## PyCon TW 2019 Summary
<!-- Put the link to this slide here so people can follow -->
slide: https://hackmd.io/@4OZR5JJAQDOUM7OgLejuAw/rkgy6i13B
[slide](https://hackmd.io/PVTjuwaIQFiW0wK0AcxRSg?view)

---
## PyCon Day1
## 基調演講 - 林守德
### Understanding Deep Neural Networks
[hackmd](https://hackmd.io/@pycontw/SJEpwWmvH/%2F%40pycontw%2FHySErshLB)
---
* Learn f(x) = y
* ML vs Deep Learning
* RNN (recurrent neural network)
* RNN approaches
* Components of Seq2Seq
* Design of Decoder
* Train a Seq2Seq model
---
### 我們無法了解機器是否有了解或推論,只能從他表現去間接推斷
---
### AI vs ML vs DL

[pic source](https://www.prowesscorp.com/whats-the-difference-between-artificial-intelligence-ai-machine-learning-and-deep-learning/)
---

pic from: https://blog.csdn.net/u012328159/article/details/87907739
$z_{t}$ = Update gate
$r_{t}$ = Reset gate
---
### Use of RNN
* Language modeling
* y 對應到每個 character/word 的機率
* Classification/Regression
* 例如:檢查文法有沒有錯、預測文章讚數
* Neural machine translation
* Article summarization
* [小冰寫詩]https://poem.msxiaobing.com/)
---
### Seq2Seq
* Encoder
* Input representation: word embedding, CNN feature maps
* e.g., Uni/Bidirectional RNN
* Word Embedding: 把字轉成向量
* Decoder
* Bridge(Initial state of RNN)
