# Setting up Apache Spark with Hadoop
Welcome to my guide, it walks through the process of creating a multi DataNode cluster with Virtual box VMs.
This offers more extensibility then the single-node setup that is the default way for a new comer to take to Hadoop. The problem with the single node is there is not much of a performance gain in just
using a single node.
## Topics
- [ ] Apache Spark Setup
- [ ] Master Node configuration
- [ ] Work node configuration
- [ ] Hadoop Setup
- [ ] Master Nodes
- [ ] Worker Nodes
## References
The guide was constructed from the following:
- https://medium.com/@jootorres_11979/how-to-install-and-set-up-an-apache-spark-cluster-on-hadoop-18-04-b4d70650ed42
- [https://medium.com/@jootorres_11979/how-to-set-up-a-hadoop-3-2-1-multi-node-cluster-on-ubuntu-18-04-2-nodes-567ca44a3b12](https://medium.com/@jootorres_11979/how-to-set-up-a-hadoop-3-2-1-multi-node-cluster-on-ubuntu-18-04-2-nodes-567ca44a3b12)
- https://medium.com/@madtopcoder/install-a-spark-cluster-on-virtualbox-fad075449521
- https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/spark-standalone.html
# Setup and requirements
### Download Ubuntu 22.04.3
- https://ubuntu.com/download/server
# VirtualBox
Create a VM with the same setting for each of the three VM, with hostnames hdp-master, node-1, node-2 or whatever names you prefer.
- Create a new VM
- Insert screenshot CreateAnode
- 10GB of RAM is preferred
- settings png
## Create Virtual Network
### **Set up a Virtual Network in VirtualBox.**
_Cite: https://medium.com/@madtopcoder/install-a-spark-cluster-on-virtualbox-fad075449521_
Here I am skipping the steps of installing Oracle VirtualBox application on my ubuntu desktop since I believe most of you guys already know how.
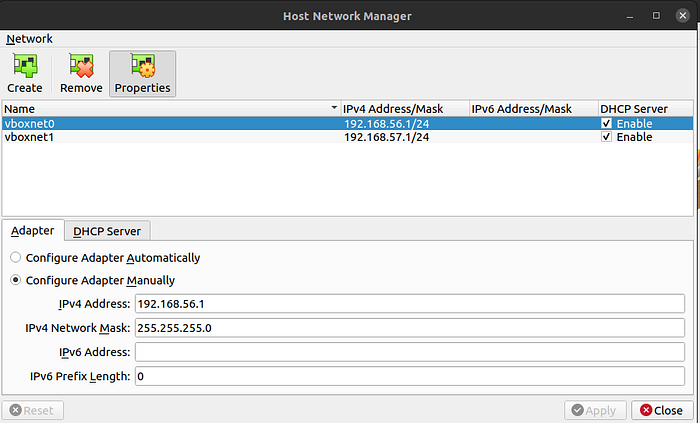
Before we can build a cluster in which machines can communicate with each other, we need a virtual network. Launch VirtualBox application and select “Host Network Manager …” from the File menu. It will present you a screen where you can set up a virtual network. Click on the “Create” button on the top to create a new network adapter with DHCP server option enabled. Here is a screenshot of my network adapter settings.
# Master Node Configuration
## Tools
- vim; everyone's favorite IDE :)
- python3; Spark required.
- java; Spark required.
- openssh; connecting to Guest OS (VM).
- rsync; copying files from host to Guest.
```sh
sudo apt install vim openjdk-8-jdk python3 openssh-server openssh-client rsync -y
```
### Config
After getting the to be master node created next step is to get the IP address, then add that IP and the next sequential two; one will confirm that they are sequential after cloning the master node.
1. Add to /etc/hosts:
```sh
# Please Check IPs before copying.
# <YOUR NODE IP> hostname
192.168.10.56.10 hpd-master
192.168.10.56.11 hpd-node-1
192.168.10.56.12 hpd-node-2
```
## Install Apache Spark
1. Get Spark:
```sh
wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/spark/spark-3.5.0/spark-3.5.0-bin-hadoop3.tgz
```
2. On the same terminal, issue this command to extract the directory:
```sh
tar xvf spark-3.5.0-bin-hadoop3.tgz
```
3. Issue the move directory command:
```sh
sudo mv spark-3.5.0-bin-hadoop3 /opt/spark
```
This command will move all the content under “spark-3.2.1-bin-hadoop3.2 folder to “/opt/spark” directory.
# Worker Node Configuration
## Clone the Master
after clone ensure that the ips are different. If they aren't then issue:
```sh
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname hpd-node-1
sudo rm -r /etc/machine-id
sudo dbus-uuidgen --ensure=/etc/machine-id
sudo rm /var/lib/dbus/machine-id
sudo dbus-uuidgen --ensure
reboot
```
change the hostname
```sh
hostnamectl set-hostname new-hostname #I named my hdp-node-1 and my second hdp-node-2
```
## On each Node
1. Ensure, and change master node ip if it is not set:
`vim /opt/spark/conf/spark-env.sh`
`SPARK_MASTER_HOST = <ip address of the master node>`
2. Add the Node:
`start-worker.sh spark://<MASTER_IP>:7077`
## View the active workers.
1. Visit: `http://MASTER_HOST:8080`
For example mine is `http://192.168.56.10:8080` but your VM network may be different.
## Optional configuration
1. Generate authorization keys to control workers from the master:
1. ssh-keygen -t rsa -P ""
2. cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
3. Copy this authorized key to all the workers:
```sh
# your username on each node/master might be different
ssh-copy-id master@hpd-master
ssh-copy-id master@hpd-node-1
ssh-copy-id master@hpd-node-2
```
2. Set up `/opt/spark/conf/workers`:
Add your hosts to your `/opt/spark/conf/workers`
```sh
hdp-master
hpd-node-1
hpd-node-2
```
This allows you to start all workers from the master node.

