity.
- **SQL's Powerful Data Management**: Serves as the robust foundation for data storage.
- **The Goal**: To bridge the gap between TypeScript's strict type system and SQL's schema.
This blog explores the seamless integration of TypeScript types with SQL schemas to promote a more dynamic and reliable coding environment.

## Understanding TypeScript for Database Interactions
TypeScript's type system offers safety and predictability, enhancing JavaScript development with robustness and maintainability. However, when interfacing with databases, unique challenges arise.
```typescript
// Example: TypeScript interface representing a SQL user table
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
email: string;
}
// Example: Function querying a user by ID
async function getUserById(userId: number): Promise<User> {
//... SQL query and return user
}
```
- **Libraries Variety**: Various libraries in the TypeScript ecosystem address database interactions, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks.
- **Ideal Interaction**: Seamlessly maps query results to TypeScript types, minimizing overhead and errors.
## Deep Dive into SQL Schemas
SQL schemas are the blueprint of a database, defining the structure and rules of data. They include tables, views, relationships, and user-defined types.
```sql
-- Example: SQL Schema for a User table
CREATE TABLE Users (
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(100),
Email VARCHAR(100)
);
```
- **User-defined Types**: These are vital for representing complex data structures within the database.
- **Complex Structures**: SQL's capacity for defining and manipulating these structures presents an opportunity to align them with TypeScript's type definitions.
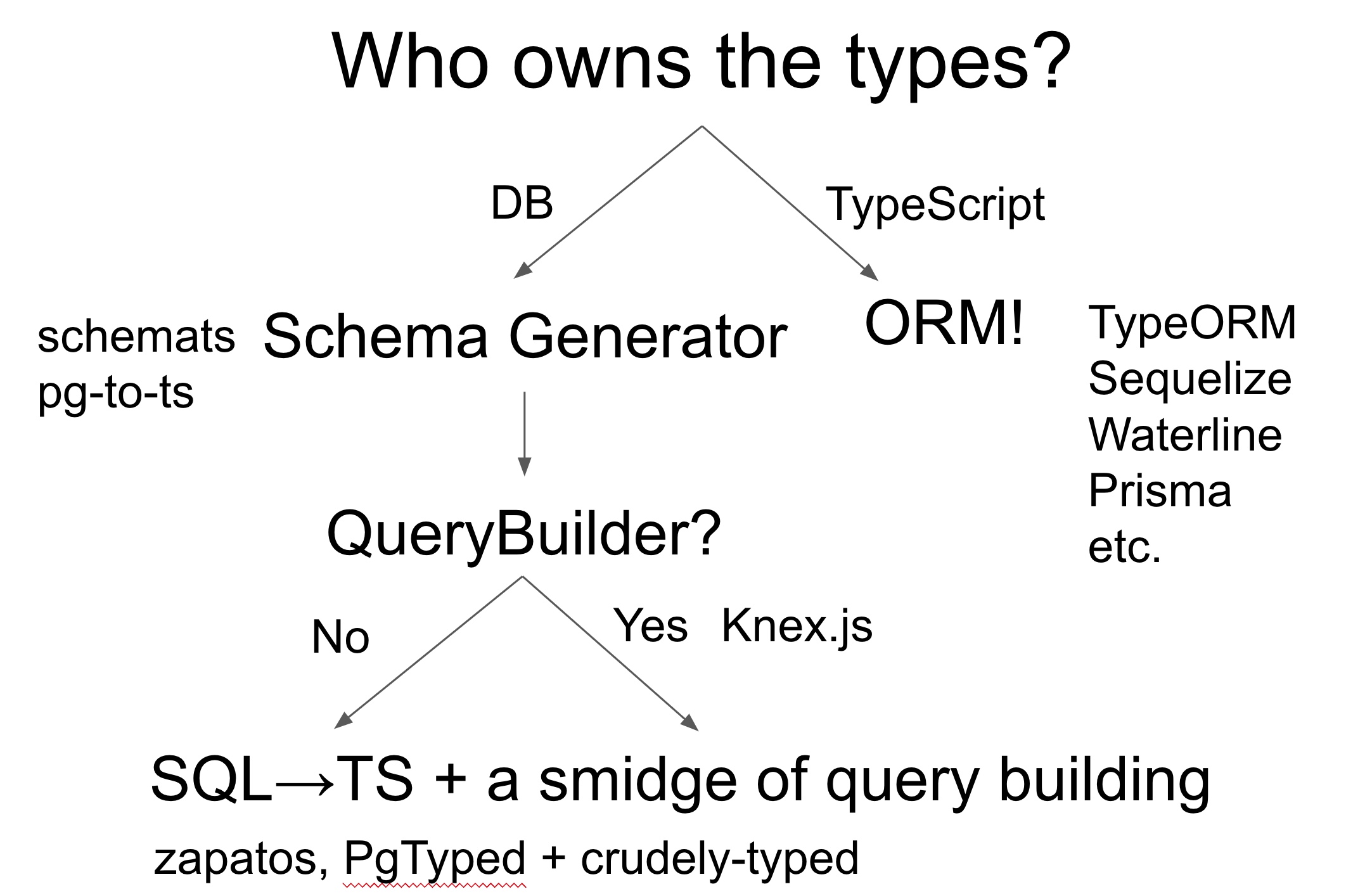
## Object Relation Mappers (ORMs) and TypeScript
ORMs provide a high-level abstraction for database interactions, simplifying CRUD operations and database synchronization. They enable developers to work with database objects as native TypeScript objects. However, they also bring challenges, especially with complex queries and performance optimization. The choice of ORM significantly affects the synchronization process between TypeScript types and SQL schemas.
```typescript
// Example: Using an ORM to define a User model
@Entity()
export class User {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column()
name: string;
@Column()
email: string;
}
```
- **Simplifying CRUD**: ORMs simplify CRUD operations and database synchronization.
- **Performance Optimization**: They also bring challenges, especially with complex queries and performance optimization.