* RNN(Usually unidirectional RNN)
---
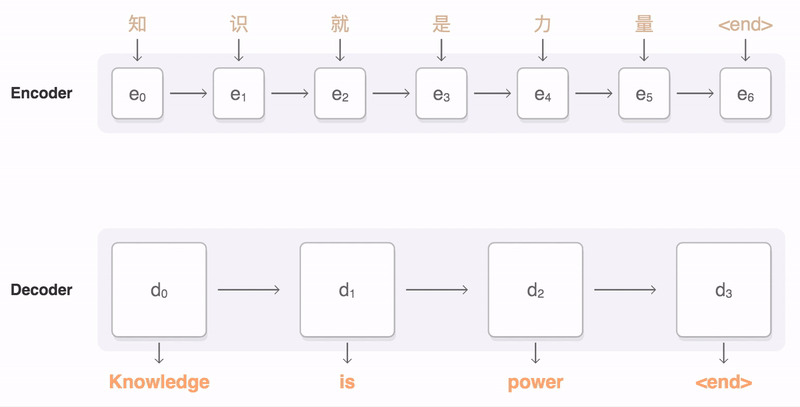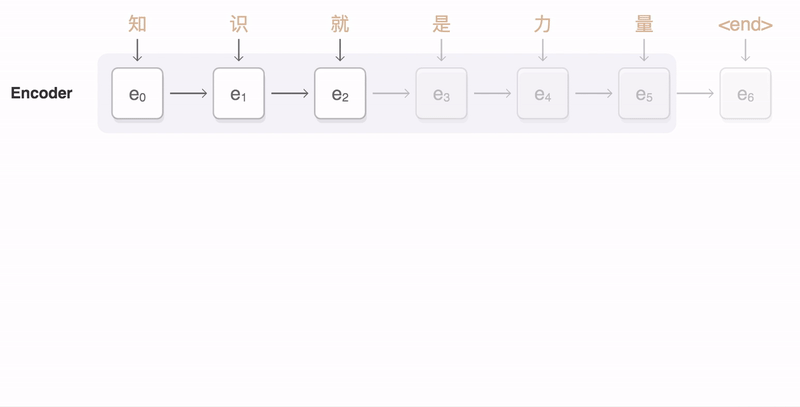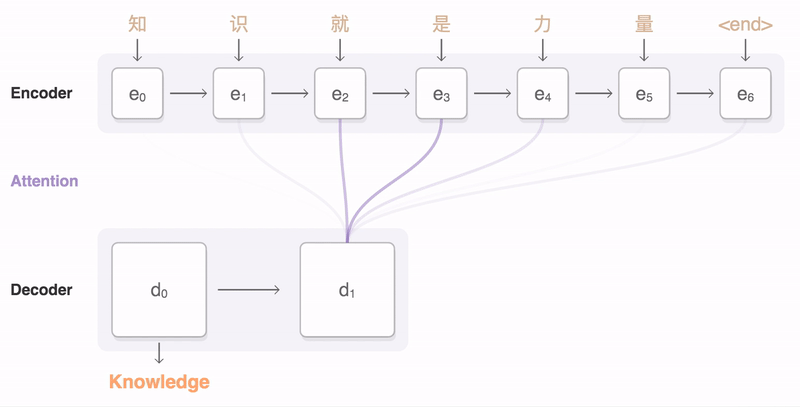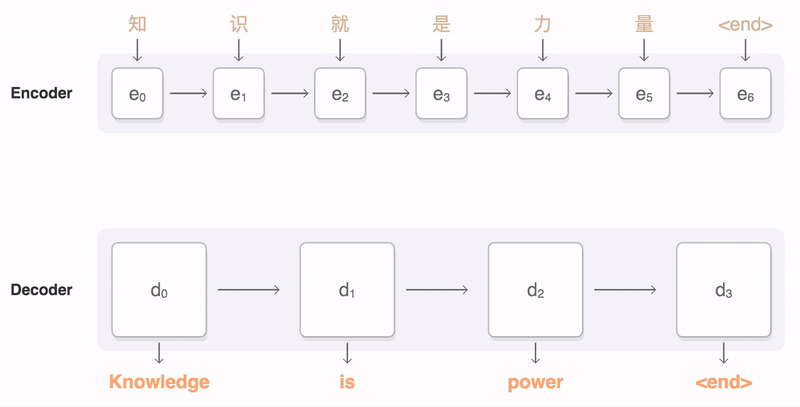
pic from: https://google.github.io/seq2seq/
---
## 驢車 (Donkey Car),一個基於 Raspberry Pi 與機器學習的自走車專案介紹 - sosorry
* 由 DIY Robocars 開始,而且ML 的效果比 Computer vision 好
* 以遙控車(1/16 HSP RC Car)為載體、Raspberry Pi 3B+、魚眼相機
* Input: picture, NN model (CNN?)
[DonkeyCar](http://docs.donkeycar.com/guide/train_autopilot/)
[hackmd](https://hackmd.io/@pycontw/SJEpwWmvH/%2F%40pycontw%2FS1gDBs3IS)
---
{%youtube 4fXbDf_QWM4 %}
---
## async def Serial() await Serial_connection - Yi-Chieh Chen
* Synchronous vs Async
* Protocol:
* application 抽象
* socket connection 抽象
* Generator
* Implement `__enter__` method and `__exit__` method.
---
* Open Space: Async flow
* async producer
* async queue (when comsumer wifi disconnect, data will be storaged in queue)
* async comsumer
[hackmd](https://hackmd.io/@pycontw/SJEpwWmvH/%2F%40pycontw%2FBknvronLB)
---
### `__call__`
`object.__call__(self[, args...])`
Called when the instance is “called” as a function;
if this method is defined, `x(arg1, arg2, ...)`
is a shorthand for `x.__call__(arg1, arg2, ...)`.
