---
canonical_url: https://www.scaler.com/topics/difference-between-ddl-and-dml/
title: Difference Between DDL and DML - Scaler Topics
description: This article by Scaler Topics defines DDL and DML and explains the commands used in DDL and DML along with the syntax.
author: Dev Kumar
category: DBMS
amphtml: https://www.scaler.com/topics/difference-between-ddl-and-dml/amp/
publish_date: 2022-02-10
---
:::section{.abstract}
## Overview
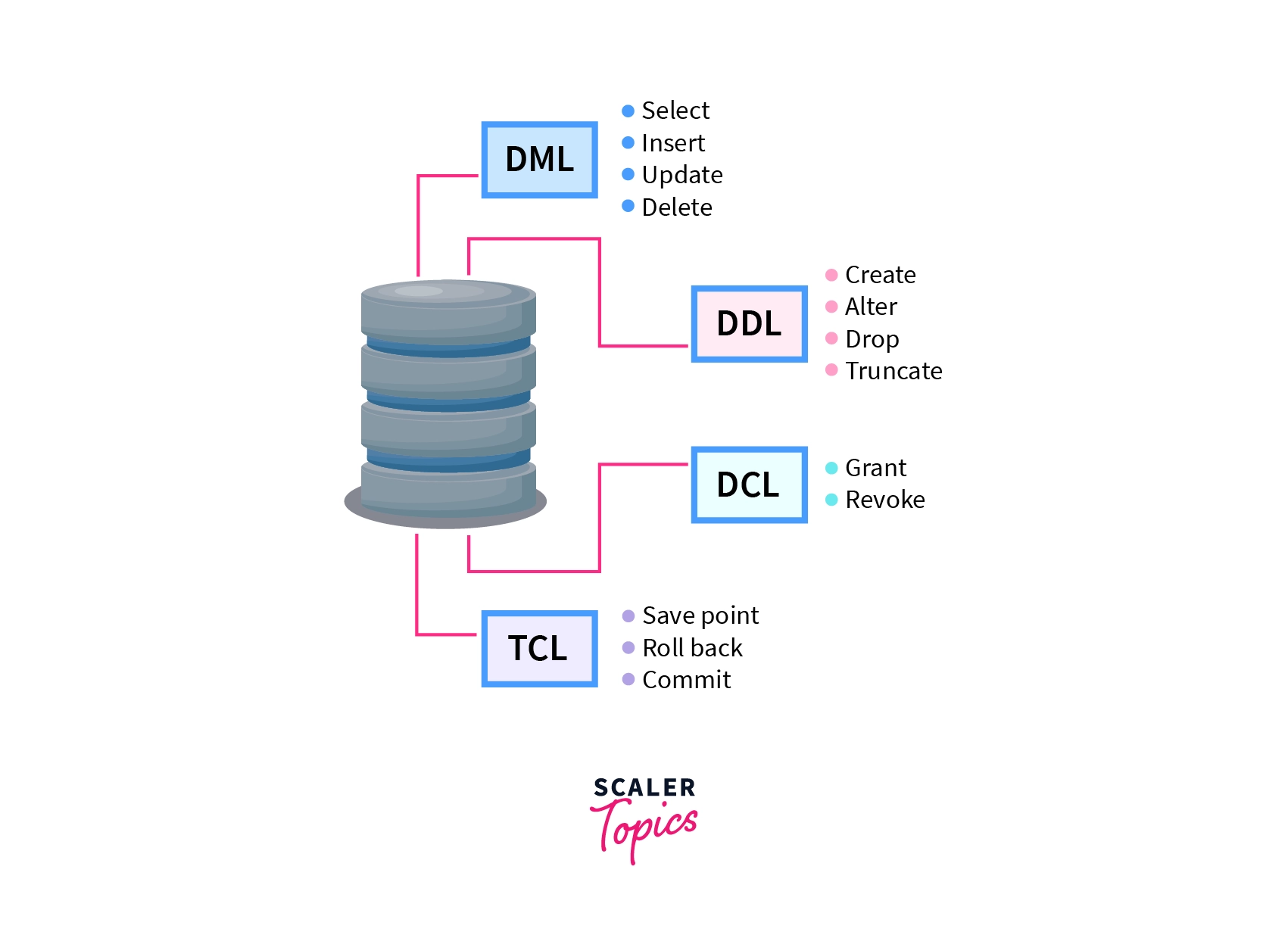
A database system is a repository of organized information, maintained through a set of SQL commands categorized into DML (Data Manipulation Language), DDL (Data Definition Language), DQL (Data Query Language), and DCL (Data Control Language). In this discussion, we'll delve into DML and DDL, emphasizing the distinctions between them. DDL primarily concerns the architecture of the database, encompassing tasks such as defining tables, indexes, and relationships. On the other hand, DML revolves around modifying the data stored within the database, including tasks like insertion, retrieval, updating, and deletion of records. This fundamental divergence between DDL and DML plays a pivotal role in how database systems are structured and operated.