## Query Builders and ORM Combinations
Query builders and ORM combinations strike a balance between abstraction and direct control. Tools like Prisma and Mikro-ORM allow developers to define schemas in a database-agnostic manner while still providing the power of raw SQL when necessary. They automate type generation and database synchronization, aiding in the maintenance of accurate TypeScript types.
- **Tools like Prisma and Mikro-ORM**: Allow developers to define schemas in a database-agnostic manner while still providing the power of raw SQL when necessary.
- **Automated Type Generation**: They automate type generation and database synchronization.
## Synchronizing TypeScript with SQL Schema
Achieving perfect synchronization between TypeScript types and SQL schemas is a continuous endeavor that ensures type safety, reduces runtime errors, and enhances the development experience.
- **Continuous Endeavor**: Synchronization is not a one-time task but a continuous aspect of development.
- **Best Practices**: Discuss strategies, tools, and best practices for maintaining this synchronization.
## Best Practices and Patterns
Maintaining a synchronized and well-structured codebase requires adherence to best practices and established patterns. This includes regularly updating TypeScript types to reflect SQL schema changes, understanding the capabilities and limitations of your chosen tools, effectively handling complex and custom types, and implementing robust error handling.
1. **Regularly Update TypeScript Types**: Reflect changes in the SQL schema.
2. **Understand Capabilities and Limitations**: Of your chosen ORM or query builder.
3. **Implement Robust Error Handling**: Critical for maintaining a reliable codebase.
## Case Studies and Examples
Real-world examples and case studies provide valuable insights into the practical challenges and solutions in synchronizing TypeScript types with SQL schemas. We'll present detailed accounts of projects that have successfully implemented synchronization, discussing strategies, challenges, and outcomes.
- **Case Study 1**: Detailing a project's strategy and challenges.
- **Case Study 2**: Discussing the outcomes and lessons learned.
## Conclusion
Synchronizing TypeScript types with SQL schemas is a critical aspect of developing robust, efficient, and maintainable applications. It's a continuous journey that evolves with your application, requiring an understanding of the available tools, practices, and strategies.
- **Continuous Journey**: Keep abreast of the latest developments and community discussions.
- **Tools and Practices**: Embrace the tools and practices discussed in this post for a more synchronized, efficient, and error-free development experience.