[source](https://docs.python.org/3/reference/datamodel.html#object.__call__)
---
#### 如何使用 concurrent.futures 裡的 threadpool 與 asyncio 裡的 run_in_executor 方法讓 Synchronous 從 callable 變成 awaitable
#### 運用 Python decorator
---
```python=
from serial import Serial
ser = Serial('com3', 9600)
def get(ser):
msg = ser.read_until('\r\n')
return msg
```
---
```python=
class SyncToAsync:
# ...略
async def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
future = loop.run_in_executor(
None, # Run in the default loop's executor:
functools.partial(self.thread_handler, loop, *args, **kwargs),
)
return await asyncio.wait_for(future, timeout=None)
# ...略
sync_to_async = SyncToAsync
```
---
```python=
from serial import Serial
from SyncToAsync import *
ser = Serial('com3', 9600)
@sync_to_async
def get(ser):
msg await ser.read_until('\r\n')
return msg
```
---
The `@asynccontextmanager` decorator returns the generator wrapped by
the _AsyncGeneratorContextManager object
```python=
import aiohttp
import asyncio
from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
URL = 'www.google.com'
@asynccontextmanager
async def open_session():
s = aiohttp.ClientSession()
yield s
await s.close()
async def main():
async with open_session() as session:
response = await session.obj.get(URL)
text = await response.text()
asyncio.run(main())
```
---
Use as Class
```python=
import aiohttp
import asyncio
from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
URL = 'www.google.com'
class TheSession:
def __init__(self):
self.obj = None
async def __aenter__(self):
self.obj = aiohttp.ClientSession()
async def __aecit__(self, typ, value, tb):
await self.obj.close()
async def main():
async with TheSession() as session:
response = await session.obj.get(URL)
text = await response.text()
asyncio.run(main())
```
---
## How to Transform Research Oriented Code into Machine Learning APIs with Python - Tetsuya Jesse Hirata
主要是在講解資料的前處理過程的簡化、測試等
[Slide](https://speakerdeck.com/tetsuya0617/how-to-transform-research-oriented-code-into-machine-learning-apis-with-python?slide=11)
日本人的英文口音...
(略)
---
## PEP 572: The Walrus Operator - Dustin Ingram
#### 來自 Google 的講師
[Slides](https://github.com/di/talks/tree/master/2019/pycontw_2019)
[Github](https://github.com/di)
---
### What is PEP?
* Python 的聖經
* 就像是美國的立國宣言一樣
---
### PEP8
* Style guide for python code
---
### PEP 20 -- The Zen of Python
* Python 精神
```
Beautiful is better than ugly.
Explicit is better than implicit.
Simple is better than complex.
Complex is better than complicated.
Flat is better than nested.
Sparse is better than dense.
Readability counts.
Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules.
Although practicality beats purity.
Errors should never pass silently.
Unless explicitly silenced.
In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess.
There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it.
Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch.
Now is better than never.
Although never is often better than *right* now.
If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea.
If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea.
Namespaces are one honking great idea -- let's do more of those!
```
---
### PEP 572
**`:=`**
---
#### Example
```python=
foo = [f(x), f(x)**2, f(x)**3]
```
```python=
y = f(x)
foo = [y, y**2, y**3]
```
```python=
foo = [y := f(x), y**2, y**3]
```
---
#### Example cont.
```python=
results = []
for x in data:
result = f(x)
if result:
results.append(result)
```
```python=
results = [
f(x) for x in data
if f(x)
]
```
```python=
results = [
y for x in data
if (y := f(x))
]
```
---
#### Example cont.
```python=
match = pattern.search(data)
if match:
do_something(match)if f(x)
```
```python=
if (match := pattern.search(data)):
do_something(match)
```
---
#### Example cont.
```python=
chunk = file.read(8192)
while chunk:
process(chunk)
chunk = file.read(8192)
```
```python=
while chunk := file.read(8192):
process(chunk)
```
---
#### Example cont.
```python=
x = y = z = 0 # Yes
(z := (y := (x := 0))) # No
a[i] = x # Yes
a[i] := x # No
self.rest = [] # Yes
self.rest := [] # No
x = 1, 2 # Sets x to (1, 2)
(x := 1, 2) # Sets x to 1
total += tax # Yes
total +:= tax # No
```
---
In Python 3.8
如果不想用就別用!?(嗆)
> BUT I DON'T LIKE IT
THEN DON'T WRITE IT!