:::

:::section{.scope}
## Scope of Article
- This article defines DDL and DML and explains the commands used in DDL and DML.
- We will also discuss commands used in DDL, DML along with the syntax.
- This articles also show the difference between DDL and DML.
:::
:::section{.main}
## DDL
DDL stands for Data Definition Language. The DDL commands help us to define the structure of the database or schema and other database objects. DDL commands are auto-committed, which means the changes made in the database using DDL commands are saved permanently.
The commands that come under DDL language are:
- CREATE
- ALTER
- TRUNCATE
- DROP
- RENAME
**Why DDL language?**
- DDL allows us to create and structure our database.
- DDL improves the security efficiency of the data access.
- Multiple users can work on the same database.
### 1. CREATE STATEMENT
This statement is used to create the database and its objects like creating tables, functions, views, etc.
**Syntax:**
```sql=
CREATE OBJECT_TYPE OBJECT_NAME;
```
**Example:**
**Creating Database**
```sql=
CREATE DATABASE ABCCOMPANY;
```
**Creating Table**
```sql=
CREATE TABLE CUSTOMER_ID(ID INT);
CREATE TABLE SALES(ID INT);
```
### 2. ALTER STATEMENT
This statement is used to alter the existing structure/objects in the database.
**Syntax for adding a column in the existing table:**
```sql=
ALTER TABLE TABLE_NAME ADD COLUMN COLUMN_NAME DATATYPE;
```
**Example:**
```sql=
ALTER TABLE SALES ADD COLUMN PURCHASE_ID INT;
```
### 3. TRUNCATE STATEMENT
Truncate statement is used to remove the data from the table, as well as it removes the entire data including objects, structure, and continues to have the table as an object in the database.
**Syntax:**
```sql=
TRUNCATE OBJECT_TYPE OBJECT_NAME;
```
**Example:**
```sql=
TRUNCATE TABLE SALES;
```
### 4. DROP STATEMENT
It is used for deleting a database object permanently.
**Syntax:**
```sql=
DROP OBJECT_TYPE OBJECT_NAME;
```
**Example:**
```sql=
DROP TABLE SALES;
```
It will delete the table `sales` completely, if we want the sales again, we have to re-create it using the `CREATE` statement.
### 5. RENAME STATEMENT
This statement is used to rename the database and its objects.
**Syntax:**
```sql=
RENAME OBJECT_TYPE OBJECT_NAME TO NEW_OBJECT_NAME;
```
**Example:**
```sql=
RENAME TABLE CUSTOMER_ID TO ALT_CUSTOMER_ID;
```
:::
:::section{.main}
## DML
DML stands for Data Manipulation Language. As its name says, it manipulates the existing data in the database. The changes made by DML commands aren't saved permanently. In DML, we can roll back our changes. Hence, DML commands aren't auto committed.
The commands that come under DML language are:
- SELECT
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
**Why DML language:**
- It helps us to manipulate the data.
- It helps us to specify which data to be manipulated.
### 1. SELECT STATEMENT
This statement is used to retrieve data from the database objects like tables.