### Commands for nodes:
Now a new level has been unlocked. All the nodes can be managed by the master.
#### Favorites:
`stop-all.sh`
`start-all.sh`
`start-master.sh`
`start-workers.sh`
# Additional Configuration
(configuration_for_spark.docx conversion)
1. Add the log4j configuration:
```sh
cp /opt/spark/conf/log4j2.properties.template /opt/spark/conf/log4j2.properties
```
1. Change to warn:
```
# Set everything to be logged to the console
rootLogger.level = WARN
rootLogger.appenderRef.stdout.ref = console
```
2. Installing required libraries for python:
```sh
sudo apt install pip
pip install numpy scipy matplotlib ipython pandas sympy nose
```
3. Add to ~/.bashrc
```
export PATH=$PATH:/home/master/.local/bin
```
4. Follow the course module prerequisite check:
- SPARK_HOME is defined
- python can import scipy numpy
- Log4j2 properties are set.
5. Add Event logging:
- Be default there is not any logging for apache. Let's change this easily.
```sh
mkdir /tmp/spark-events # default location for spark logs```
```
``` sh
# Edit /opt/spark/conf/spark-defaults.conf
# If it doesn't exist use the template to create one.
if [ ! /opt/spark/conf/spark-defaults.conf ]; then
mv /opt/spark/conf/spark-defaults.template /opt/spark/conf/spark-defaults.conf
fi
vim /opt/spark/conf/spark-defaults.conf
# Uncomment spark.master and set to you master url
# Uncomment eventLog.enabled
spark.master spark://hpd-master:7077
spark.eventLog.enabled true
```

- Now all your jobs will show on http://hpd-master:8080

- Notice that we have three workers, we have included the master in our `/opt/spark/conf/works` this is optional and you can remove the master from this if you so wish.
# [Running Alongside Hadoop](https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/spark-standalone.html#running-alongside-hadoop)
You can run Spark alongside your existing Hadoop cluster by just launching it as a separate service on the same machines. To access Hadoop data from Spark, just use an hdfs:// URL (typically `hdfs://<namenode>:9000/path`, but you can find the right URL on your Hadoop Namenode’s web UI). Alternatively, you can set up a separate cluster for Spark, and still have it access HDFS over the network; this will be slower than disk-local access, but may not be a concern if you are still running in the same local area network (e.g. you place a few Spark machines on each rack that you have Hadoop on).
1. Download
```sh
wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.3.6/hadoop-3.3.6.tar.gz
```
2. For ease of configuration place this here before moving it to
```sh
tar xvf hadoop-3.3.6.tar.gz
mv hadoop-3.3.6 hadoop
# Open and set Java home for Hadoop
vim hadoop/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh
# Find JAVA_HOME
JAVA_HOME="/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/jre"
```
```sh
sudo mv hadoop /usr/local/hadoop
```
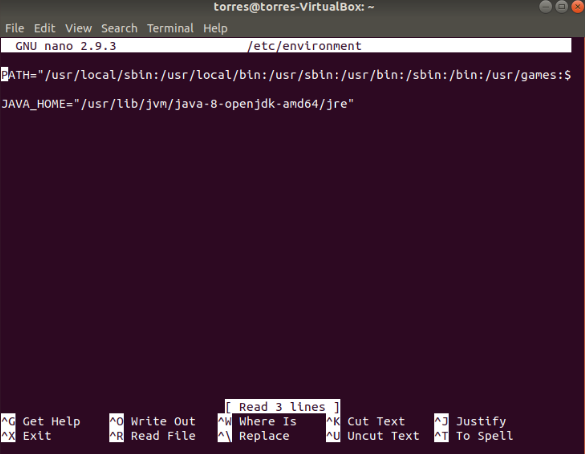
3. Add: /usr/local/hadoop/sbin to env path.
```sh
vim /etc/environment`
PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/usr/local/hadoop/bin:/usr/local/hadoop/sbin"
```
- Do the same on each of the worker nodes
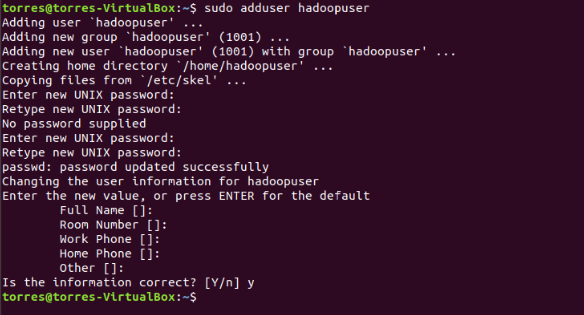
4. Now we will add a user called **hadoopuser**, and we will set up it’s configurations:
```sh
sudo adduser hadoopuser
```
5. Provide the password and you can leave the rest blank, just press **Enter.**
6. Now type these commands:
```sh
sudo usermod -aG hadoopuser hadoopuser
sudo chown hadoopuser:root -R /usr/local/hadoop/
sudo chmod g+rwx -R /usr/local/hadoop/
sudo adduser hadoopuser sudo
```
7. Configuring Hadoop ports (master/main only)
- This step should be done on **ONLY** the master/main node. We’ll need to configure Hadoop ports and write more configuration files. Here’s the command:
```sh
sudo nano /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml
```