---
## 寫個能幹的中文斷詞系統…然後讓它養我 - PeterWolf
[Slides](https://github.com/Droidtown/PyConTW2019)
---
### 中文三歧義
* 組合型歧義
* 小紅帽
* 小/紅帽
* 小紅/帽
* 小紅帽
---
* 真歧義
* 「語言層」和「知識層」維度(而不是依據頻率)
* 美國會派特使來訪
* 美國派出?
* 美國國會派出?
---
* 交集型歧義
* 我幫爸媽買了一份超值保險套餐
* 你再做一次試試看!
* 「語言層」和「語境層」維度
---
### 語言學概論
#### 現代理論語言學提出的句法樹結構X-bar(70年, 61087顆樹)
* 語言學家的心中只有一棵樹
---
#### 語言學假設
* 所有人大腦結構一致
* 所有人有一樣的語言處理機制
* 人類的母語語言習得機制允許參數改變
* 所有語言的差異是來自參數的差異
* 參數的變化是有限的
---
中文/日文可以用同一顆句法樹 & 參數調整
因為大部分語言學家不會程式,所以發展受限
---
### Articut 斷詞引擎 (工商時間)
* 詞性與斷詞同時發生
* 以結構來處理,而非使用大數據訓練的模型
* 錯誤是有可解釋性的
* 犯錯是知識(常識)的缺乏,但因為有可解釋性,所以修正起來很快,相對於頻率統計學派,只能表示是因為訓練資料的受限,但不知道確切的原因。
---
### Example
* 餃子 / 包 / 高麗菜
* 麵 / 包 / 牛奶
* 借600萬養老金
* 借 600 萬 / 養老金
* 借 600 萬 / 養 / 老金
* 魅力無窮
* 魅力 / 無窮
* 魅力無 / 窮
---
### Example cont
* 四十年/前/的/這/一天/台灣/關係法/通過/了/促進/臺美/關係 (可分辨"關係法"與"關係")
* 齁/盡量/不要/買/武器/了
* 今天/台北/忠孝東路
* 這時/川董/拿出/鋼筆/開始/簽名/在/杯墊/上
#### 效能比對: Articut 92.55 vs. CKIP 97
請語言學碩士逐條比對 93~94就是頂天了,97就overfit了
---
### Python 中文 re 問題
```python=
# Test on Python 3.5, 3.6, 3.7
import re
pat = re.compile('\d樓|\d號(\d樓)?')
re.findall(pat, '4號') # [''] re bug!
re.finditer(pat, '4號') # Correct!
```
---
文件說會修正,但是並沒有!
> Note Due to the limitation of the current implementation the character following an empty match is not included in a next match, so findall(r’^|\w+’, ‘two words’) returns [’’, ‘wo’, ‘words’] (note missed “t”). This is changed in Python 3.7.
[3.6](https://docs.python.org/3.6/library/re.html?highlight=findall#re.findall)
[3.7](https://docs.python.org/3.7/library/re.html?highlight=findall#re.findall)
---
### 中文斷詞
* Jieba
* CKIP
* Monpa
* CKIPtagger
---
### 有誰採用語言學規則做為解決方案呢?(Rule-Base)
* Droidtown: Articut (文截)
* bitext: NLP core
* UCI 加州大學爾灣分校:Language Science
---
## 工業4.0-CNC刀具健康監測 - 張楦涵, 徐仕杰
#### 主講人背景:富士康
#### 主要講者:張楦涵
---
### 動機:
* 刀具是消耗品
* 過度使用傷害主軸
* 過度使用造成產品不良
---
#### 傳統方式:
* 聲音、震動、火花
* 老師傅經驗
* 無法傳承
* 人工成本高
* 數據採集:傳感器、控制器
* 數據分析:數據鑑定刀具健康度
* 數據工程:資料串接、系統搭建、界面呈現
---
### 數據分析
#### 數據理解
* 震度數據
* 反映加工震動量
* 25600 Hz
* 全生命週期
* tdms 儲存數據 (The NI TDMS file format – a file format optimized for saving measurement data to disk.)
