# IB Chemistry Notes
[TOC]
### Definitions
relative atomic mass ($A_r$)
~ a the mass of an atom of an element relative to $\frac{1}{12}$ the mass of an atom of $^{12}C$.
The formula for relative atomic mass is as follows:
$$A_r=\frac{M_1\times a_1\%+M_2\times a_2\%+...M_n\times a_n\%}{a_1+a_2+...a_n}\times 100\%$$
relative molecular mass ($M_r$)
~ the mass of one molecule of that substance relative to $\frac{1}{12}$ of the mass of $^{12}C$ atom. Obtained by adding the masses of the individual elements of the compound multiplied by their respective subscripts.
moles from concentration and volume of solution
~ $$n = \frac{C \cdot V}{1000}$$
## Module 1+11: stoichometry
### Checklist
> - [x] Evidence that the introductory video has been watched and understood.
> #### Structure of the learning
> - [x] Evidence that the “Structure of the Learning module” has been completed.
> - [x] Evidence that the “Why is chemistry so challenging” has been watched and [understood](https://hackmd.io/fPpQ0eFHRdC4O_KrlIKY_A?view#Why-is-Chemistry-so-challenging).
> - [x] Evidence that the “How do we learn module” has been completed.
> - [x] Evidence that the “Math skills module” has been completed.
> - [x] Evidence that the “IB Assessment and Reporting module” has been completed.
> #### IB Organised
> - [x] Evidence that the “IB organised module” has been completed.
> - [x] Download All the KLO’s
> - [x] Download a copy of Benton’s system
> - [x] Download a copy of the SL or HL definitions
> - [x] Download All of the command terms
> - [x] Download a copy of the IB learner profile
> - [x] Download a copy of the assessment details
> - [x] Download a copy of the data booklet
> - [x] Download a soft copy of the Module 1 student guide
> - [x] Download a soft copy of the practical portfolio
> - [x] Evidence that Module folders have been set up.
> #### Health and safety
> - [x] Evidence that the HS module has been completed. (Certificate must be obtained)
> #### Module 1
> - [x] Evidence that the Y12IB Topic 1 pre assessment task has been completed and self marked.
> - [x] Evidence of before we starts [completed](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1fluaWbxGNzGt0afZ97yeIrr1e0Fapu-W/view?usp=sharing)
> - [x] Evidence of experiments completed
> - [x] Appropriate Module 1+11 notes in portfolio
> - [x] Evidence of you working with your “critical buddy”
> - [x] Evidence of “mission impossible” completed
> - [x] Evidence of at least 1 mini tests being completed
> - [x] Evidence that you have download and saved a copy of
> * All the IB Glossaries.
> * All the Fast fact sheets
> * All Spark chart revisions sheets.
> * A copy of the Formula used in the chemistry sheet.
> * A copy of quantitative chemistry steps to success downloaded
> - [ ] Evidence of Module assessment score has been recorded
> - [x] Evidence of pre-assessment task in desktop folders BWS'es.pdf
> - [x] Evidence of the module 1 assessment and next steps reflection has been completed.
> - [x] Evidence that you have begun to explore some of the “Useful links and Resources” in Bentons’ World
### Why is Chemistry so challenging?
Hardest topics:
* Organic chemistry
* Energetics
* Redox chemistry
* Stoichometry
* Equilibrium
* Designing investigations
Reasons why Chemistry is so difficult:
* The abstract nature of the subject
* The use of symbols and language
* The mathematical demands of the subject
* The need for multi-level thought processes
#### Ex. lead (I) iodide precipitate
##### Macroscopic level
> two colourless solutions mix together to make a yellow mixture
:::success
:thumbsup: easy to describe
:::
To understand deeper about what’s happening, we need to use abstract ideas with symbols and a range of language, e.g. ``ion``, ``compounds``, ``mixtures``, ``deplacement``, ``solubility``, ``valencies``.
##### More abstract explanations
> Potassium iodide solution is added to lead sulfate solution.
> Lead (I) iodide precipitates out.
##### Equation
:::success
2KI(aq) +2Pb(NO~3~)~2~(aq) -> PbI~2~(s) + 2KNO~3~(aq)
:::
To write this equation we have to have an understanding of:—
* ions
* compounds
* valencies
* balancing equations
* states of matter
* solubilities of salts
* displacement reactions
#### Key takeaways from this video
1. Constant revision of acquired knowledge to ensure understanding
2. Cooperate with others to learn from them
3. Actively visualise learning and share your knowledge
4. Practice using new language and terms to ensure accurate usage in the long term
5. Improve attention, working memory and visualisation skills
6. Learn through analogy
## Module 2+12: atomic structure
:::info
- [x] Download Module 2+12 guide
- [x] Download 2+12 pre-assessment task
- [x] Complete 2+12 pre-assessment task
- [x] Evidence that How stuff works: Ancient Philosophy about the elements has been viewed
> Video no longer available
> [name=Horace LEUNG]
- [x] Evidence that the [scale](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uaGEjrADGPA) of [things](/kE8dN-H8Q7uU8VOfEZA1DA) has been viewed
{%youtube uaGEjrADGPA %}
- [ ] Evidence that the ToK module has been completed.