- And then, in the file, inside the configuration segment, write:
```
<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>hdfs://hpd-master:9000</value>
</property>
```
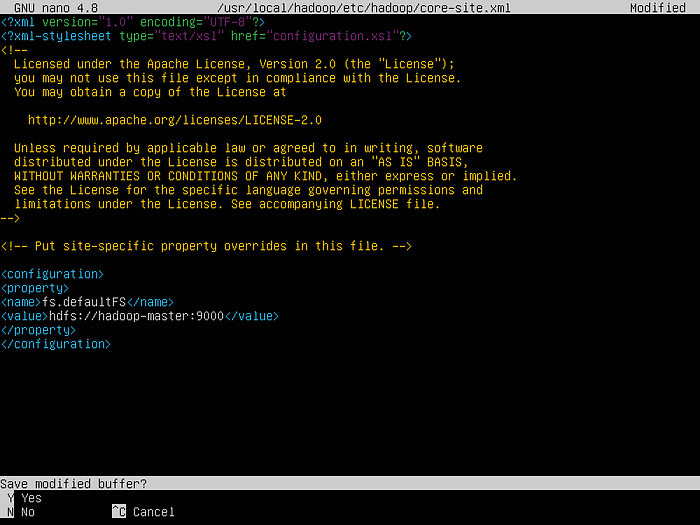
Visual Representation of how the core-site file needs to look like.
8. Configuring HDFS (Master/main only)
- We’ll be configuring HDFS this time around, **on the Master/main node only!**Command is:
```
sudo vim /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml
```

Visual Representation of the command to the hdfs site file
- Once again, in the file in the configuration segment, write:
```
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.name.dir</name>
<value>/usr/local/hadoop/data/nameNode</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name>
<value>/usr/local/hadoop/data/dataNode</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.replication</name>
<value>2</value>
</property>
```
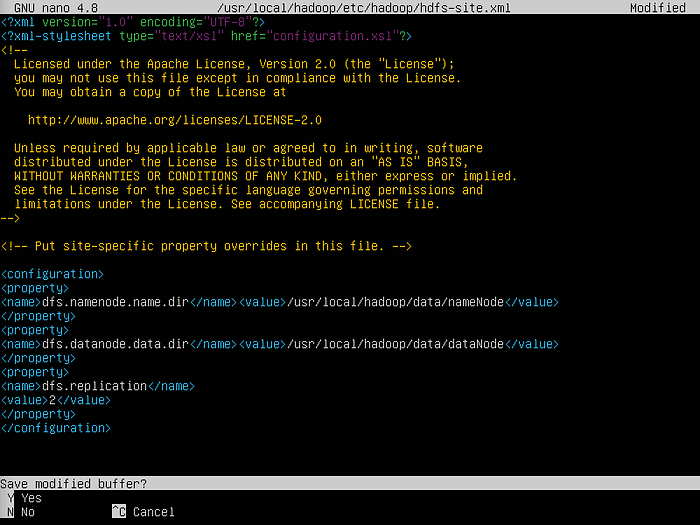
- Visual Representation of the HDFS file
9. Source env:
`source /etc/environment`
10. format the HDFS system:
```sh
hdfs namenode -format
```
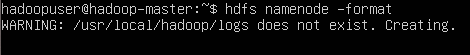
- Visual Representation of how to format HDFS.
- It’ll look like this:
- Visual Representation of HDFS formatting.
11. Now, start hdfs:
```sh
start-dfs.sh
```
12. Add the Hadoop_CONF_DIR
```
vim /opt/spark/conf
# Find HADOOP_CONF_DIR and set the following
HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/
```
# RDBMS Optional
### References:
- https://www.machinelearningplus.com/pyspark/pyspark-connect-to-postgresql/
A couple of guides mention getting a MySQL or PostgreSQL Database connected to the Apache Spark cluster.
Options:
1. Configure another VM.
2. Use Docker Postgres container on Master Node
There are enough guides out that I will leave the first option to the reader to solve, and pursue the second option as the configuration is simple and puts the focus on Spark.