---
#### 數據理解 cont.
* 控制器數據
* 33 Hz
* 機械設定數據
* 磨耗數據
* 線性插補缺失值
#### 應用:異常、健康、故障類型
---
### 前處理
* 單位時間的資料數量不同
* 缺失值
* 干擾
* 去除冗餘數據
* 保留真正加工數據
* 利用機械設定欄位過濾
* 還原加工路徑
* 請教領域專家
---
#### 去除離群值
* Anomaly detection
* Gaussian mixture model (GMM)
---
#### 轉換為分析單位
* Concern: 太大喪失局部特徵, 太小觀察到的頻率有限
* 連續訊號重疊滑窗
---
### 特徵工程
* MK test (McDonald–Kreitman test)
* K-S test (Kolmogorov-smirnov test)
* Permutation test (Resampling)
### 模型建立
* XGBOOST
---
## Practicing Statistics in Python: Hypothesis Testing - Mosky Liu
:star2: slide: https://speakerdeck.com/mosky/hypothesis-testing-with-python
:star2: github: https://github.com/moskytw/hypothesis-testing-with-python
---
### 名詞解釋
* Build our bad reviews in statistics*
* Build a statical model by a hypothesis
* Hypothesis contains **equal** = null hypothesis
* Hypothesis contains **not equal** = alternative hypothesis
---
### 定義
* α: significance level and 5% usually, decided by your context.
If p-value < α:
* Can reject the null (equal).
* Can accept the alternative (not equal).
If α ≤ p-value ≤ 50%
* Can't reject the null (equal).
* Can't accept the alternative (not equal).
* May just need more data.
---
* 虛無假設(null hypothesis,一般用$H_{0}$表示)
* 對立假設(alternative hypothesis,一般用$H_{1}$表示)
* 虛無假設($H_{0}$): 平均數($X_{1}$) $=$ 平均數($X_{2}$)
* 對立假設($H_{1}$): 平均數($X_{1}$) $\neq$ 平均數($X_{2}$)
* α: significance level and 5% usually, decided by your context.
* p => a; 我們不能拒絕**虛無假設($H_{0}$)**
* 無統計上顯著差異的
* p < a; 我們可以拒絕**虛無假設($H_{0}$)**
* 有統計上顯著差異的
---
### 小結
p-value < α:
* 代表兩組資料有統計學上顯著差異
a ≤ p-value ≤ 50% :
* 代表兩組資料沒有統計學上顯著差異
* 或是需要更多資料
---
### 補充
[統計學:大家都喜歡問的系列-p值是什麼 - Tommy Huang](https://medium.com/@chih.sheng.huang821/%E7%B5%B1%E8%A8%88%E5%AD%B8-%E5%A4%A7%E5%AE%B6%E9%83%BD%E5%96%9C%E6%AD%A1%E5%95%8F%E7%9A%84%E7%B3%BB%E5%88%97-p%E5%80%BC%E6%98%AF%E4%BB%80%E9%BA%BC-2c03dbe8fddf)
[Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/P-value)
[Selecting Commonly Used Statistical Tests – Bates College](http://abacus.bates.edu/~ganderso/biology/resources/stats_flow_chart_v2014.pdf)
[Choosing a statistical test – HBS](http://www.biostathandbook.com/testchoice.html)
---
## Sim-to-Real:用物理引擎打造能虛實轉移的機器人 - Jiawei Chen
[hackmd](https://hackmd.io/@pycontw/2019/%2F%40pycontw%2FHy7dBs2IH)
[uTensor](https://github.com/uTensor/uTensor)
[Unified Robot Description Format (URDF)](https://industrial-training-master.readthedocs.io/en/melodic/_source/session3/Intro-to-URDF.html)
沒有投影片
---
## Building Data Pipelines on Apache NiFi with Python - Shuhsi Lin
[hackmd](https://hackmd.io/@pycontw/2019/%2F%40pycontw%2FSyFvrinIS)
---
Why NiFi