- [x] Evidence that Expt. 1.1 has been completed
- [x] Evidence of notes and understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- [x] Evidence of qualitative data from Expt 2.3a
- [x] Evidence that qualitative observations from Expt. 2.3b completed
- [x] Evidence of notes on absorption and emission spectra.
- [x] Evidence that How stuff works: JJ Thompson and the electron has been viewed
> Video no longer available
> [name=Horace LEUNG]
- [x] Evidence that How stuff works: Millikan oil drop experiment has been viewed
- [x] Evidence that Rutherford Gold foil experiment has been viewed
- [x] Evidence that Chadwick’s discovery of the neutron Millikan has been viewed
- [x] Evidence of processed data from experiment 2.6 using excel
- [x] Evidence of processed data from experiment 2.7 using loggerPro
- [x] Evidence of “spot the difference activity completed
- [x] Evidence of writing $s$, $p$, $d$, $f$ notations for elements
- [x] Evidence of understanding of the function and application of the Mass spectrometer
- [x] Evidence of $M_r$ calculations
- [x] Evidence of fragmentation in Mass spectrometry to help identify structural formulae
- [x] Evidence of mini tests being completed
- [x] Evidence of a final assessment score and % recorded
> to be recorded 2022-12-09 break
> [name=Horace LEUNG]
- [x] Evidence that definitions are being learnt
- [x] Evidence that critical buddy is being actively used to support learning.
:::
### Bohr model
### electron configuration

Above is a diagram offfff
> *1s^2^2s^2^2p^6^3s^1^* = Na^+^: 1s22s22p6
### Discovery of the electron
{%youtube Rb6MguN0Uj4 %}
#### Cathode ray tube

* The cathode ray tube is a near-vacuum glass tube containing two electrodes.
* When high voltage was applied across the electrodes, a cathode ray appeared between them.
### Rutherford and the gold foil experiment
{%youtube XBqHkraf8iE %}
#### Plum pudding model of the atom
* At the time of Rutherford's experiment, people thought that the atom was a blob of positive charge with the negative electrons embedded inside it
#### Rutherford's experiment
* Rutherford directed a beam of $\alpha$-particles through a very thin gold foil.
* The particles are then detected by two detectors at the back.
* one detector counts the rate of the particles going straight ahead
* the other detector counts the rate of scattering
* Occasionally one or two $\alpha$-particles will hit the gold nucleus, bounce back and be detected by the scattering rate detector.
* This experiment shows that the atom has a heavy nucleus with mostly empty space with light electrons distributed around it.
* This is basically what happens in a large hadron collider.
### Milikan oil drop experiment
{%youtube nwnjYERS66U %}

1908-1970
* A fine mist of oil was sprayed with an **atomiser** on a charged plate
* Some of the tiny droplets fell through the hole on the upper floor onto the lower chamber
* Milikan could work out the mass of an oil drop from its terminal velocity
* He used an X-ray to ionise gas particles in the chamber
* Electrons from the gas particles adhered to the oil droplets. The oil droplets now carry a negative charge.
* The negatively charged droplets can be halted by altering the voltage across the plate
* As the voltage of the plate increases, the velocity of the drops slows
* As the voltage increases further, some drops will begin to go upwards
* An oil drop is suspended when $$q\cdot E=m\cdot g$$ where $q$ stands for charge, $E$ for energy and $m$ the mass of the oil drop. The electrical charge upwards balance the gravitational force downwards on the droplet.
* Milikan found that all the charges of the droplets were whole number multiples of a smaller charge, enabling him to work out the charge of an electron, which is $-1.60\times 10^{-10}$ C.
* mass of electron $$=-1.60\times10^{19}C\times\frac{1g}{-1.76\times 10^8C}=9.10\times 10^{-28}g$$
### Chadwick's discovery of the neutron
{%youtube ZK-yeuu_p9k %}
* every object in the world is made of smaller particles
* microscopic particles are molecules
* molecules are made of atoms
* protons have a positive charge and electrons have a negative charge
* with some particles, the weight was much larger than the weight of the protons and electrons combined
* therefore, he proposed the discovery of a new subatomic particle, the neutron
* all atoms are split by shooting protons or neutrons at it.