**Syntax:**
```sql=
SELECT COLUMN_NAME FROM TABLE_NAME;
```
Example:
```sql=
SELECT ID FROM ALT_CUSTOMER_ID;
```
Here, we extract **'ID'** column from table **'ALT_CUSTOMER_ID'** which was changed while renaming our **'CUSTOMER_ID'** table.
### 2. INSERT STATEMENT
This statement is used to insert the data into rows of the table.
**Syntax:**
```sql=
INSERT INTO OBJECT_NAME(COL1,COL2,...) VALUES(VALUE1,VALUE2,...);
```
**Example:**
```sql=
INSERT INTO ALT_CUSTOMER_ID(ID) VALUES(1);
INSERT INTO ALT_CUSTOMER_ID(ID) VALUES(10);
```
### 3. UPDATE STATEMENT
It allows us to update the existing data of the tables.
**Syntax:**
```sql=
UPDATE TABLE_NAME
SET [COL1 = VALUE1, COL2 = VALUE2]
WHERE CONDITION;
```
**Example:**
```sql=
UPDATE ALT_CUSTOMER_ID;
SET ID = 2
WHERE ID = 10;
```
### 4. DELETE STATEMENT
This is similar to the truncate statement, in the truncate statement, it will delete all the records in the table and only leave with an empty table, whereas in the delete statement, it can either delete all the records or any number of records.
**Syntax:**
```sql=
DELETE FROM TABLE_NAME
WHERE CONDITION;
```
Example:
```sql=
DELETE FROM ALT_CUSTOMER_ID
WHERE ID = 2;
```
In this statement, it will delete only that record that has 'ID' = 2.
```sql=
DELETE FROM ALT_CUSTOMER_ID;
```
In the above statement, we have not mentioned any condition, so it will delete all the existing records in the entire table.
:::
:::section{.main}
## Key Difference between DDL and DML
The key difference between DDL (Data Definition Language) and DML (Data Manipulation Language) lies in their core functions within a database system. DDL is primarily concerned with defining and structuring the database itself, encompassing tasks such as creating tables, altering schemas, and managing the database's architecture. In contrast, DML is focused on manipulating the data stored within the database, including operations like insertion, retrieval, updating, and deletion of records. While DDL commands bring about permanent changes to the database structure and are auto-committed, DML commands deal with the transient manipulation of data and can be rolled back, making them essential for data management tasks.
:::
:::section{.main}
## Difference between DDL and DML
| DDL | DML |
| - | - |
| DDL stands for Data Definition Language. | DML stands for Data Manipulation Language. |
| It helps us to define the structure of the database.| It helps us to manage the data. |
| It affects the whole table. | It only affects the specified row(s) of the table. |
| Changes are permanent. | We can roll back our changes in the DML language. |
| It helps in defining the fields or columns of the tables. | It helps us in defining rows or records of the tables. |
| They are auto-committed (changes made are permanent). | They are not auto-committed (changes are not permanent).
| They don't have further classification. | They are classified into procedural and non-procedural. |
| Commands used: CREATE, ALTER, TRUNCATE, RENAME, DROP. | Commands used: SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT. |
DDL does not use WHERE clause in its statement. | While DML uses WHERE clause in its statement. |
DDL is typically executed by database administrators and developers to define and maintain the overall database structure.| DML is often used by application developers and end-users to interact with and manipulate the data stored in the database. |
:::
:::section{.summary}
## Conclusion
- SQL commands are categorized into four main groups: DML (Data Manipulation Language), DDL (Data Definition Language), DCL (Data Control Language), and DQL (Data Query Language).
- This article focuses on DDL (Data Definition Language) and DML (Data Manipulation Language). DDL is used to define the structure of a database, while DML is employed to manage the data within it.
- **DDL vs DML:** DDL commands include CREATE, ALTER, TRUNCATE, RENAME, and DROP, which shape the database's architecture while DML commands encompass SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE, allowing for the manipulation of data stored in the database.
- DDL commands are auto-committed, meaning the changes made using them are permanent, whereas DML commands are not auto-committed, enabling the possibility of reverting changes.
- Unlike DML, changes initiated through DDL cannot be easily rolled back, making it essential to carefully plan and execute structural alterations in a database.
:::