* Single ingestion platform
* Scalable(Clustering)
* Reliability
* Fast develop/deploy cycle
* Better data flow visibility
---
### GUI :+1:

---
* GUI 介面 vs Airflow
* Java vs Python
* REST Api
來個Python 點:
[Nifi-Python-Api: A rich Apache NiFi Python Client SDK](https://github.com/Chaffelson/nipyapi)
---
## Introduction to Deep Probabilistic Programming with Pyro - 柯維然
[Slide](https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1qOIqK5MmE-b43yTYgQL7b7Opu-AmkqGGCgmvgdHhqfg/edit#slide=id.p)
[hackmd](https://hackmd.io/@pycontw/2019/%2F%40pycontw%2FBJ7jSo38S)
---
## BI前的悲哀 - 那些User所謂的Big(?) Data - 高振倫
[Slide](https://github.com/bingroom/PyConTW2019/blob/master/slides.pdf)
[hackmd](https://hackmd.io/@pycontw/2019/%2F%40pycontw%2FHyd6ronLS)
---
* Text Extraction
* textract
* Parsing Word
* docx2csv
* PDF
* pdfminer
* Bug Data Search System
* data source: JIRA/SVN…
* Elasticsearch
* Google like searching experience
* Modularizing qry strategy
* Domain-based label
* JQL
---
## 金融中的人工智慧 - Yves J Hilpisch
[Slides](http://hilpisch.com/pycontw.pdf) | [Notebook](http://hilpisch.com/pycontw.html)
[hackmd](https://hackmd.io/@pycontw/2019/%2F%40pycontw%2Frk0ESjn8B)
---
## GraphQL with Graphene and Django, laughter and tear - Keith Yang
[hackmd](https://hackmd.io/@pycontw/2019/%2F%40pycontw%2FrysCSo38S)
---
* Aging REST API docs & schemes
* Stoplight or Swagger
* Hard to maintain
* Easily outdated
---
Alternative to REST-based architectures
Tool: [GraphIQL - An in-browser IDE for exploring GraphQL](https://github.com/graphql/graphiql).
---

---
Flexible
* Multiple resource in single request
* Flexible Query Versionless
Type-safe, self-documenting API
* Typed schema
---
Graphene - GraphQL in Python
* Pros
* 只要出一個 endpoint 就收工了
* Cons
* 跟傳統 rest 相比,不能限流量,要再額外開一個新的 url
---
## Wait, IPython can do that? - Sebastian Witowski
[hackmd](https://hackmd.io/@pycontw/2019/%2F%40pycontw%2FryioSjnLH)
---
## Async contextmanager for Python 3.7 - Sammy Wen
[slide](https://gamekingga.com/pycontw2019.pdf)
[hackmd](https://hackmd.io/@pycontw/2019/%2F%40pycontw%2FSkVtrjnIS)
---
## 程序員們選擇的不同道路 - Tracy Osborn
[hackmd](https://hackmd.io/@pycontw/2019/%2F%40pycontw%2FB1GBHjnUH)
### About the speaker
* @tracymakes
* [Hello Web Books](https://hellowebbooks.com/)
* [WeddingLovely Blog](https://weddinglovely.com/blog/)
{"metaMigratedAt":"2023-06-15T01:43:13.488Z","metaMigratedFrom":"YAML","title":"PyCon TW 2019 summary","breaks":true,"description":"View the slide with \"Slide Mode\".","contributors":"[{\"id\":\"e0e651e4-9240-4033-9433-b3a02de8ee03\",\"add\":21701,\"del\":3007}]"}