* however protons are repulsive and can only be used to split small atoms
* Chadwick won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his discovery
### Electromagnetic spectrum
$$v=f\lambda$$
$v$ is velocity, $f$ is frequency, $\lambda$ is wavelength
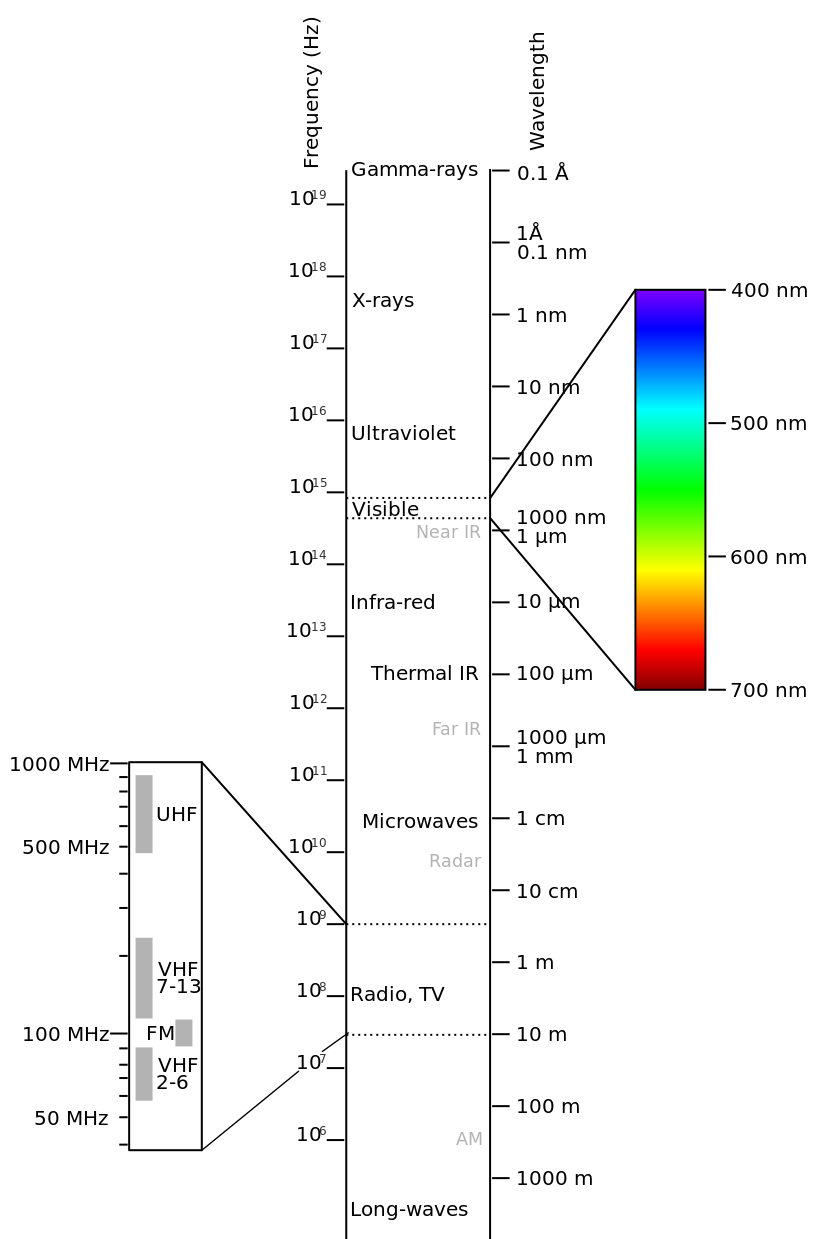

## Module 10+20: organic chemistry
###
- [x] Download module 10+20 guide
- [x] Evidence that 10+20 pre-assessment task is completed
- [x] Evidence that pre-test marked by critical buddy. Desk top folders
- [ ] Evidence that video: [describe the features of a homologous family](https://youtu.be/g1lDvqfgmsI) has been watched and notes taken.
- [ ] Evidence that video: Predict and explain trends in the b.p. of a homologous family have been watched and notes taken.
- [ ] Evidence that video: describing the reactions of Alkanes with halogens has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Apply IUPAC naming rules for straight chain Alkanes has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Explaining the chemical properties of alkanes has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: explaining reactivity of alkanes has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Apply IUPAC naming to straight chain Alkene isomers has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Describing reactions of Alkenes with halogens and hydrogen has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Describing reactions of Alkenes with halogens and water has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Outline the economic importance of alkenes has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Explaining hydroxide as a nucleophile has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Describe substitution reactions of HA with Hydroxide ions has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Explaining substitution reactions in HA has been watched and notes taken.
- [ ] Module 10+20 resources Before lesson 3
- [ ] Evidence that video: Explain reactions of HA with ammonia and potassium cyanide has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Describe elimination reactions in HA has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Describe mechanisms for elimination reactions in HA has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Describe the complete combustion of alcohols has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Discussing the volatility and solubility of organic compounds has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Identifying primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Describe oxidation reactions of alcohols has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: determine the oxidation products of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Alcohols, Aldehydes, carboxylic acids and halogenoalkanes has been watched and notes taken.
- [ ] Evidence that a review of learning has taken place and problems for discussion session have been identified.
- [ ] Evidence that video: Amines, Amides, nitriles and esters have been watched and notes taken.
- [ ] Evidence that video: Benzene, amine and esters has been watched and notes taken.
- [ ] Evidence that video: Describe structural isomers has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Deduce structural isomers up to C~6~ has been watched and notes taken
- [ ] Evidence that video: Apply IUPAC naming system to straight chain isomers has been watched and notes taken
### Describe the features of a homologous family
* Focusing on the *alkanes* and the *alkenes*
* General formula for alkanes: **C~n~H~2n+2~**
* General formula for alkenes: **C~n~H~2n~**
* Chemical properties of a homologous series are mostly the same
* *Physical* properties vary
*